Even though Linux remains the most widely used operating system in enterprise environments, Microsoft's dedicated server platform, Windows Server, also has a strong presence. This is especially true for organizations that are already invested in Microsoft technologies such as SQL Server, Azure, and Active Directory.
Windows Server is optimized for Windows-centric, virtualized, and cloud environments. It provides a centralized graphical management interface, advanced clustering and security features, and is backed by Microsoft's long-term support guarantee.
Find out how to install Windows Server 2025 and prepare it for production workloads.

What Is a Windows Server
Windows Server is Microsoft's operating system, built specifically for deploying and running servers. Unlike consumer editions, such as Windows 10 and 11, Windows Server is designed to:
- Provide services to multiple clients simultaneously.
- Stay lightweight and resource-efficient by leaving out non-essential desktop features.
- Run continuously in an always-on environment.
- Enhance security by installing only the required server roles and features. This role-based deployment enables administrators to eliminate unnecessary services and reduce the attack surface.
You can deploy Windows Server on bare-metal servers, run it as a virtual machine using VirtualBox, Hyper-V or VMware, or host it in the cloud on services like Azure and AWS.
Windows Server Features
Some of the Windows Server features you are likely to rely on the most include:
- Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). This server role allows you to manage user accounts, security policies, and authentication/authorization for your entire network from a single directory.
- Hyper-V virtualization. With Hyper-V, you can run multiple operating systems as virtual machines on the same server hardware. For example, install Ubuntu on a Windows system with Hyper-V. This enables you to utilize resources more efficiently and reduce hardware costs.
- File and Storage Services. Windows Server includes advanced file sharing, disk quotas, and replication options to simplify storage management and ensure that data is available to users and applications when needed.
- Internet Information Services (IIS). IIS is a built-in, highly configurable web server in Windows Server. It's widely used for hosting websites, APIs, and web applications.
- Failover Clustering. When deployed across multiple servers (nodes), this feature helps ensure high availability. If one node goes down, workloads are automatically transferred to another available node in the cluster.
- Windows Admin Center. This free, browser-based management tool provides a modern dashboard for configuring and monitoring individual servers and clusters, all from a single console.
- Enhanced security features. Windows Server supports Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), includes built-in antivirus protection with Windows Defender, and offers Secured-core server capabilities to protect against credential theft and various types of cyber attacks.
Windows Server Versions
The following table lists the currently active (supported) Windows Server versions:
| Version | Released | Mainstream Support | Extended Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2025 | September 2024 | October 2029 | October 2034 |
| Windows Server 2022 | August 2021 | October 2026 | October 2031 |
| Windows Server 2019 | October 2018 | January 2024 (ended) | January 2029 (security updates only) |
| Windows Server 2016 | October 2016 | January 2022 (ended) | January 2027 (security updates only) |
Note: Windows Server versions older than 2016 are out of extended support and no longer receive security updates.
Windows Server Benefits
Running a Windows Server has the following advantages:
- Continuous uptime. Windows Server is built for continuous 24/7 operations. Features like Failover Clustering and live workload migration keep services available during maintenance or even if the underlying hardware fails.
- Built to scale. Windows Server can manage thousands of users and devices, supporting everything from lightweight apps to mission-critical databases.
- Enterprise-grade security. Security features are enabled from the moment you boot for the first time. The platform has multiple defense layers that combine firewalls, role-based access controls, and antivirus software to defend against advanced threats. Administrators also benefit from Microsoft's regular security patches and updates, which help eliminate known vulnerabilities.
- Rapid server virtualization. With Hyper-V, you can clone existing servers or deploy new virtual machines within minutes. This built-in capability eliminates the need for third-party hypervisors, even when running workloads in enterprise environments.
- Integration with Microsoft Azure. Organizations looking to extend their on-premises deployments into the cloud can utilize built-in Windows Server features that integrate directly with Azure. For example, Active Directory can be extended to Azure AD, Azure Site Recovery provides cloud disaster recovery, and Azure Storage supports off-site data backups.
- Management tools. Windows Server has multiple options for administering individual servers and multi-node clusters from a single interface. These include tools such as PowerShell for automating and scripting tasks, Server Manager for GUI-based management, and the browser-based Windows Admin Center dashboard.
Windows Server 2025 and AI
Windows Server 2025 is optimized for AI and machine learning through cloud support, containerization, and hardware acceleration. The platform supports:
- GPUs and NPUs. With the right drivers installed, Windows Server 2025 can use GPUs and NPUs to accelerate AI training and inference. This enables you to run deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch directly on Windows-based infrastructure.
- Containerization. Windows Server natively supports Docker and Kubernetes, which allow you to deploy AI microservices in isolated, lightweight environments (containers). This makes it easier to scale AI services and move them between on-premises and cloud deployments.
- Enhanced security and isolation. Built-in security features like Virtualization-Based Security (VBS), RBAC, and improved process isolation help protect sensitive AI workloads. Companies can leverage these tools to train and deploy AI models and meet compliance regulations at the same time.
- Closer integration with Azure AI services. In hybrid cloud setups, Windows Server can tie into Azure AI services to offload heavy workloads to the cloud. This is especially useful for organizations in regulated industries where sensitive data must stay on-premises, but they still need the extra scale and flexibility the cloud provides.
Note: Find out which 13 AI processors dominate today's market for advanced AI use cases.
How to Install Windows Server?
Windows Server 2025 can be installed on physical hardware or inside a virtual machine. The process is almost identical; the only difference is whether you boot from a USB or mount the ISO file in a hypervisor. The following steps show how to install and configure Windows Server 2025 on a VirtualBox VM.
Download the ISO
To download Windows Server 2025:
1. Go to the official Microsoft Evaluation Center page for Windows Server 2025.
2. Select Download the ISO option in the Get started for free section.
3. Fill out a short online form with your name, email, and company details.
4. Click the ISO 64-bit edition link in your preferred language, for example, English (United States).
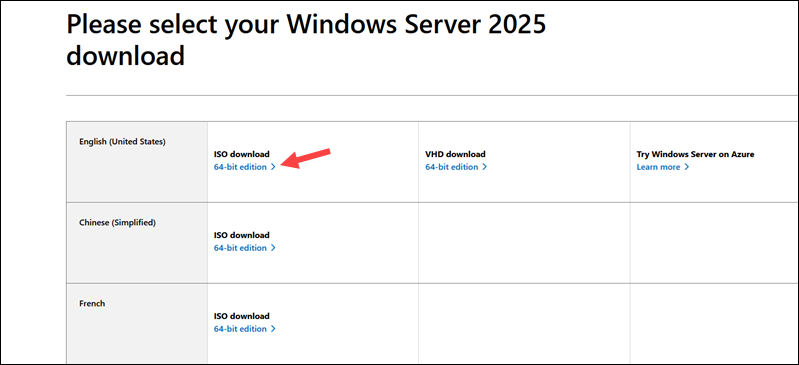
5. Once you select the edition, the download starts automatically.
Note: The evaluation copy is free for 180 days. After the trial period expires, Windows Server 2025 will deactivate. To continue using it, you can purchase a license and convert the evaluation into a full licensed product.
