The Windows operating system includes over 280 CMD (Command Prompt) commands. These commands enable users to interact directly with the OS and perform various troubleshooting and IT automation tasks.
Many CMD commands work on specific Windows desktop versions, while others are only available for Windows Server editions.
This extensive guide lists all Windows CMD commands and provides hands-on examples of the most commonly used ones.

Prerequisites
- Access to the command prompt (CMD).
- Administrator privileges (for some commands).
Essential Command Prompt Commands
Commands are built-in programs that run through the Command Prompt program. The main use for commands is to automate various tasks, such as user provisioning and other routine actions.
Below is an overview of essential Windows CMD (Command Prompt) commands. Every command has a brief explanation and an example use case.
1. arp Command
The arp (Address Resolution Protocol) command shows and modifies entries in the ARP cache. The cache contains one or multiple tables that map IP addresses to physical (MAC) addresses for devices on the local network.
The syntax for the command is:
arp [options] [address]Without any parameters, the arp command shows the help window.
To show the ARP cache table, run the following command:
arp -a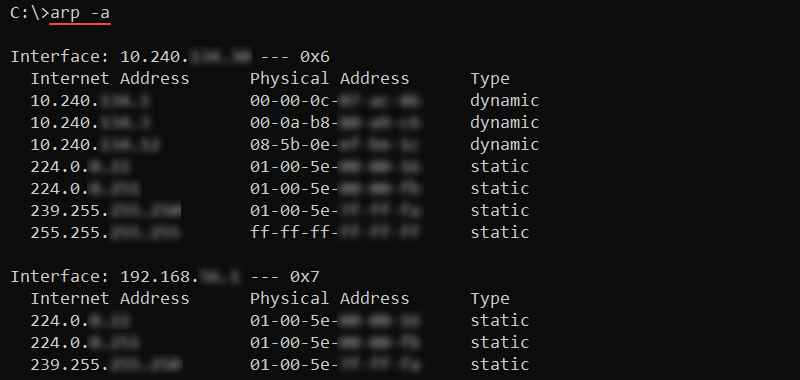
The output lists all the current ARP entries grouped by network interface.
2. assoc Command
The assoc (association) command lists and modifies file extension associations on the system. The syntax for the command is:
assoc .[extension]=[filetype]Without any parameters, the command prints the current file extension associations.
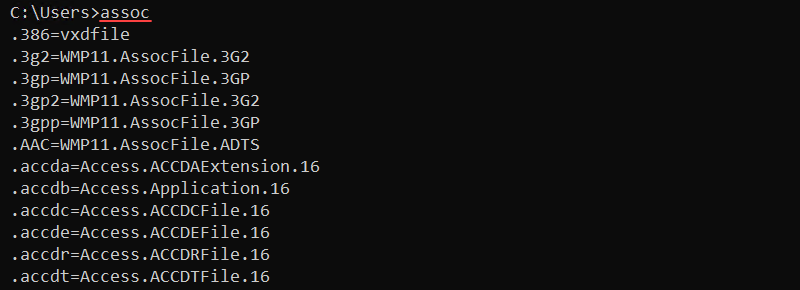
Use the assoc command to view, change, or remove file associations. For example, to view the .log file associations, enter:
assoc .log
Change the file association with:
assoc .log=txtfileAlternatively, to remove all file associations for files with the .log extension, use:
assoc .log= Add a space after the equals sign to remove the association.
3. attrib Command
The attrib (attribute) command displays or changes file attributes. The possible attributes are:
- R - Read-only.
- H - Hidden.
- S - System file.
The syntax for the attrib command is:
attrib [+/-] [attribute] [file_or_directory]Use the plus sign (+) to set an attribute or the minus sign (-) to remove an attribute from a file. Without any options, the command shows the file attributes in the current directory.
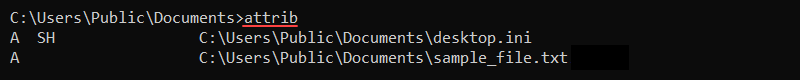
To set a file to have the read-only (R) and hidden (H) attributes, use the following command:
attrib +R +H sample_file.txt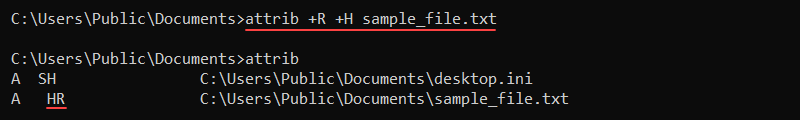
To make a file visible, remove the hidden (H) attribute:
attrib -H sample_file.txt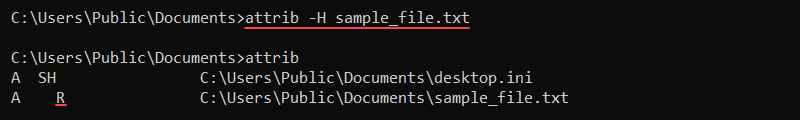
The minus (-) removes the attribute from the file and returns the file to the default visible state.
4. bcdboot Command
The bcdboot (Boot Configuration Data Boot) command sets up a system partition by copying BCD files into an empty partition.
The syntax for the command is:
bcdboot [path]For example, to copy the BCD files into C:\Windows, use:
bcdboot C:\Windows
The message confirms the file has been created.
5. cd Command
The cd (change directory) command shows or changes the current location. The syntax for the command is:
cd [directory]The directory parameter is optional, and without it, the command prints the current working directory.
For example, to change the location to a directory named Public, add the directory name after the command:
cd Public
The prompt reflects the change and shows the new location.
To change the location to a different drive, add the /d option before the path. For example, to change to drive S:\ use:
cd /d S:
cd only displays the path without switching to the specified drive if the /d option is not used.
To change to the parent directory one level up, use the following shortcut:
cd ..
The current directory changes to the parent of the previous location.
6. chkdsk Command
The chkdsk command scans the local file system and metadata for errors. The syntax for checking a disk is:
chkdsk [volume] [options]Without additional parameters, chkdsk displays the current disk state without fixing any errors.
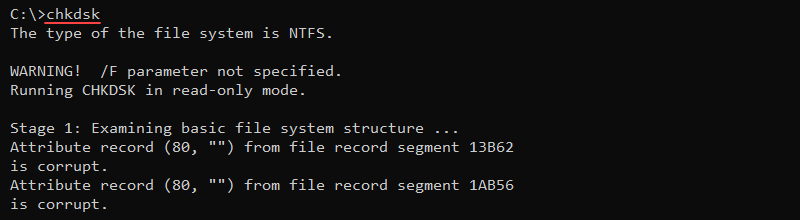
Additional parameters allow you to fix errors on a disk, for example, the /f option:
chkdsk [volume] /f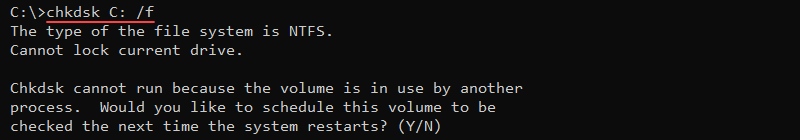
The command attempts to fix errors on the disk. If the disk is in use, run the check on the next system restart. Interrupting chkdsk while it's running is generally safe, but it’s recommended to complete the scan later to address potential data corruption.
7. choice Command
The choice command prompts a user to choose an answer from a list of options. Without any parameters, the command prompts the user to choose between Y and N options.
Additional options control the number of choices and the prompt text. For example, to add a third choice, use the /c parameter and list the three option names:
choice /c ync
Insert additional text to explain the available options with the /m parameter. For example:
choice /c ync /m "Yes, No, Continue"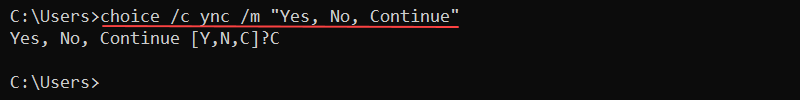
In all cases, the command returns the choice index and exits.
8. cipher Command
The cipher command shows and modifies the encryption status of files or directories on NTFS file systems. The command syntax is:
cipher [options] [file_or_directory]Without any options, cipher shows the encryption state for all files and directories in the current location. The U represents "unencrypted," whereas E is "encrypted."
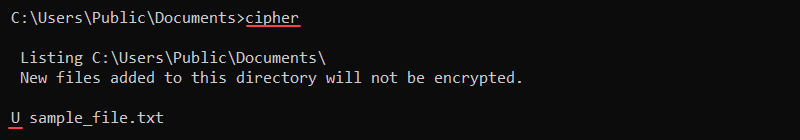
To encrypt a file in the current directory, use the /e parameter:
cipher /e [file name]The file's indicator changes from U to E to mark the file as encrypted.
9. clip Command
The clip command copies a command output or file contents to the Windows clipboard. The syntax for copying a command's output in CMD is:
[command] | clipFor example, to copy the current directory path, pipe the cd command to clip:
cd | clipPaste the contents anywhere in the window using CTRL+V (or right-click in CMD).
To copy the contents of a file, use redirection:
clip < [filename]For example, to copy the contents of a sample.txt file to the clipboard, run:
clip < sample.txtThe file's contents are saved to the clipboard, so you can paste them anywhere.
10. cls Command
The cls command clears the text in a command prompt window and returns a blank surface. Use the command to clear the screen contents.