Create Virtual Machine
To create a dedicated machine for the Windows Server instance:
1. Open the hypervisor (VirtualBox in this example) and create a new VM.
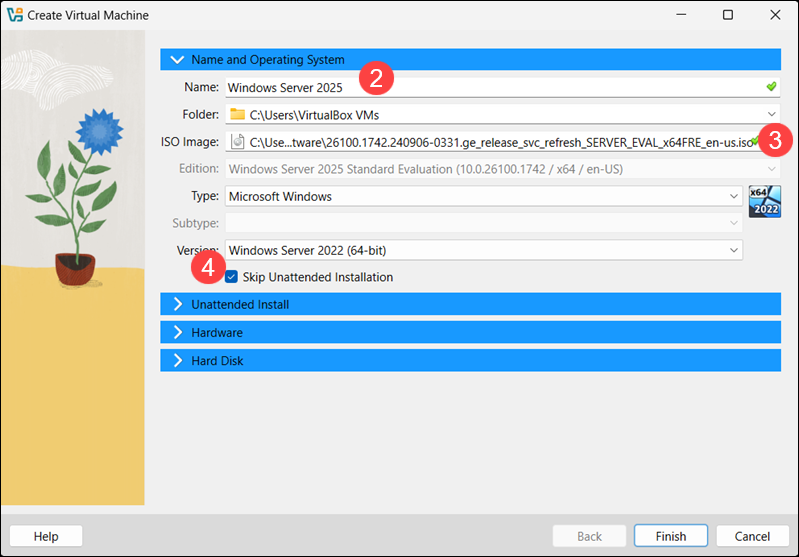
2. Enter a name for the machine, for example, Windows Server 2025.
3. Use the ISO Image dropdown to select the Windows Server 2025 ISO image you downloaded.
4. Check the Skip Unattended Installation option.
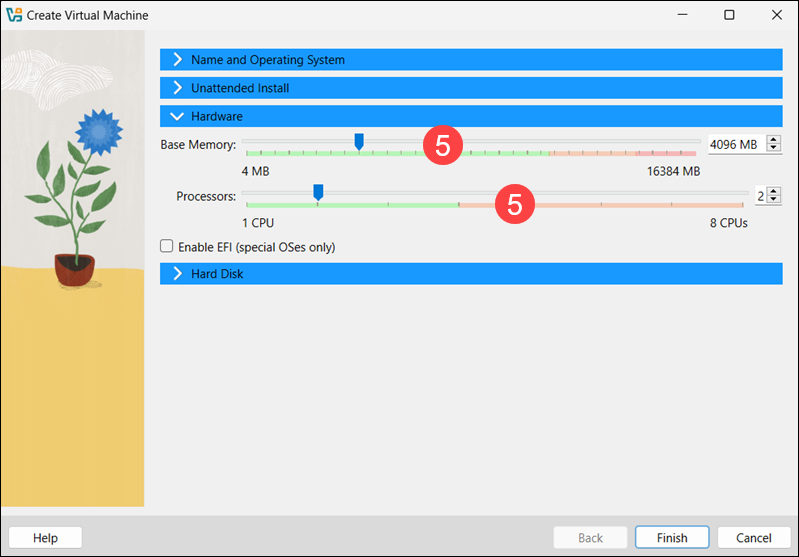
5. Open the Hardware tab and assign a minimum of 4 GB of RAM (8 GB recommended) and 2 vCPUs (4 vCPUs recommended).
6. Expand the Hard Disk section and add a 50 GB virtual disk.
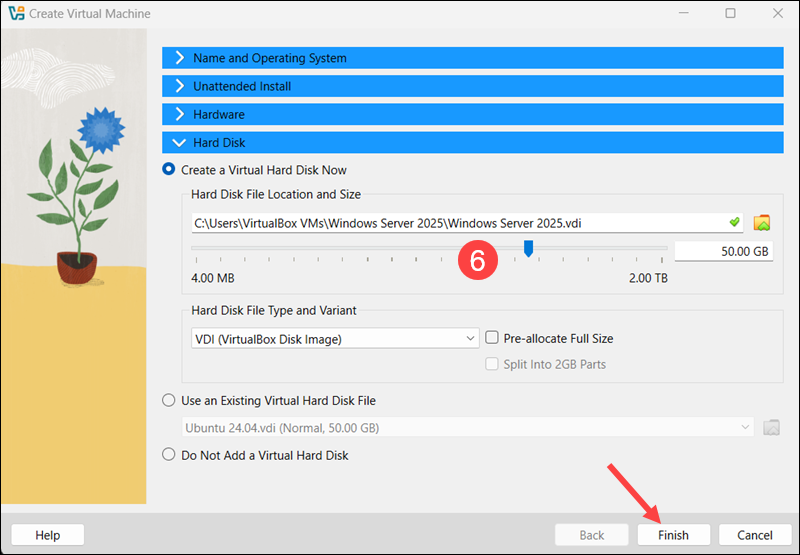
Review the summary of the selected configuration and click Finish to create the VM.
Run Windows Server Setup
To install Windows Server 2025:
1. Start the VM. It will boot directly into the Windows Server setup program.
2. Choose your language, time and currency format, and keyboard preferences.
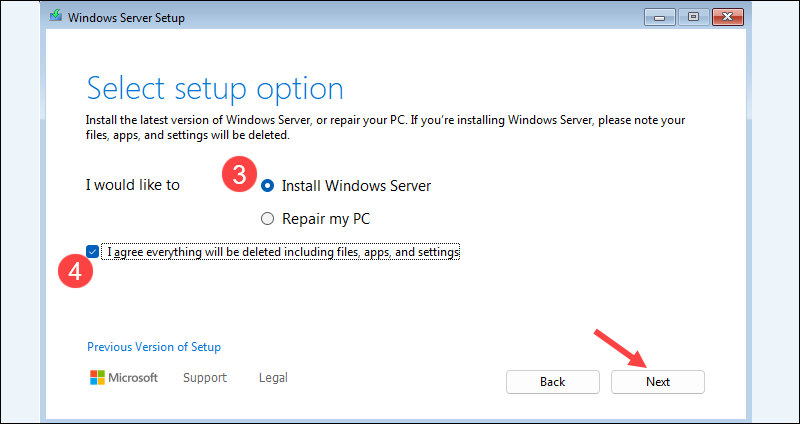
3. Select Install Windows Server.
4. Check the I agree everything will be deleted.. checkbox, and click Next.
5. Select the software version to install:
- Standard Evaluation. Includes core Windows Server features and is suitable for smaller deployments. Needs to be managed via the command line or through remote tools.
- Datacenter Evaluation. Adds advanced features for large-scale or highly virtualized environments. Needs to be managed via the command line or through remote tools.
- Desktop Experience. Includes a GUI for admins who prefer managing servers through a desktop environment.
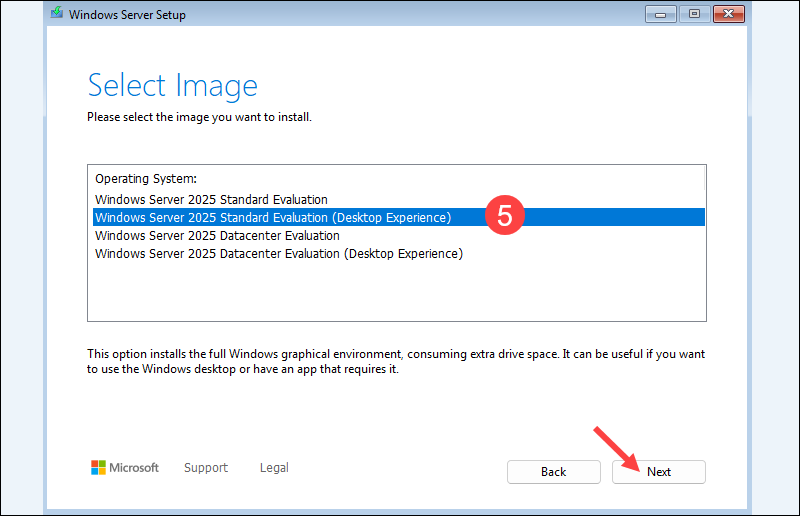
In this example, the installation uses Standard Evaluation (Desktop Experience).
6. Accept the license terms.
7. Select the virtual hard disk you created earlier and click Next.
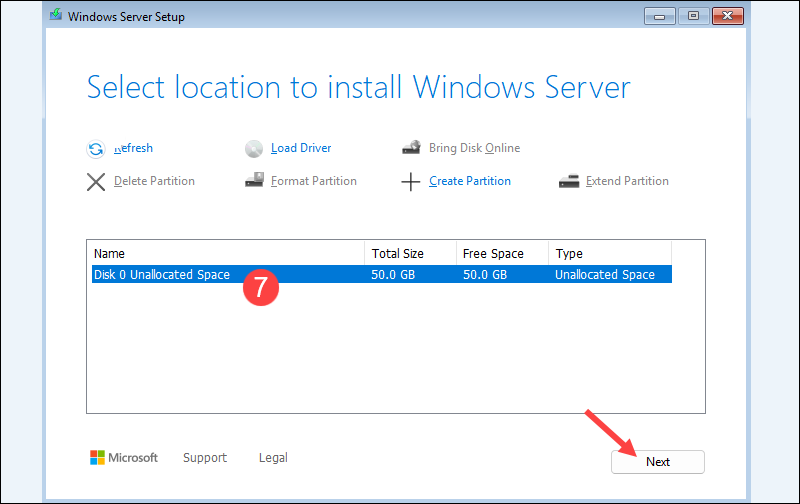
8. Click Install to begin the setup.
The Windows Setup Wizard will automatically copy files, install features, and restart the VM.
Initial Configuration
After the installation, complete the following steps:
Set Admin Password
On first boot, you are prompted to set the Administrator password. This is the main account used to manage the server.
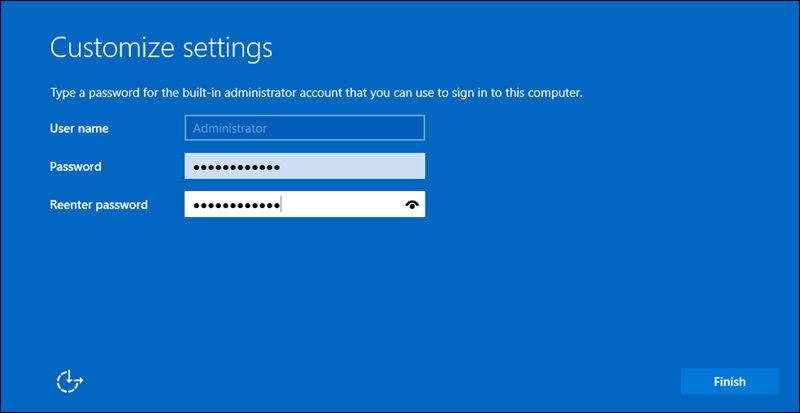
Use the credentials you created to access the system.
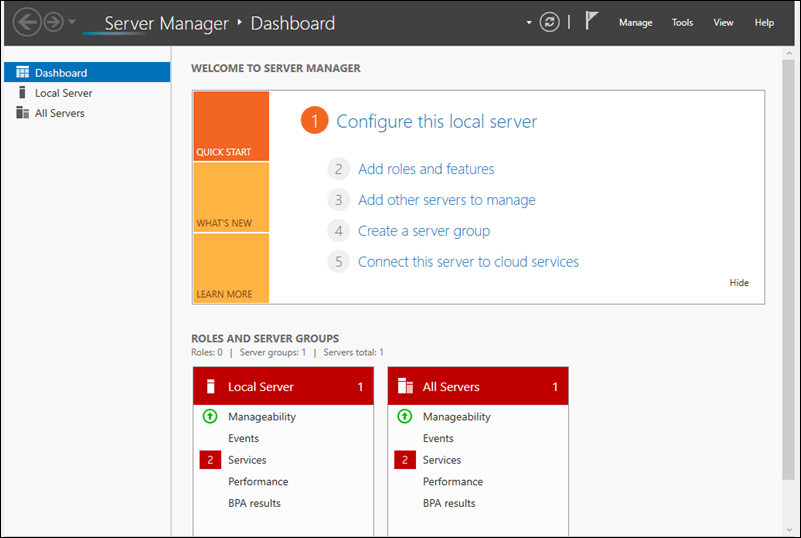
Since this is the Desktop Experience version, the Server Manager app opens automatically. From here, you can manage the server in a GUI environment.
Set Static IP
To ensure your services are always reachable at the same address, you can set a static IP:
1. Open the Local Server tab from the left panel.
2. Click the Ethernet link.
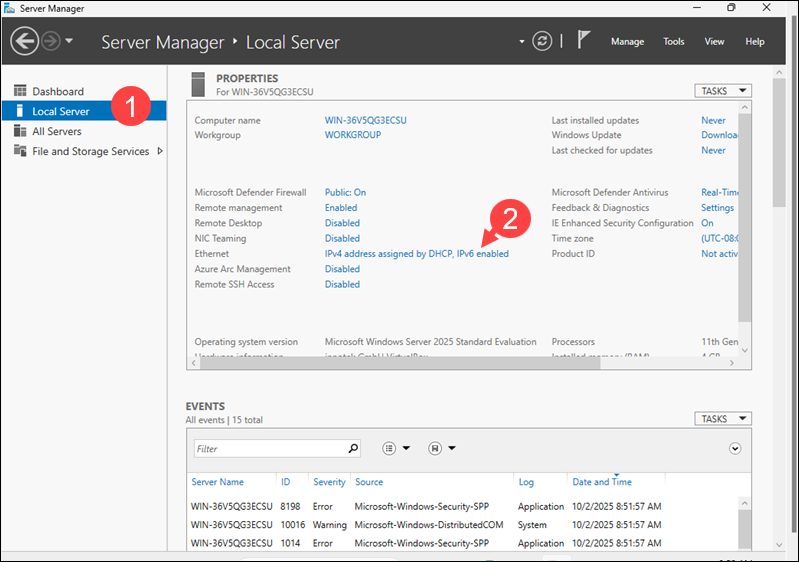
3. Right-click the active Ethernet adapter and select Properties.
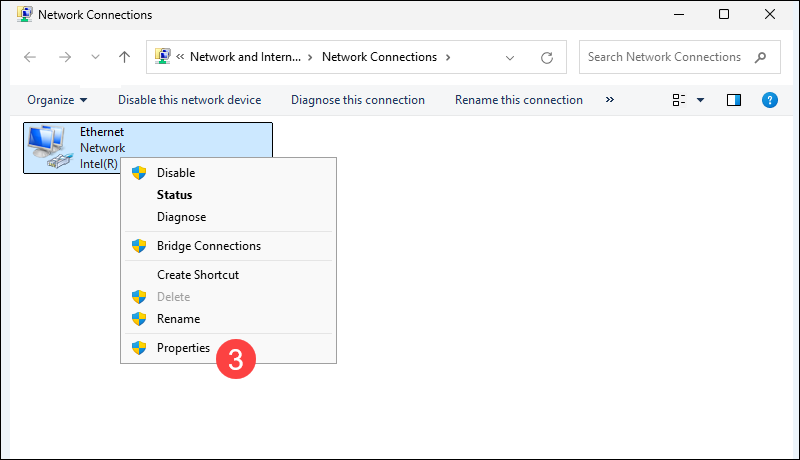
4. Highlight Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
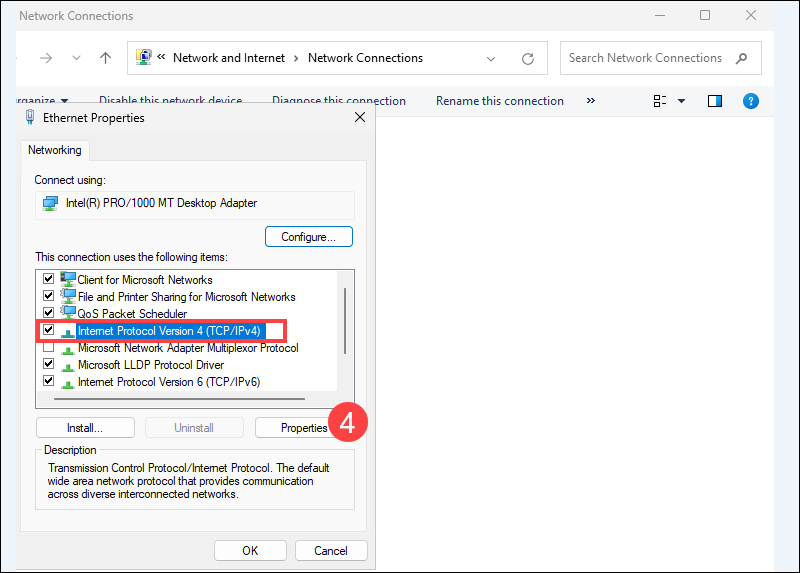
5. Select Use the following IP address and enter your server's:
- IP address
- Subnet mask (usually 255.255.255.0)
- Default gateway (your router's IP)
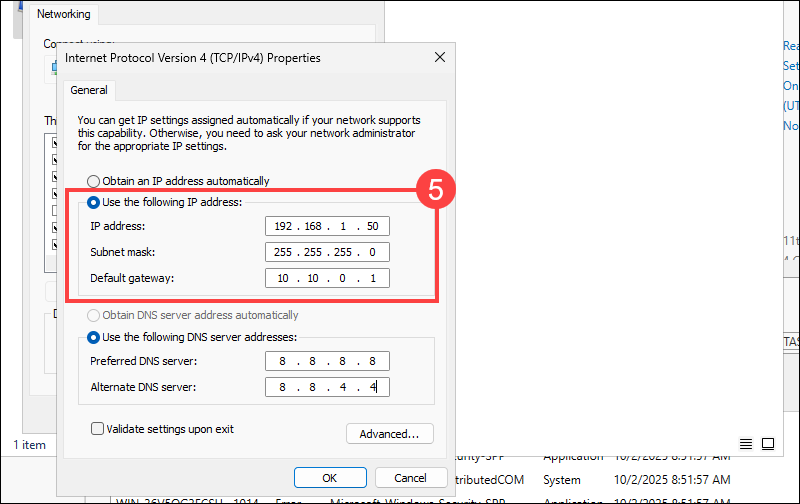
6. In the DNS section, enter:
- Preferred DNS Server. Use the IP of your internal DNS server, or 8.8.8.8 for Google.
- Alternate DNS Server. Enter 8.8.4.4 or another DNS if available.
7. Click OK, then Close to apply the settings.
8. To verify if the settings were applied, open the Command Prompt and enter the following command:
ipconfig /all 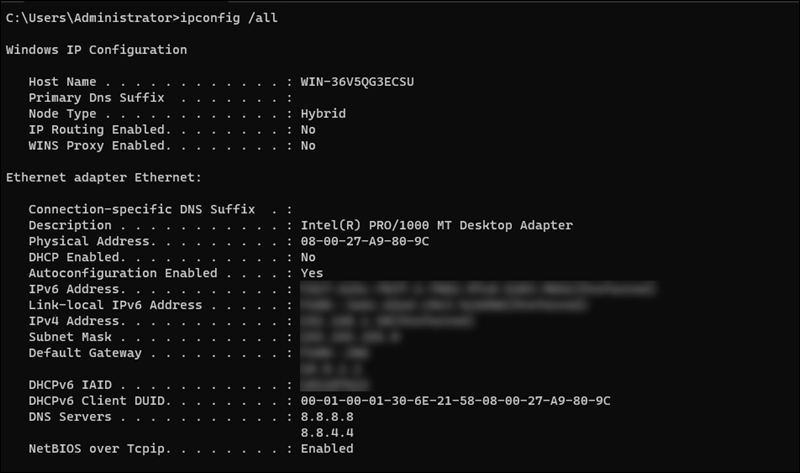
Confirm that the values in the output match the ones you entered in the Ethernet settings.
Update Windows Server
To protect the server from known vulnerabilities, install the latest security patches using Windows Update:
1. Select the Local Server tab and click the Windows Update link.
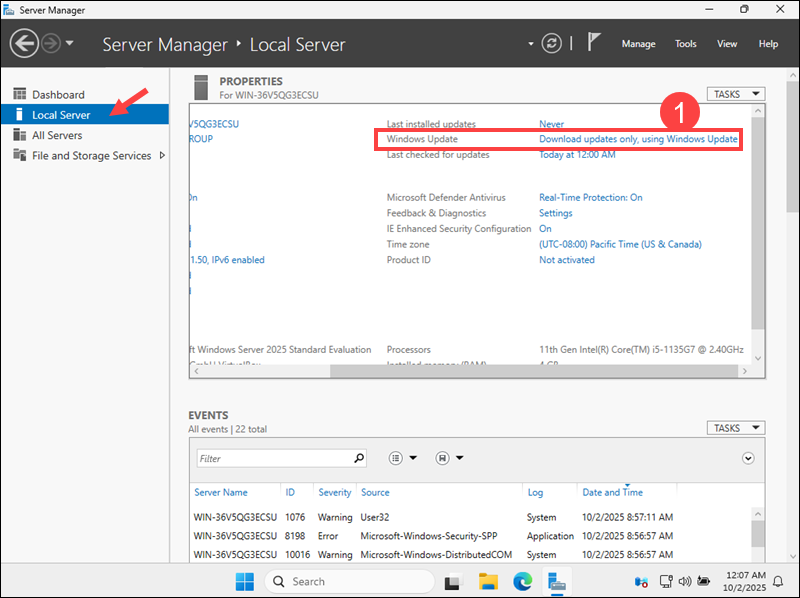
2. Click Install All to apply the available updates.
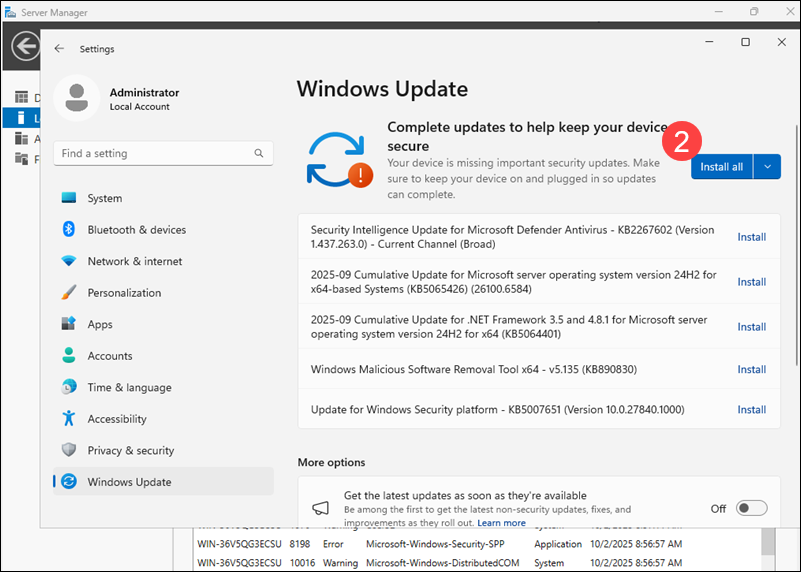
Restart the server if prompted and repeat the check until no new updates appear on the list.
Post-Installation Setup
Once Windows Server 2025 is installed and updated, use Server Manager to configure additional settings:
Rename the Server
You can add a descriptive server name to identify the server within a network easily:
1. Access the Local Server tab and click the link in the Computer name field.
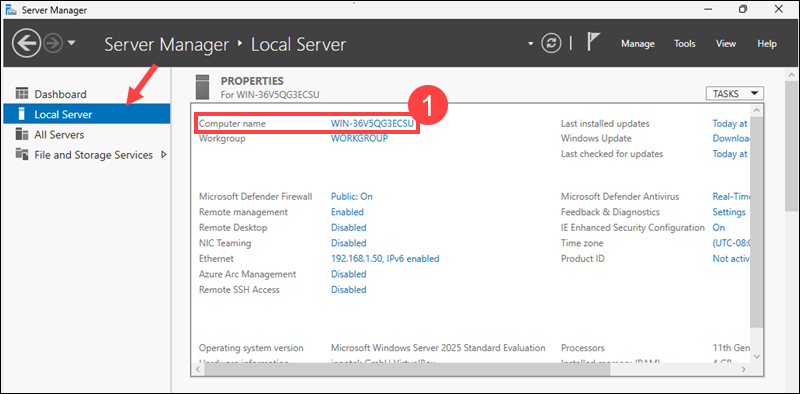
2. Click Change in the System Properties window.
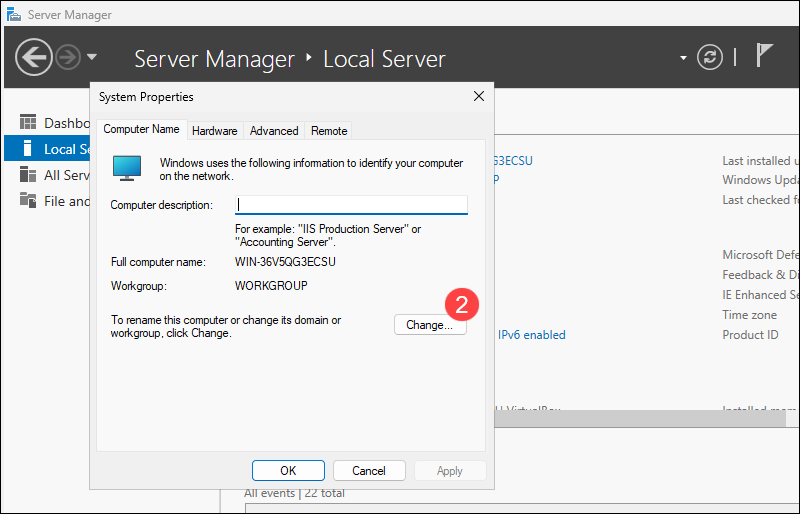
3. Enter a new hostname, for example, WinServer1, and click OK.
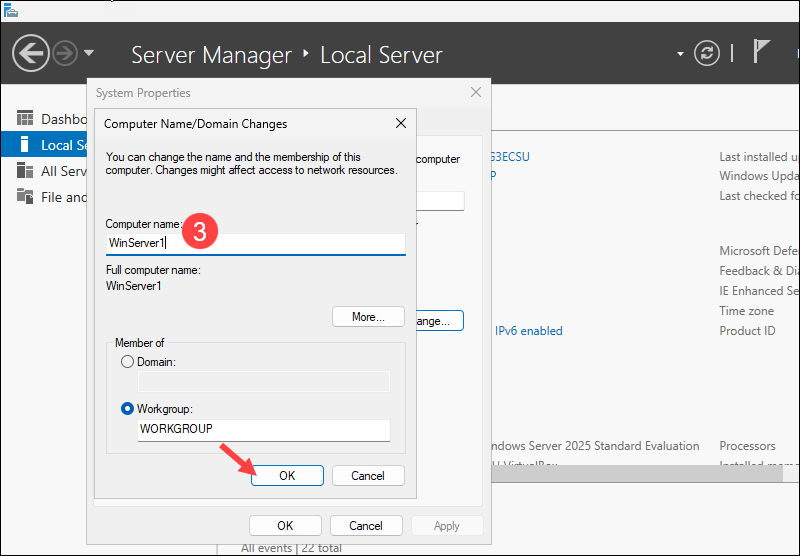
Restart the server for the change to take effect.