Note that the previous contents and output cannot be restored.
11. cmd Command
The cmd command starts a new instance of the command interpreter. Use the following syntax to run the command:
cmd [options] [command]Without additional parameters, the cmd command shows the current cmd.exe program version.
Use cmd to run commands without affecting the current session. For example, to test a command and return to the current command interpreter session, use the /c parameter:
cmd /c cd ..The new interpreter changes the directory. However, the /c tag ensures the interpreter returns to the original session, and the directory stays unchanged.
To run a command and stay in the new session, use the /k parameter:
cmd /k cd ..
The /k parameter switches to the new session and runs the cd command to switch to the parent directory.
12. color Command
The color command changes the default console background and text colors. The command syntax is:
color [background][font]The color attributes are hexadecimal numbers from 0 to f. The help window displays all the possible color options:
help color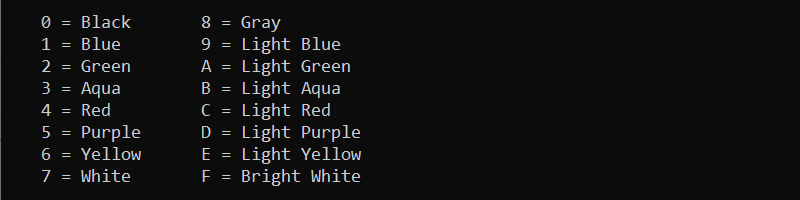
For example, to change the background to blue (1) and the font to light aqua (b), run:
color 1b
To return to the default console colors, run the color command without options.
13. comp Command
The comp command compares the contents of two files. The program inspects file bytes and outputs characters where the two files differ.
The syntax for the command is:
comp [file 1] [file 2] [options]Without any options, the comp command starts an interactive prompt to enter file names and additional options.
To demonstrate how the command works, compare two text files with the following contents:
- sample_file_1.txt contains test
- sample_file_2.txt contains text
Run the comp command and provide the two file names:
comp sample_file_1.txt sample_file_2.txt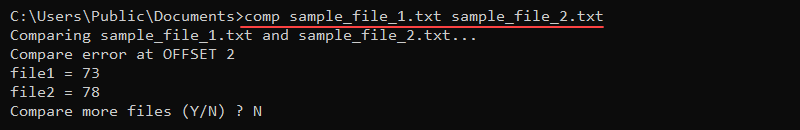
The output prints the comparison error as characters in hexadecimal format and asks to compare more files (enter N to exit).
To print the comp results in human-readable format, use the /a option:
comp /a sample_file_1.txt sample_file_2.txt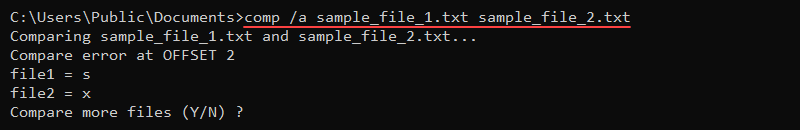
The comparison fails at character s in the first file and character x in the second file.
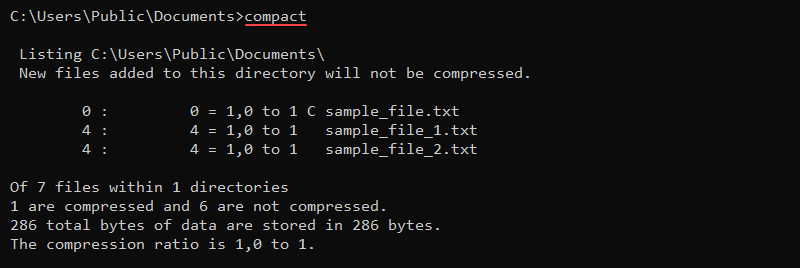
14. compact Command
The compact command is a built-in feature for compressing files and folders. The syntax for the command is:
compact [options] [file_or_directory]Without any options or parameters, compact displays the compression state in the current directory.
To compress a file, use the /c parameter and provide the file name:
compact /c sample_file.txt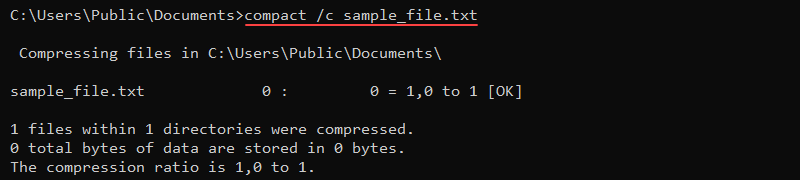
To uncompress a file, use the /u parameter:
compact /u sample_file_1.txt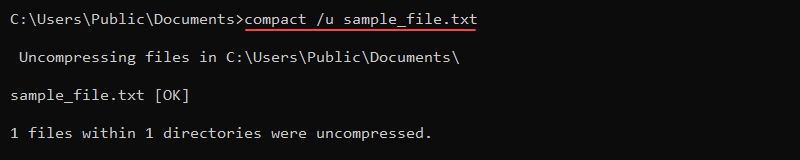
The sample_file_1.txt file is returned to its previous, uncompressed state. Use the compact command to save disk space and compress large files and directories.
15. copy Command
The copy command copies one or multiple files from one location to another. The command syntax is:
copy [options] [source] [destination]For example, to copy a file's contents into a new file in the same location, use:
copy sample_file.txt sample_file_copy.txtThe command creates the new file and copies all the contents from the source file.
16. date Command
The date command shows and modifies the current date on the system. Without any parameters, the command prints the current date and requests to enter a new date:
date
Enter the date as mm-dd-yyyy to change the current date on the system or exit with CTRL+C.
Use the /t parameter to avoid modifying the system state and only print the current date:
date /t
The command shows the day of the week and the current date.
17. defrag Command
The defrag (defragmentation) command finds and aggregates fragmented files on the system. The command reduces unnecessary empty data blocks and improves system performance.
The syntax for the defrag command is:
defrag [volumes] [options]For example, to defragment the C:\ drive, run:
defrag C:\ /u /v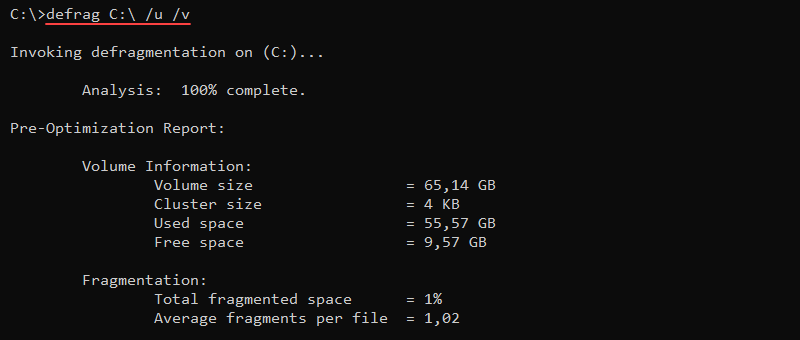
The /u parameter displays progress updates, while /v provides a verbose output. These parameters are optional.
18. del and erase Commands
The del and erase commands delete one or more files. The syntax for the commands is:
del [options] [file(s)]erase [options] [files(s)]Both commands permanently delete the specified file or files from a disk and are irretrievable.
For example, to delete a file with the name sample.txt, run:
del sample.txtOr alternatively:
erase sample.txtTo avoid accidental deletion, use the /p parameter:
del /p sample.txt
The output shows a prompt with the file name and requires confirmation before deleting the file.
19. dir Command
The dir (directory) command lists directory contents, including files and subdirectories. The syntax for the command is:
dir [drive][path][filename] [options]The dir command without options shows information for the current directory.
To show the C:\ drive contents, run:
dir C:\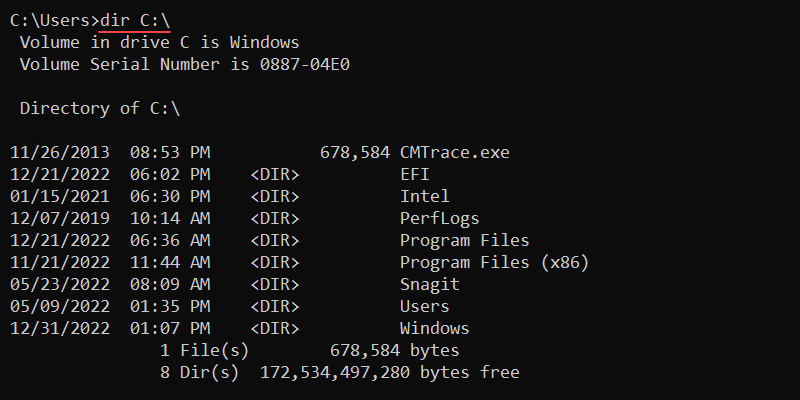
The output shows the following information:
- Volume label and drive letter.
- Volume serial number.
- Directory contents with modification time.
- File and directory count with their combined size.
20. diskpart Command
The diskpart command is a disk partitioning tool used to create, delete, and format partitions.
Enter the following command to access the diskpart interface:
diskpartOnce in diskpart, use the following command to list all disks:
list disk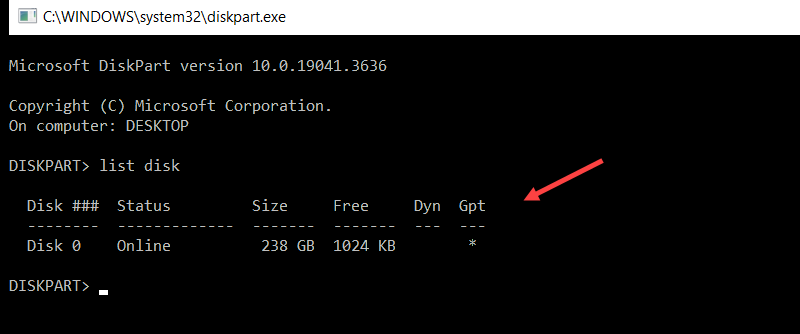
The interface displays all available disks on the system and allows you to use diskpart commands to manage partitions.
21. DISM Command
The Deployment Imaging Service and Management (DISM) command is used to service and manage Windows images. It required administrator privileges. The command is useful for repairing system files or preparing images for deployment.
The general syntax for the DISM command is:
DISM /[target_image] /[operation] /[option]For example, to repair corrupted files on the current Windows instance, use the following command:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth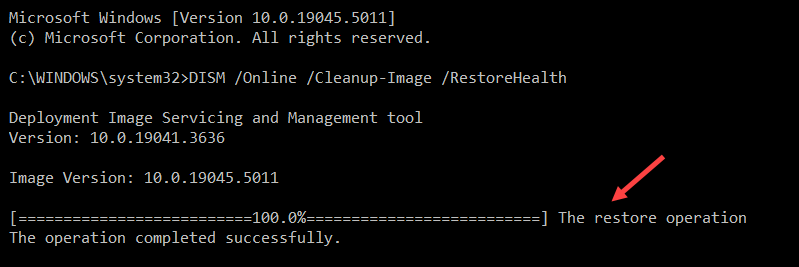
DISM is often used alongside the sfc command to ensure system integrity.
22. doskey Command
The doskey command starts the Doskey.exe program for the previously entered commands. The command helps recall command history and create macros.
For example, to see the command history from the current command prompt session, run:
doskey /history
The output shows all the commands from the CMD session from oldest to newest.
23. driverquery Command
The driverquery command displays the installed device drivers and their information. The command works for both local and remote access machines.
The syntax for the command is:
driverquery [options]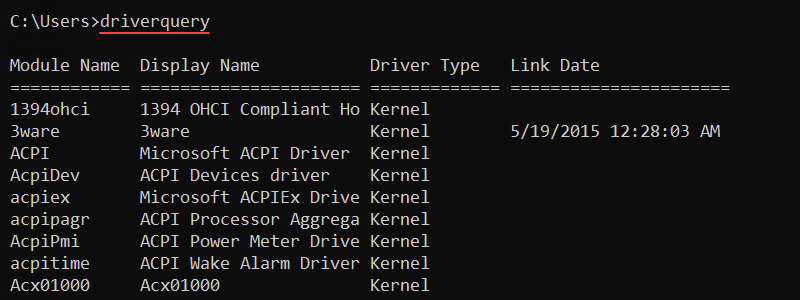
Without options, driverquery shows device drivers on the local machine. Additional options control the output format or allow users to query remote machine drivers.
24. echo Command
The echo command prints a message to the console and controls command echoing in scripts. The syntax for the command is:
echo [message]Without parameters, the command shows the current settings.
To display a "Hello, world!" message, enter:
echo "Hello, world!"
The echo command often appears in scripts to print useful information while the script runs.
Note: Learn how to use the echo command in PowerShell.
25. exit Command
The exit command ends the current batch script or the command interpreter session. The syntax for the command is:
exit [/b]- Use the
/bparameter to exit a batch script but keep the Command Prompt session open. - Without the
/boption, theexitcommand closes the Command Prompt session entirely.
26. fc Command
The fc (file compare) command compares two or more files and displays their differences.
The syntax for fc is:
fc [options] [file1] [file2] For example, to compare two sample files, sample_file_1.txt and sample_file_2.txt, run:
fc sample_file_1.txt sample_file_2.txt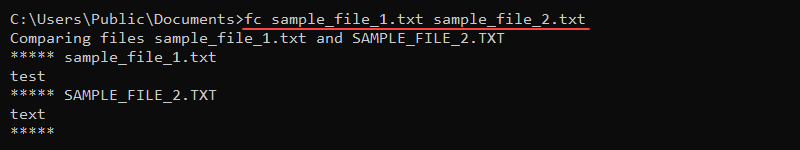
The command prints the file contents, indicating a difference between the two files.
27. find Command
The find command searches for a string within a file and prints matching lines. The command syntax is:
find ["string"] [file]For example, to search for the string "text" in a file, use:
find "text" [file]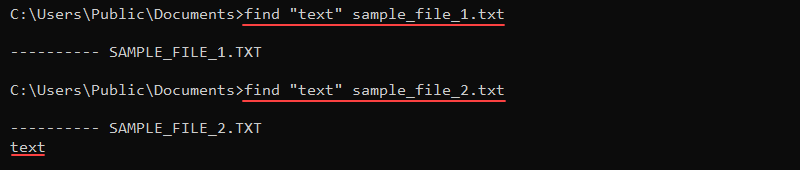
The command looks for an exact match and returns the file name along with the line of text that contains the string. If a file does not contain the text, the command returns the file name without the text.
28. findstr Command
The findstr (find string) command performs a similar task to the find command. The command returns the whole line where the text is located without the file name. This feature makes it more convenient for use in scripts.
The command syntax is:
findstr ["string"] [file]For example, to find a string "text" in a file, run:
findstr "text" [file]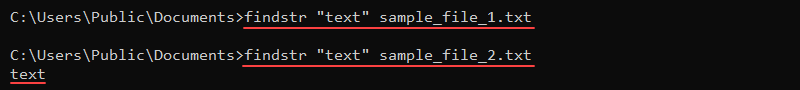
If the command does not return a result, the string is not in the file.
29. ftype Command
The ftype (file type) command shows and changes a file type and extension association. The command syntax is:
ftype [filetype]=[open_command]The filetype parameter is the file to show or modify (such as txtfile), while the open_command option is a string that calls a program to read the file type. The open_command string substitutes the file name into the open command to run a file in the provided program.
Without any options, ftype prints all file types and extension associations.
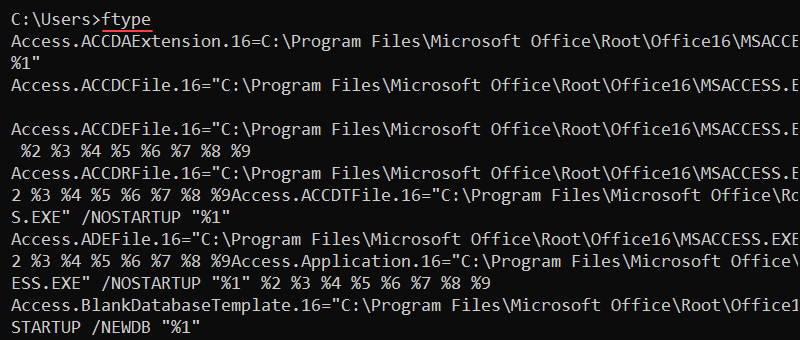
To show the current file type and extension association for text files, enter:
ftype txtfile
To remove file type association, append an (=) sign:
ftype txtfile=The command omits the program for opening files and removes the program association.
30. getmac Command
The getmac command retrieves MAC addresses for all network cards on the computer or in the network. Additionally, it displays the network transport protocols associated with each MAC address.
The syntax is:
getmac [options]Adding options provide detailed information about a remote computer or control the output display. For example, to show the MAC addresses in the CSV format, use:
getmac /fo csv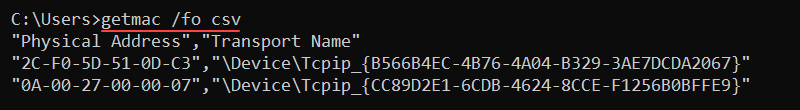
Use the command to parse the MAC address to a network monitoring tool or to check the protocols on network adapters.
31. help Command
The help command shows detailed information about a specific command. Without any parameters, help lists all available system commands.
The syntax for the command is:
help [command]For example, to view the help menu for the cd command, run:
help cd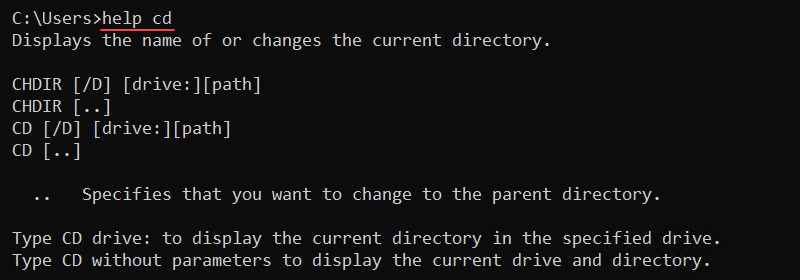
Use any key to go through the pages if the help page is larger than the command line window. Alternatively, press CTRL+C to exit.
Note: For non-system commands, use the following format to see the help window:
[command] /?
32. hostname Command
The hostname command displays a machine's host name. Run the command to see the name of the current machine:
hostname
The command does not have options, and providing additional parameters results in an error. The hostname command is available for systems with TCP/IP installed on a network adapter.