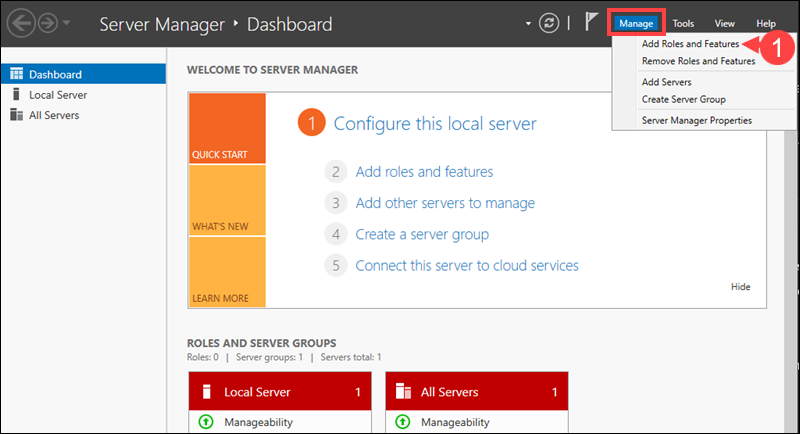
Add Roles and Features
Roles and features are added through the Manage option.
1. Select Manage and then Add Roles and Features.
2. In the Add Roles and Features Wizard, choose Role-based or feature-based installation, and click Next.
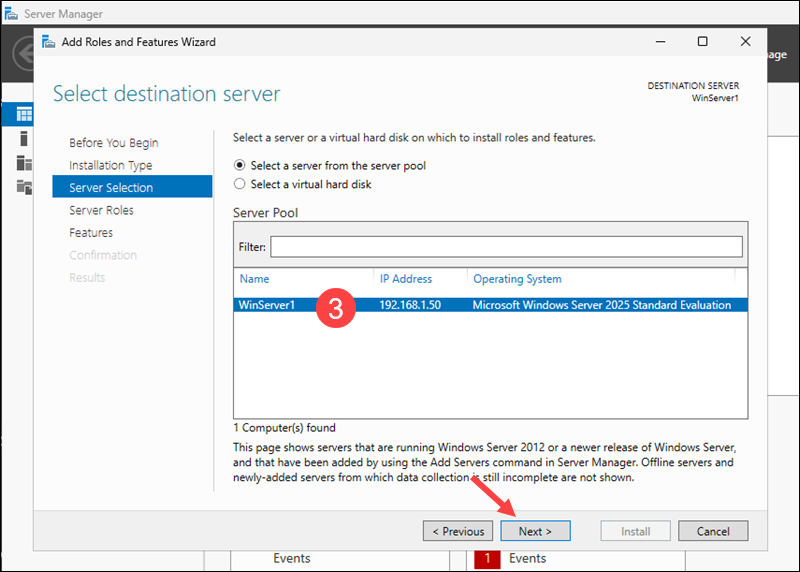
3. Choose the destination server from the Server Pool and click Next.
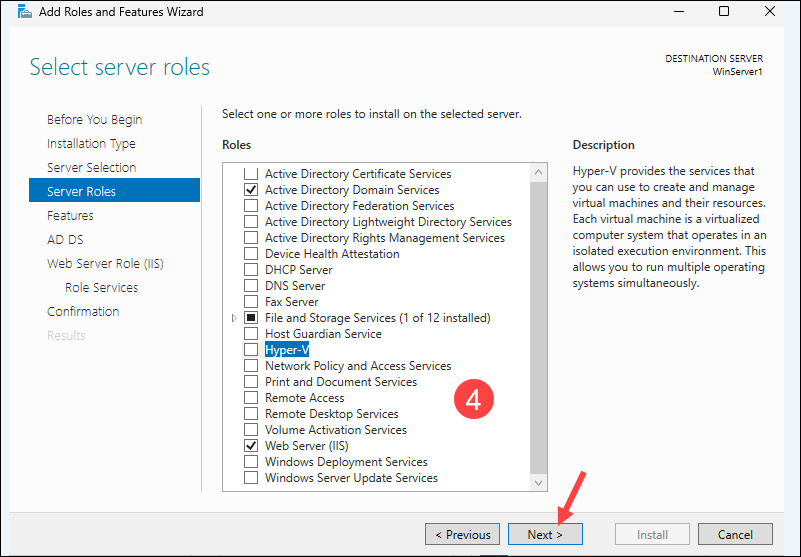
4. Select specific server roles from the list to install, such as Active Directory Domain Service (AD DS), Web Server (IIS), Hyper-V, and click Next.
5. Select additional features, confirm the required dependencies, and proceed with the installation steps.
6. Click Install to confirm your selection and start the installation.
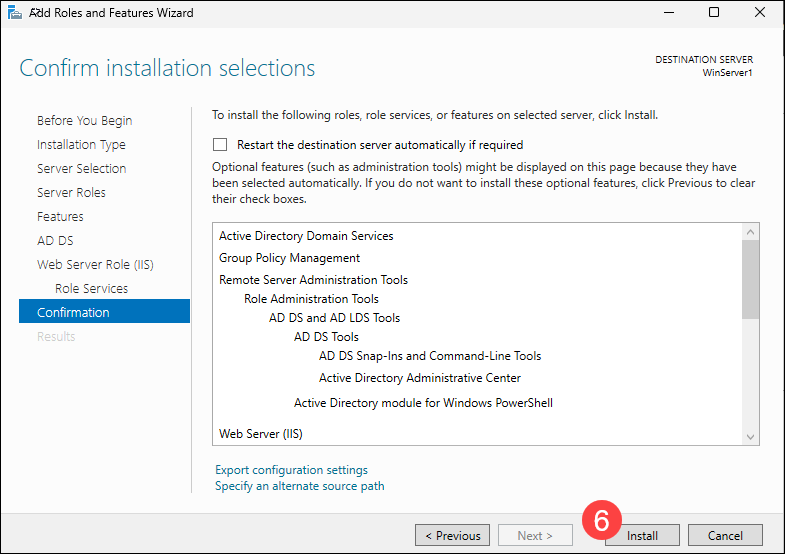
After the installation is complete, it may be necessary to restart the machine.
Enable Remote Desktop
To enable RDP in Windows and manage the server remotely:
1. Access the Local Server tab.
2. Find the Remote Desktop option, and click Disabled.
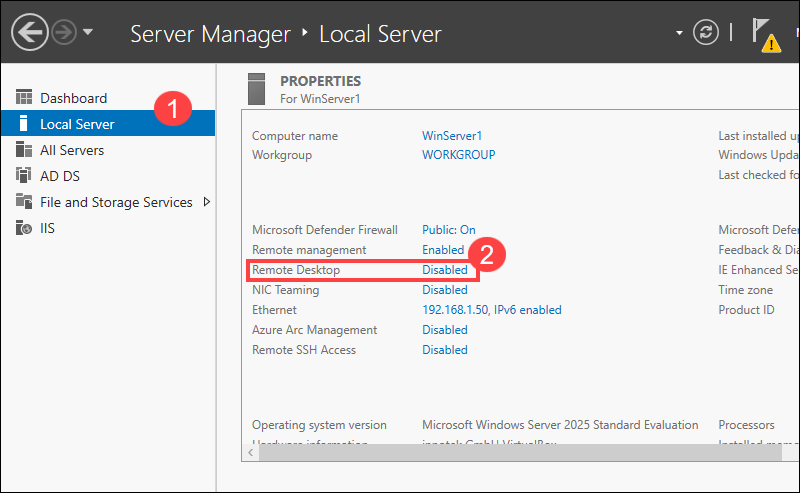
3. Select the Allow remote connections to this computer option.
4. Use the Select Users tab to add additional remote desktop users or groups if necessary.
5. Click Apply to save the settings.
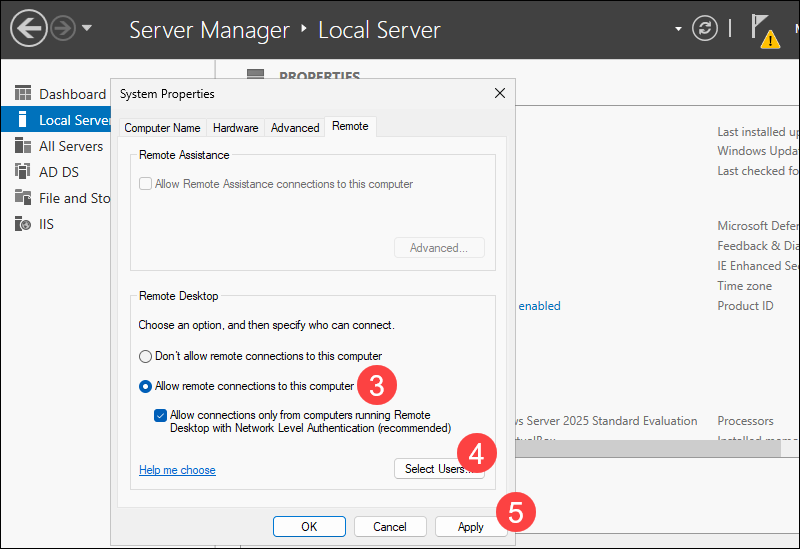
When you return to the Local Server tab, the Remote Desktop option will be Enabled.
Configure Time Synchronization
Accurate timekeeping is essential for authentication and logging. You can point your server to a reliable NTP source:
1. Open the Local Server tab and click the Time zone link.
2. Access the Internet Time tab and click Change settings.
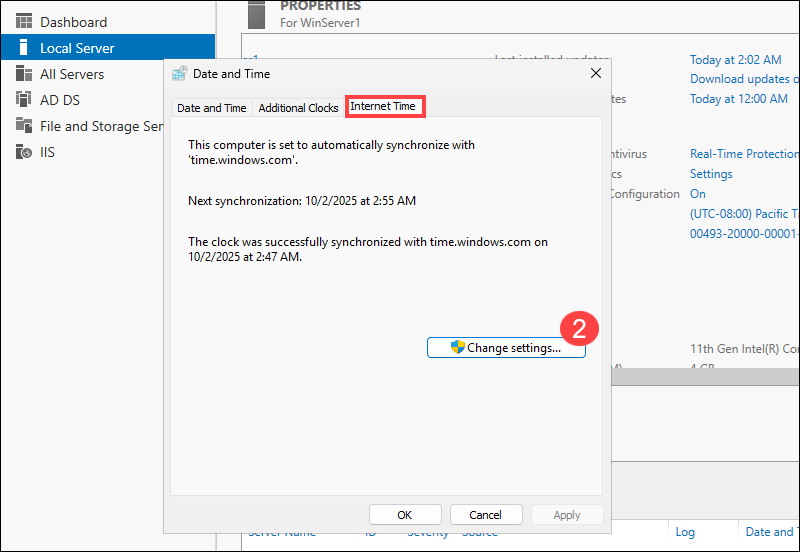
3. Select time.windows.com or enter a custom NTP server (such as your internal NTP server), and click Update now.
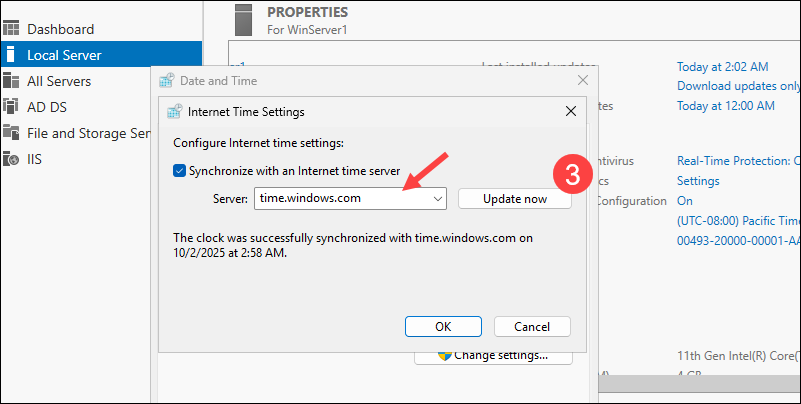
4. Open the Command Prompt and enter the following command to test the synchronization:
w32tm /resync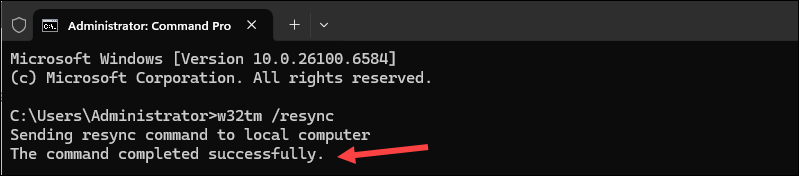
The output confirms the resync is successful.
Check Antivirus and Firewall
To confirm that Windows Defender Antivirus and Windows Firewall are enabled:
1. Access the Local Server tab.
2. Check the Microsoft Defender Firewall field and confirm it displays the Public: On message.
3. Also, check the Microsoft Defender Antivirus field. It should display Real-Time Protection: On.
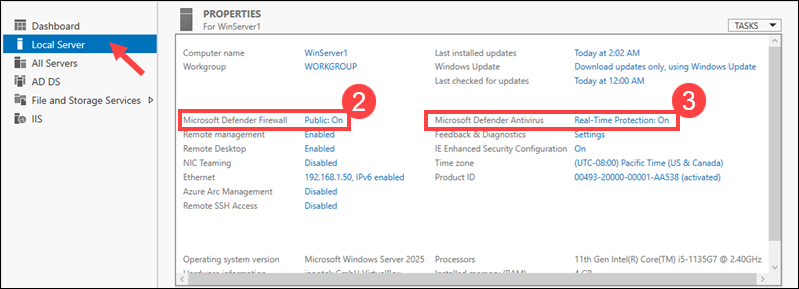
By clicking on the links, you can adjust firewall rules or antivirus settings. For example, creating exemptions for specific ports and services to allow them through the firewall.
Automate Backups
You can use the built-in Windows Server Backup feature to protect your system against data loss. To install and configure Windows Server Backup:
1. Click Manage and select the Add Roles and Features option.
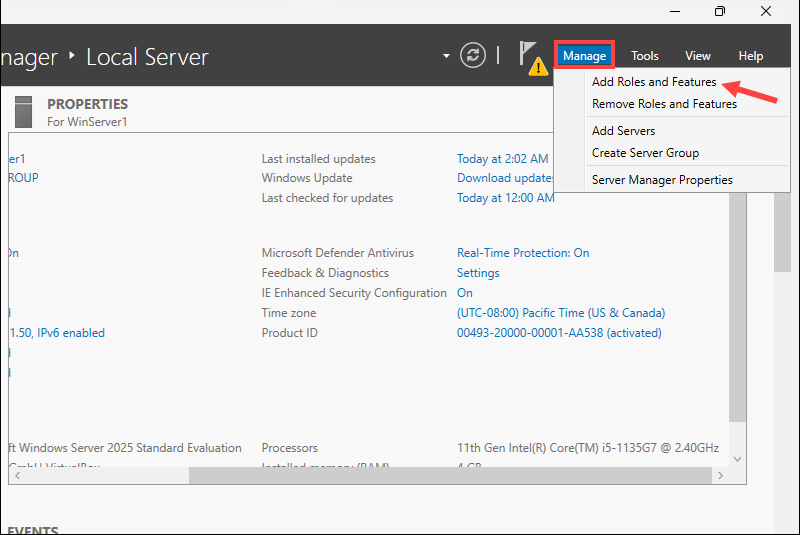
2. In the wizard, go to the Features section.
3. Select the Windows Server Backup feature and click Next.
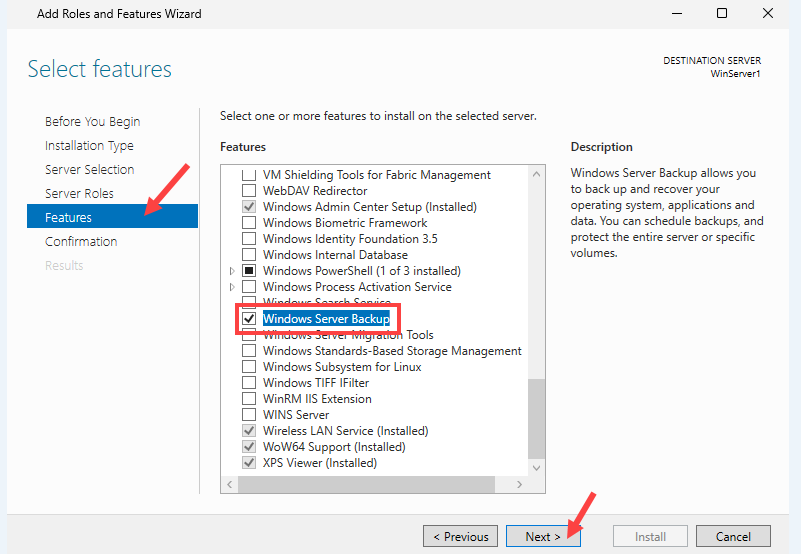
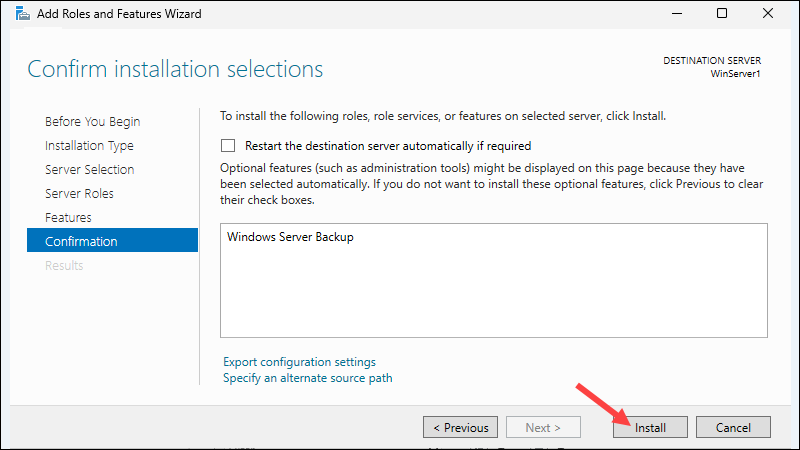
4. Click Install to confirm the installation.
5. After the installation, click Tools and select Windows Server Backup from the list.
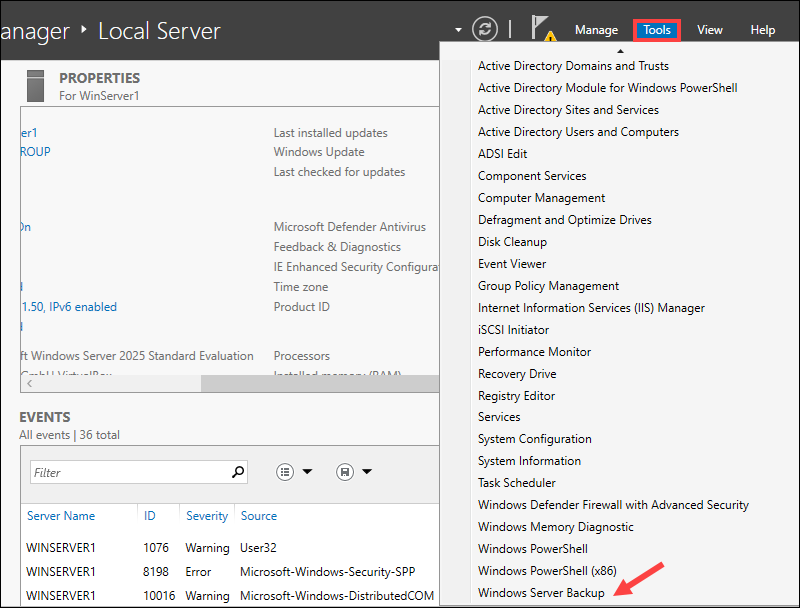
6. Click Local Backup and then Backup Schedule to set up a timetable for automatic backups.
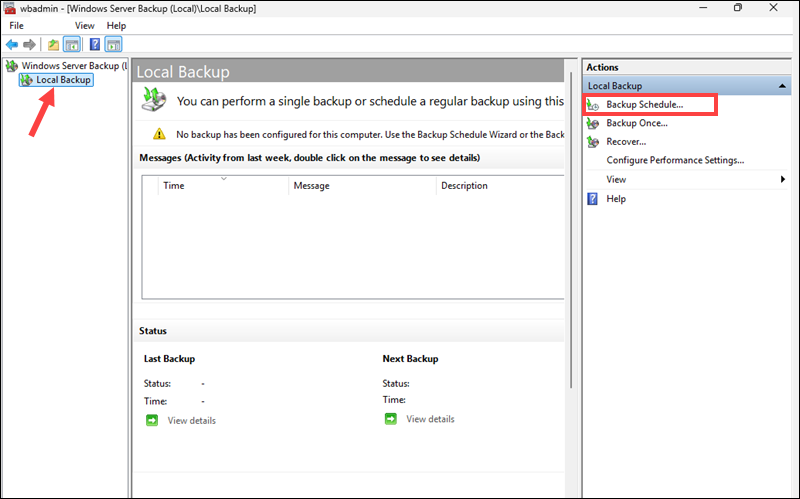
If you do not have an external storage system, you can add a secondary virtual disk in your hypervisor and use it to test backups.
Conclusion
You have successfully installed the latest stable version of Windows Server 2025 on a VirtualBox VM. The instance is secure, up-to-date, and ready to host roles and workloads.
If you need a database solution to support the applications running on your server, also learn how to install MySQL on Windows Server.