33. ipconfig Command
The ipconfig (IP configuration) command is a networking tool that shows all current TCP/IP network configuration information. The command also refreshes DHCP and DNS settings.
The syntax for the command is:
ipconfig [options]Omitting options shows the basic TCP/IP configuration for all adapters:
ipconfig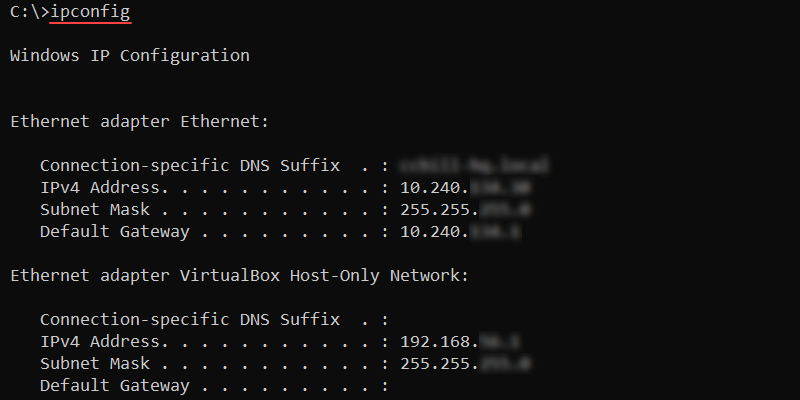
To show the full TCP/IP configuration for all adapters, run:
ipconfig /allRenew the DHCP IP address for the local area connection with:
ipconfig /renew Local Area ConnectionTo flush the DNS cache, use:
ipconfig /flushdnsUse the command when troubleshooting DNS and network connectivity issues.
34. label Command
The label command shows, changes, or removes the volume label (name) of a disk. The command requires administrator privileges to perform any changes.
Without any options, the label command shows the label for the C:\ drive and starts a prompt to change the name:
label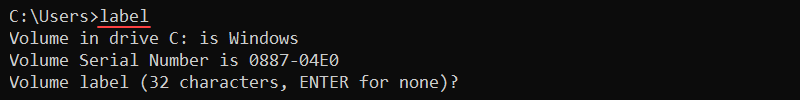
Press Enter to remove the label, or enter a new name to change the current label name. Confirm the change with Y or press N to keep the existing name.
35. makecab Command
The makecab command creates a cabinet (.cab) file. Cabinet files are an archive format specific to Windows systems with support for lossless data compression and archive integrity.
Use the following syntax to create .cab files with the makecab command:
makecab [options] [source] [destination]For example, to create a sample_cab.cab file in the current directory and add a sample_file.txt file to the archive, use:
makecab sample_file.txt sample_cab.cab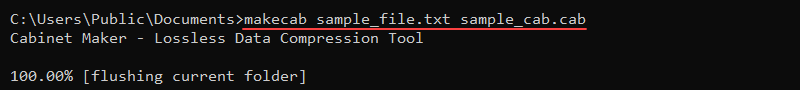
The output shows the compression progress and exits when done.
36. md and mkdir Commands
The md and mkdir (make directory) commands create a new directory or subdirectory. The command syntax is:
md [path]mkdir [path]For example, to make a new subdirectory called Subdir in the current location, run:
mkdir SubdirThe command extensions enable md and mkdir to create a directory tree:
md Subdir\Subsubdir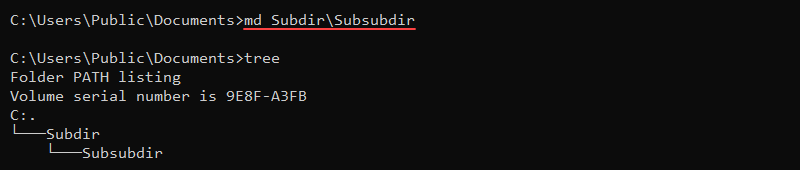
The command immediately creates all intermediate subdirectories in the specified path.
37. mklink Command
The mklink (make link) command creates a hard or symbolic link to a file or directory. The command requires administrator privileges to run and uses the following syntax:
mklink [options] [link] [target]Without any additional options, the mlink command creates a symbolic link to a file. For example:
mklink my_link sample_file.txt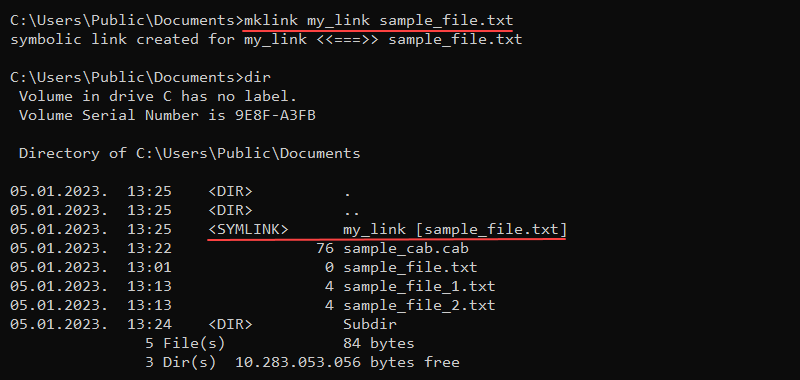
To create a hard link instead of a symbolic link, use the /h parameter:
mklink /h my_link sample_file.txtCreate a symbolic link to a directory with the /d parameter:
mklink /d \Docs \Users\user1\DocumentsThe dir command shows the links in the directory listing. To enter the directory, use the cd command and treat the link as a regular directory (cd Docs).
38. more Command
The more command is a Windows CMD utility for displaying long documents or outputs one screen at a time. To use more with a command, use the pipe (|) character:
[command] | more [options]Alternatively, use the command to display long files page by page:
more [path]For example, to view the output of the help cd command one screen at a time, use:
help cd | more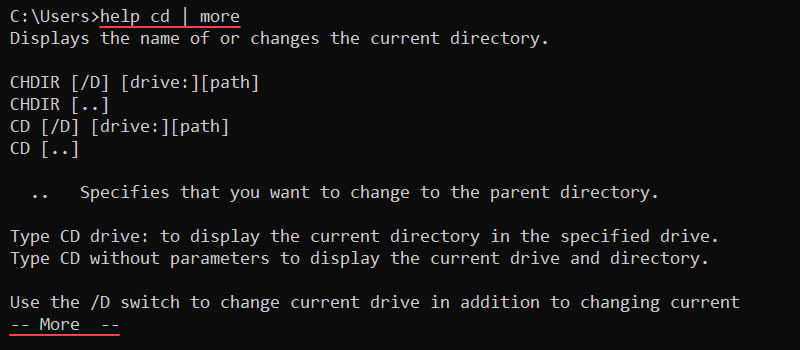
Press Enter to go to the following line and Space to go to the next page. To exit, press q.
39. mountvol Command
The mountvol command creates, removes, or shows a volume mount point. Mounting a volume makes data on a storage device available for local users through the file system.
The command syntax is:
mountvol [path] [volume_name]The command does not require a drive letter to link a volume. Without any parameters, the mountvol command shows the help menu, mount points, and possible volume names.
For example, to list the volume name and current mount point for the C:\ drive, enter:
mountvol C:\ /l
The output shows the Globally Unique Identifier (GUID) for the volume, which uniquely identifies the volume.
40. move Command
The move command transfers files or directories from one location to another. The syntax for the command is:
move [options] [source] [destination]The source and destination are either a folder or a file. The move command renames a file if the source and destination locations are the same but have different file names.
For example, the following command renames a file named sample_file.txt to file.txt:
move sample_file.txt file.txt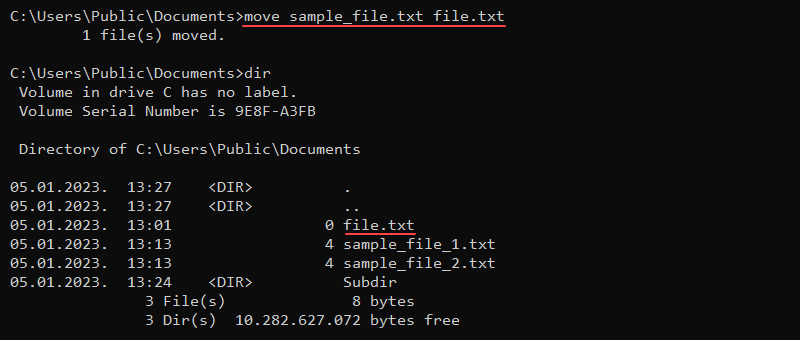
Provide the full path to move a file to another location:
move C:\Users\Public\Downloads\my_file.txt C:\Users\Public\Desktop\my_file.txt When overwriting an existing file, the command prompts for confirmation unless the command runs as part of a batch script.
Note: Learn more about working with bash scripts by referring to our articles How to Write a Bash Script and How To Run A Bash Script.
41. msiexec Command
The msiexec program runs the Windows Installer program for installing, managing, and removing .msi software packages. The command syntax is:
msiexec [options] [path_to_package]The program features various install, display, update, and repair options. Without any options, the msiexec command opens a window to show the command information.
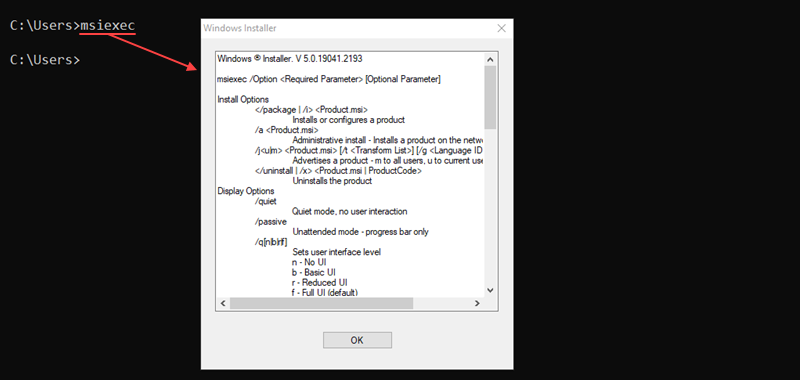
For example, to perform a normal installation of a .msi package, run:
msiexec /i "C:\example.msi"The /i option indicates a normal installation of the .msi package located at the provided path.
42. msinfo32 Command
The msinfo32 command opens the System Information window, which displays detailed information about the system.
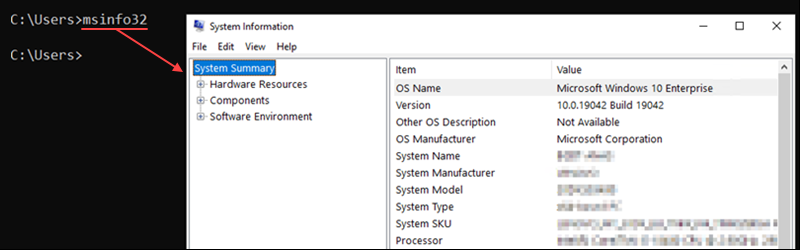
The command syntax is:
msinfo32 [options]Additional options filter the information or export data into specific file formats. For example, to export all system information into an .nfo file, use:
msinfo /nfo sysinfo.nfoThe command automatically appends the .nfo extension if omitted.
43. mstsc Command
The mstsc command launches the RDC (Remote Desktop Connection) program to connect to a remote machine. Use the command for remote connection or to alter an existing .rdp file.
The command syntax is:
mstsc [options] [file]For example, to start an RDC session in full-screen mode, use this command:
mstsc /f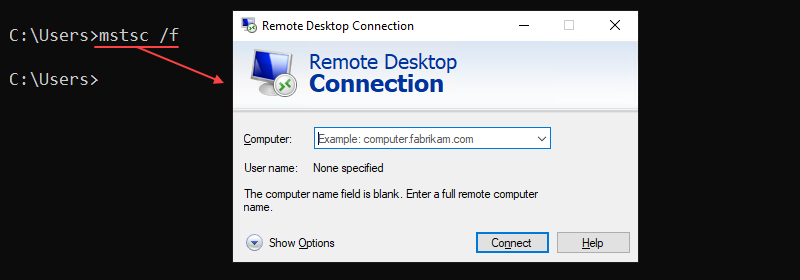
To edit an existing connection, use the /edit parameter and provide the file name:
mstsc /edit example.rdpUser-created .rdp files are stored in the Documents folder by default.
44. net Commands
net commands are a set of tools for managing various network aspects, such as users and network services.
The command syntax is:
net [subcommand] [options]Without additional parameters, the net command shows all available subcommands with a short description.
Use the net start command to list all running Windows services:
net start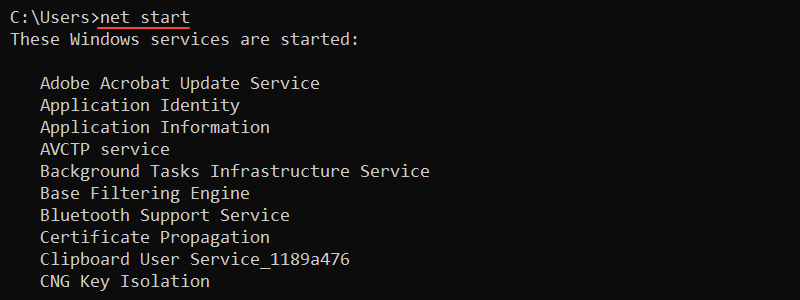
To stop a service, use the following command:
net stop [service]View the login and password requirements for a user with the following:
net accounts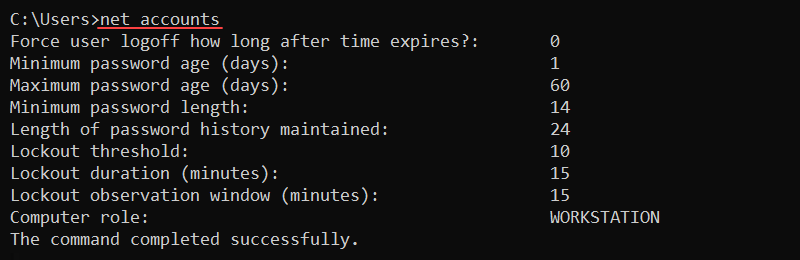
Display additional help for a subcommand using the following syntax:
net help [subcommand]The output shows a help window with detailed information for the provided subcommand.
45. netstat Command
The netstat (network statistics) command is an essential command for network administrators. The command lets you view connection details and various network statistics.
The basic syntax for the command is:
netstat [options]The command displays active TCP connections when used without options. The output shows the protocol, local and foreign addresses, and the TCP connection state.
Add the -a option to display all active TCP connections and listening TCP and UDP ports:
netstat -a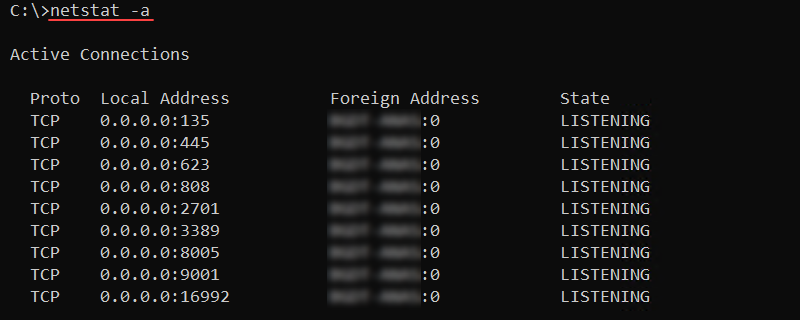
Use the command to scan for open ports or to check the port protocol type.
46. nslookup Command
The nslookup command is a DNS diagnostic tool to query DNS records for web servers. The command features a non-interactive mode for looking up a single piece of information and an interactive mode for looking up additional data.
The syntax for nslookup is:
nslookup [host] [command] [options]Without any options, nslookup enters interactive mode. To find DNS records for a specific domain name, use:
nslookup [domain]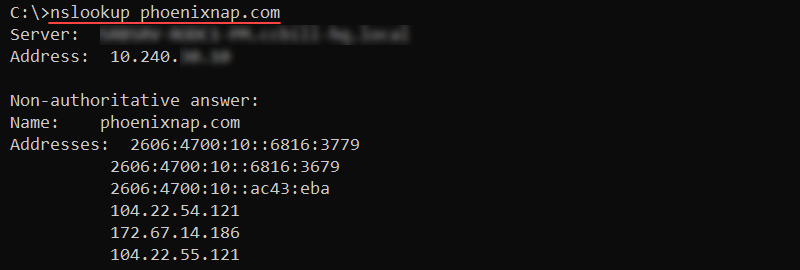
The output prints the A records for the provided domain.
47. path Command
The path command modifies the PATH environment variable. The variable contains a set of directories that point to executable files.
The command syntax looks like the following:
path [location]Without any parameters, path shows the current state of the PATH variable.
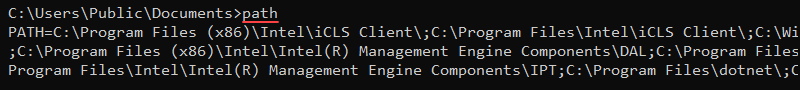
To add multiple locations to PATH, separate each location with a semicolon (;) as in the following example:
path [location 1]; [location 2]Both locations append to the variable.
48. ping Command
The ping command is an essential network troubleshooting tool used to test connectivity with another machine by sending ICMP request messages.
The syntax for the command is:
ping [options] [host]For example, to check connectivity to the phoenixNAP website, use:
ping phoenixnap.com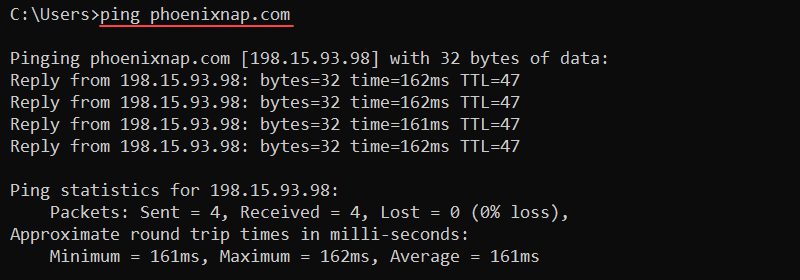
The output prints corresponding reply messages and round-trip times. Use the command to check for connectivity and name resolution issues.
49. powercfg Command
The powercfg (power configure) command runs the powercfg.exe program to manage system power plans. It also helps troubleshoot battery life and energy efficiency problems on a device.
The command syntax is:
powercfg [options] [arguments]To list available power plans on a device, use:
powercfg /list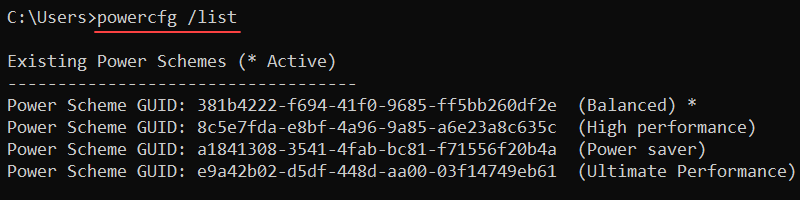
The output lists all power schemes on the system. The active power scheme has an asterisk (*).
50. powershell Command
The powershell command opens a PowerShell session within the CMD to provide access to advanced scripting and management features.
Enter the following command to invoke PowerShell from CMD:
powershellYou can now run PowerShell commands. For example, the following PowerShell command lists running processes:
Get-Process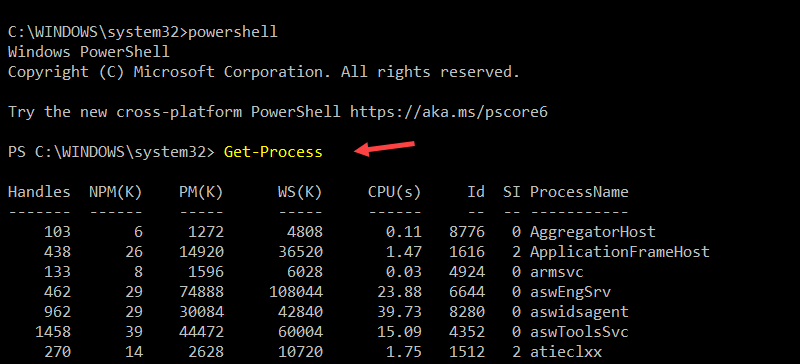
The output displays a list of active processes. To leave the PowerShell prompt and return to the CMD, type:
exitUsing PowerShell through CMD lets you quickly switch to a more robust scripting environment without leaving the session window.
Note: Learn about the differences between PowerShell and CMD.
51. prompt Command
The prompt command customizes the CMD prompt display to a specified string. By default, the prompt shows the current location and the greater-than sign (>).
The command syntax is:
prompt [string_and_variables]The prompt command supports various variables to add special characters or features. For example, to change the prompt to an arrow, use:
prompt --$g
The $g variable represents the greater-than sign (>). The prompt custom stays active during the command-line session.
52. rd and rmdir Commands
The rd and rmdir commands remove an empty directory from the system. The syntax for the commands is:
rd [path]rmdir [path]Attempting to delete a directory with files results in an error message. Add the /s parameter to delete a directory with subdirectories and files:
rd /s [path]The command deletes the complete subdirectory tree and all files.
53. ren and rename Commands
The ren and rename commands rename files or directories. The syntax for the two commands is:
ren [path][old_name] [new_name]rename [path][old_name] [new_name]The commands do not allow moving the files to a different location. Wildcard characters work for multiple files. For example, to change all .txt files to .c files, use:
ren *.txt *.c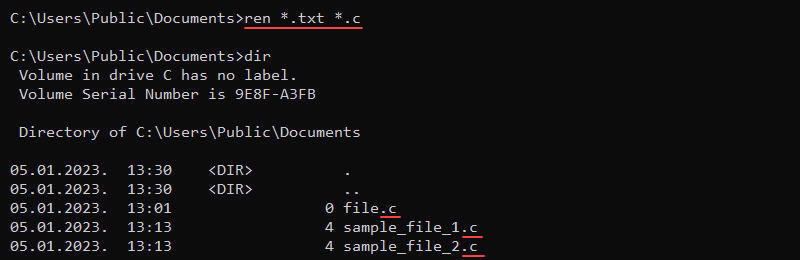
The asterisk (*) wildcard matches all .txt files in the current directory and renames the files to have the .c extension.
54. robocopy Command
The robocopy command is a powerful tool for copying files and directories. The syntax for the command is:
robocopy [source] [destination] [file] [options]The main benefit when using robocopy is the /mt parameter for higher-performance multithreading. Additionally, the /z parameter lets you restart a transfer in case of interruptions.
An example transfer looks like the following:
robocopy C:\Users\user\Downloads C:\Users\user\Documents database.db /mt /z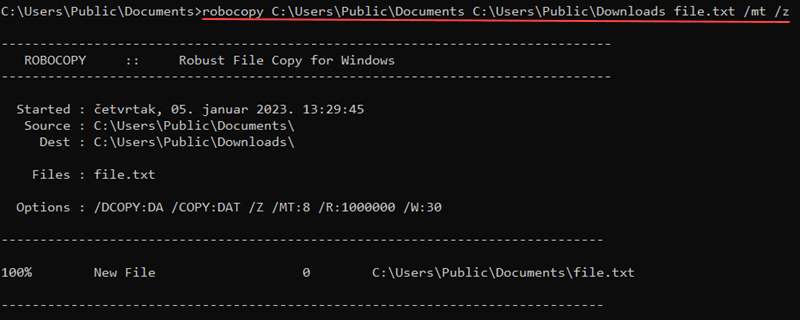
Use the command for large file transfers that are sensitive to interruptions.
55. route Command
The route command shows and alters entries in the local routing table. The command syntax is:
route [options] [command] [value]Available commands include:
add- Adds a route entry to the table.change- Modifies an entry in the table.delete- Removes a route from the table.print- Displays a route or routes.
For example, to print all routes from the table, use:
route print 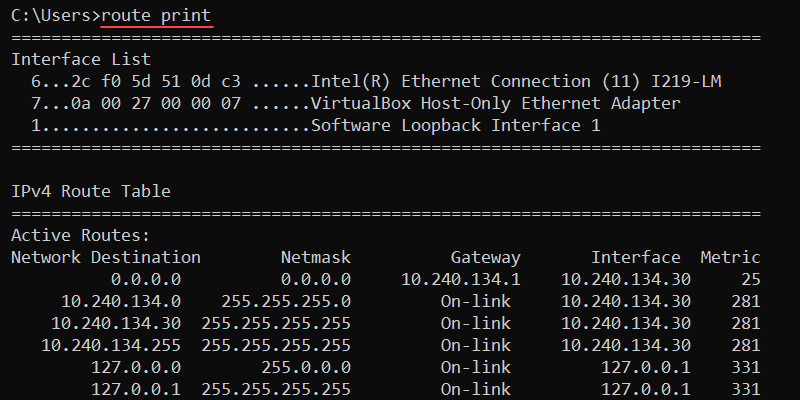
The output shows the interface list, as well as the IPv4 and IPv6 routing tables.
56. sc Command
The sc (service control) command allows users to manage Windows services without opening the Services Manager. Users can start, stop, query, and configure services from the command line.
The syntax for the sc command is:
sc query [service_name]For example, to check the status of the Windows Update service, run:
sc query wuauserv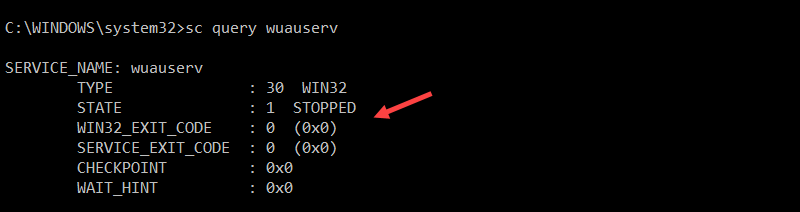
The output shows details about the service, including its status.
57. schtasks Commands
The schtasks command schedules commands or programs to run on the system at specified times or periodically and is often used to set up cron jobs. The syntax for the commands is:
schtasks /[subcommand]The following subcommands are available:
change- Modifies existing properties of a task.create- Creates a new task.delete- Removes a task.end- Stops a program started by a task.query- Prints scheduled tasks on the machine.run- Starts a scheduled task.
For example, to show currently scheduled tasks on the system, use:
schtasks /query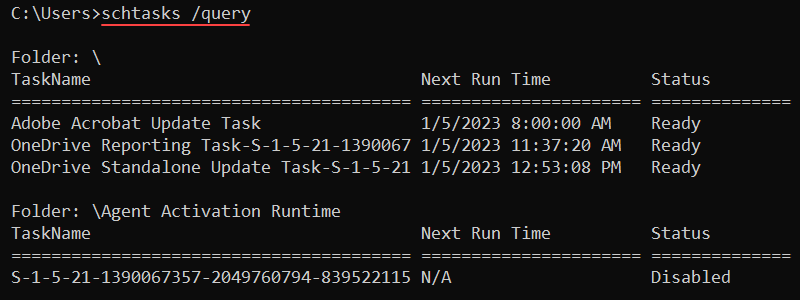
The output displays task names, next run times, and task statuses.
58. set Command
The set command shows, sets, and removes environment variables in the CMD. The syntax for the command is:
set [variable]=[value]Without additional parameters, the set command shows all environment variables.
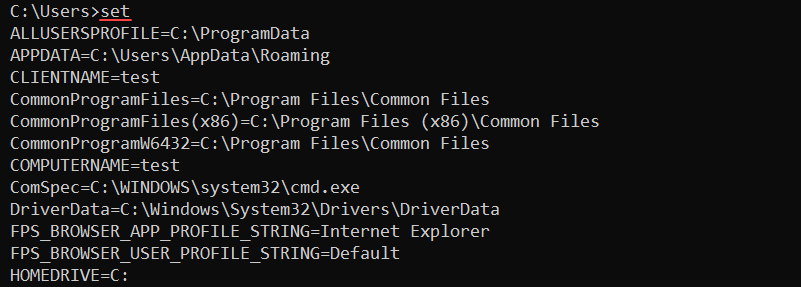
The variables are available to use with any command. For example, to create a new CMD variable called message, use:
set message="Hello, world!"Reference the variable using the following syntax:
echo %message%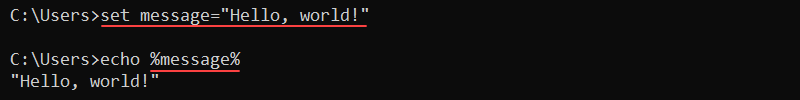
Encasing the variable in the percent signs (%) reads the value and outputs it to the screen.
Note: The variables do not persist and are only valid for the current command-prompt session.
59. sfc Command
The sfc (System File Checker) is an administrator command for checking protected file version integrity. It also replaces incorrect overwritten protected files with the correct file version.
The syntax for the command is:
sfc [options] [file_or_directory]For example, to scan the system and repair all files, use:
sfc /scannow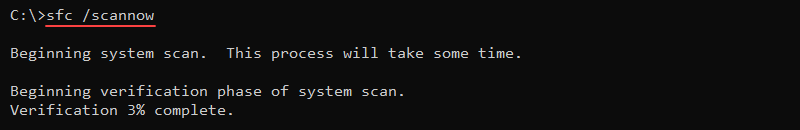
The command scans all protected system files and repairs problematic files when possible.
60. shutdown Command
The shutdown command restarts or shuts down a local or remote computer. The command syntax is:
shutdown [options]Without any arguments, the shutdown command opens the help menu. To restart the computer, use the /r option:
shutdown /r
To shut down without restarting, use the /s argument:
shutdown /sIn both cases, the shutdown is not immediate. To cancel the action, use the /a option:
shutdown /aThe option ensures that a previously executed shutdown command is aborted.
61. sort Command
The sort command allows sorting provided data from a file or user input. Additional options control the sorting mechanism and from which point to start sorting.
To use the command interactively, do the following:
1. Run sort without any options.
2. Enter a new word in each line.
3. Press CTRL+Z and Enter at the end of the list to sort the input values alphabetically.

Alternatively, use the sort command on files:
sort sample_file.txt
The command sorts the file contents and prints the result to the console.
62. start Command
The start command opens a new Command Prompt window according to the specified options. The command syntax is:
start [title] [options]For example, to open a new Command Prompt session with the title "Hello, world!" and set the path to C:\. enter the following command:
start "Hello, world!" /d C:\
A new CMD window opens with the starting path on the C:\ drive and a custom title.
63. systeminfo Command
The systeminfo command displays detailed system information about the OS and computer, including hardware properties. The command works on both local and remote machines.
Use the command without options to show the local system information:
systeminfo
Additional options allow you to retrieve system information for remote computers or control the output format. For example, show the output in CSV format with:
systeminfo /fo csvDifferent formats enable you to effectively parse the information through scripts.
64. takeown Command
The takeown (take ownership) command allows an administrator account to take ownership of a file. It provides access to a file for an administrator and makes the administrator the owner.
Add the /f option and specify the file name:
takeown /f [file]
The administrator now has full permissions over the file.
65. taskkill Command
The taskkill command terminates a running process or task on the Windows system through the command line. It is useful for forcefully ending unresponsive processes.
The syntax for the command is:
taskkill [options] [task_or_process]A common way to end a task is to find the process ID (PID) with the tasklist command and end the process with:
taskkill /pid [Process ID]
The command finds the process by ID and forcibly stops it.
66. tasklist Command
The tasklist command shows all running processes on a local or remote computer and their memory usage. It helps identify and reference specific processes.
The syntax for tasklist is:
tasklist [options]Without additional options, the command shows all currently running processes.
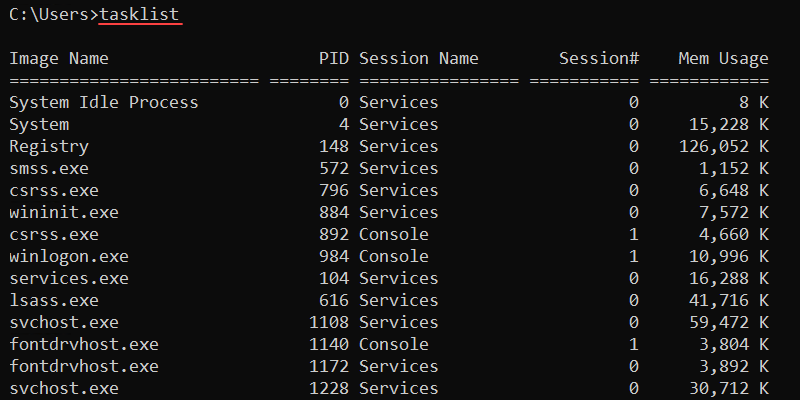
The image name and PID are unique identifiers for a process. The final column shows the memory usage for a process. This is a good indicator for identifying processes that slow down the system.
67. telnet Command
The telnet command is a Windows tool for bidirectional CLI communication. The tool uses the Telnet protocol to send messages and enable an interactive communication channel with remote devices.
The syntax for the command is:
telnet [command] [option]See our detailed guide for using Telnet on Windows.
Note: You can use the telnet command to ping a specific port on Windows.
68. time Command
The time command manages and displays the current system time. Without any options, the command prints the current time and prompts to enter a new time:
time
Enter a new time to change the system time or exit the prompt using CTRL+C. Use the /t option to avoid making modifications:
time /t
The command prints the current time and returns to the command line.
69. timeout Command
The timeout command pauses the command line for a specified number of seconds. The syntax for the command is:
timeout /t [seconds]For example, to pause the interpreter for ten seconds, run:
timeout /t 10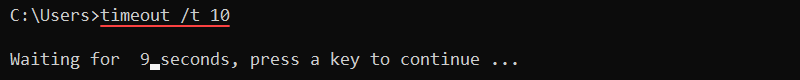
The output counts down and returns to the command line. Press any key to interrupt the timeout earlier. Use the command in scripts to wait for execution between two commands.
70. title Command
The title command is a simple utility for changing the title of the Command Prompt window. The syntax is:
title [string]For example, to set the title to "Hello, world!", use:
title "Hello, world!"
The CMD window title changes to the provided string. Use the command when running multiple batch scripts to distinguish between different command prompts.
71. tracert Command
The tracert (traceroute) command is a networking tool that maps the path from a local computer to a destination. It sends ICMP messages with increasing TTL values to map routers along the path.
The syntax for tracert is:
tracert [option] [destination]For example, to trace the path to phoenixnap.com, use:
tracert phoenixnap.comAlternatively, use the IP address of the destination.
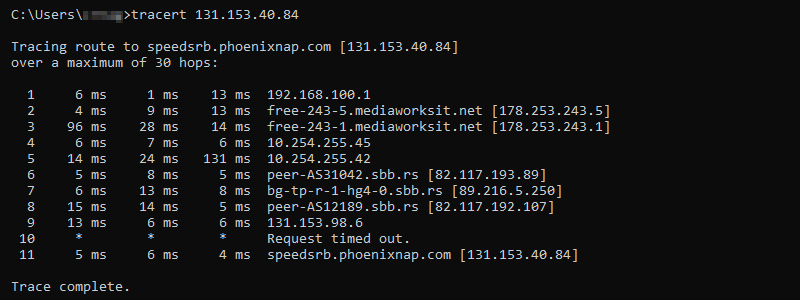
The output shows the hops between the source and destination, providing an IP address and name resolution where applicable. Use the command to discover connectivity issues to a host.
72. tree Command
The tree command displays the contents inside a drive or directory in a tree-like structure. The syntax is:
tree [option] [path]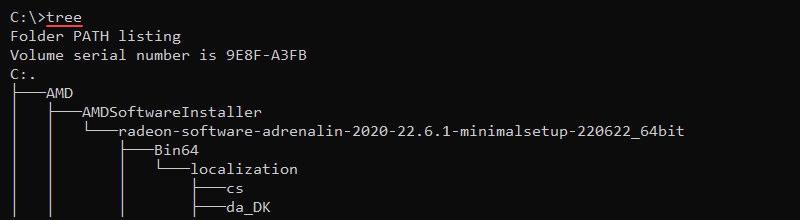
Without options, the tree command displays the directory structure of the C:\ drive.
73. type Command
The type command displays the contents of a file directly in the Command Prompt without modifying it.
The syntax for the type command is:
type [file_path]For example, to show the contents of the file called sample_file.txt, run:
type sample_file.txt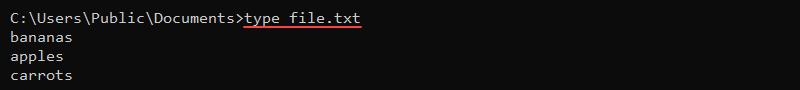
The output prints the file's contents to the command line. Use this command to preview files directly in the command prompt.
74. tzutil Command
The tzutil (time zone utility) command modifies and displays the system's timezone settings.
Display the current time zone with:
tzutil /g
The output shows the time zone ID. List all available time zone IDs with:
tzutil /l | moreThe more command helps truncate long outputs. Use the /s parameter and provide the time zone ID to change the system timezone.
75. ver Command
The ver command is a simple utility to show the operating system version. To display the OS version, enter:
ver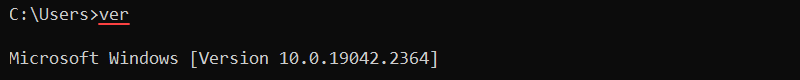
The output displays the OS version and returns to the command line.
76. vol Command
The vol command prints the disk volume label and serial number. The syntax for the command is:
vol [drive]:
Without a specified drive, the vol command shows information for the currently selected drive.
77. where Command
The where command locates a file based on the search pattern and displays its path in the command line. The syntax for the command is:
where [options] [search_location] [filename]Omitting the location searches for the file in the current directory without going through subdirectories. To perform a recursive search, add the /r parameter. For example:
where /r C:\ sample_file.txt
The command searches the C:\ drive and all subdirectories. If the file is found, the command returns the its full location path.
78. whoami Command
The whoami command shows the current user's domain and username. The syntax for the command is:
whoami [option]Without options, the command shows the domain and user name.

Add the /all parameter to show detailed information for the current user:
whoami /all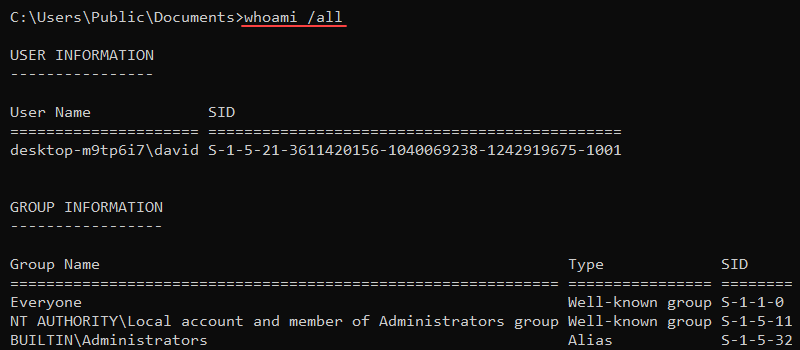
The user's name, security ID, groups, and privileges are displayed.
79. wmic Command
The wmic (Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line) is used to query hardware details, software configurations, and access other system information and settings.
The syntax for the wmic command is:
wmic [alias] [where_clause] [get/set/call] [property]- alias - Specifies the area of the system to query (e.g., cpu, os, product).
whereclause - Adds conditions to narrow down the query.- operation - Defines the action, typically
get(retrieve),set(modify), orcall(execute an action). - property - Lists specific properties to display, retrieve, or modify.
For example, to get a list of all installed applications, enter:
wmic product get name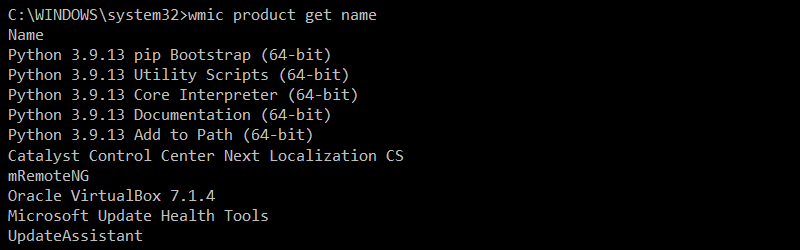
The output shows a list of installed programs.
80. xcopy Command
The xcopy command copies files, directories, and subdirectories from one location to another. The syntax for the command is:
xcopy [source] [destination] [options]For example, use the following command to copy contents from one location to another, including subdirectories (even if empty):
xcopy [source] [destination] /s /e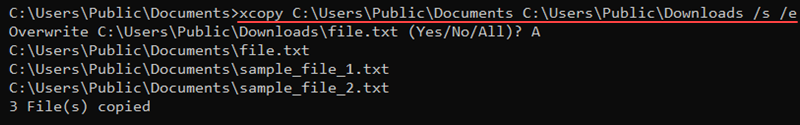
The /s parameter copies subdirectories, while /e includes empty directories. If any files with the same name exist in the destination, the command prompts before overwriting.
Windows CMD Commands Cheat Sheet
The essential commands are available in a single-page cheat sheet in PDF format. Save the cheat sheet for future use and reference by clicking the Download Windows CMD Commands Cheat Sheet button below.
Other Command Prompt Commands
The commands listed in the table are used less frequently by regular Windows users. IT professionals rely on these commands to manage Windows Servers, troubleshoot system processes, configure network settings, and perform other specialized tasks in a business environment:
| Command | Description | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|
accept | Allow the server to accept files or services from the network. | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 |
addusers | List or add users in a batch. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
adprep | Prepare a server for Active Directory installation. Server versions only | Windows Server 2003 and later |
auditpol | Set and display audit policies on a system. | Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
autoconv | Configure automatic file-system conversion during a system restart. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
autofmt | Format media for an automatic conversion. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
bcdedit | Manage boot configuration data (BCD). | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
bdehdcfg | Configure and prepare a hard drive for BitLocker Drive Encryption. | Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
bootsect | Update the master boot code for hard disk partitions to switch between bootloaders. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
call | Call a batch file from another batch file. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
certmgr | Manage certificates for a computer, service, or user. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
certreq | Manage certificate requests. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
certutil | Manage certificates and certificate stores. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
change | Adjust Terminal Server settings, logons, and COM port mappings. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
chcp | Set or display the active code page number. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
chdir | Change the current directory or display its name. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows NT, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
checknetisolation | Set up network isolation testing for Microsoft Store apps. | Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
chglogon | Enable or disable logons on a terminal server. | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 |
chgport | Display or change COM port mappings for DOS applications. | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 |
chgusr | Modify the install mode for the terminal server. | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 |
chkntfs | Modify settings or display the disk check at startup. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
cmdkey | List, create, and delete stored passwords and usernames. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
convert | Convert FAT volumes to NTFS. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
cscript | Run scripts from the command line. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
dcpromo | Promote or demote a domain controller. Server versions only | Windows Server 2000, 2003, 2008 |
diantz | Compress files for distribution. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 |
diskperf | Enable or disable disk performance counters. | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 |
diskraid | Configure and manage RAID arrays. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
dism | Manage Windows images. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
diskshadow | Create and manage shadow copies of disks. | Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
dispdiag | Dump the contents of the Windows display log. | Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
djoin | Provision a computer account in the Windows Active Directory (AD) and join the computer to a domain. | Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
dsadd | Add objects to the Windows Active Directory (AD). Server versions only | Windows Server 2003 and later |
dsget | Display object properties in the Windows Active Directory (AD). Server versions only | Windows Server 2003 and later |
dsquery | Find objects in the Active Directory. Server versions only | Windows Server 2003 and later |
endlocal | End localization of environment changes in a batch file. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
erase | Delete one or more files. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
esentutil | Utility for managing Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) databases. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
eventcreate | Create a custom event in the event log. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
expand | Expand one or more compressed files. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
finger | Display information about a user on a specified remote computer. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
fltmc | Manage system filter drivers. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
fondue | Install optional Windows features. | Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
for | Run a specified command for each file in a set or directory. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
forfiles | Select a file or set of files and execute a command on that file. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
format | Format a disk for use with Windows. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
fsutil | Perform tasks related to file systems, such as managing file system quotas. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
ftp | Transfer files to and from a remote network using FTP. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
goto | Instruct a batch program to jump to a labeled line. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
gpresult | Show Group Policy settings and RSoP for a user or device. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
gpupdate | Update Group Policy settings. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
hwrcomp | Compile handwriting recognition data. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 |
hwrreg | Register handwriting recognizer. | Windows Vista, Windows 7 |
icacls | Show or modify access control lists for files and directories. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
if | Perform conditional processing in batch files. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
inuse | Replace files used by the operating system. | Windows XP |
irftp | Send files over an infrared connection. | Windows XP, Windows Vista |
iscsicli | Manage iSCSI sessions and devices. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
klist | List Kerberos tickets for the current logon session. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
ksetup | Configure Kerberos settings and realm information. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
ktmutil | Control Kernel Transaction Manager (KTM) resource managers. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
licensingdiag | Generate a licensing diagnostics report. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
lodctr | Use to update Performance Monitor counter names and to explain text for an extensible counter. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
logman | Schedule performance counters and event trace sessions. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
logoff | Log off a user from a session. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
lpr | Send a file to a computer or printer-sharing device. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
lpq | Show the status of a printer queue for a computer or printer. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
manage-bde | Configure BitLocker Drive Encryption. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
mode | Configure a system device, like a port or printer. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
mofcomp | Compile Managed Object Format (MOF) files. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
mount | Mount a network file system. Requires additional tools to run, such as the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
mrinfo | Display information about a multicast router. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
msg | Send a message to a user or session. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
muiunattend | Manage unattended installs for Multilingual User Interface (MUI) packages. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
nbtstat | Display protocol statistics and current TCP/IP connections using NetBIOS over TCP/IP. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
net1 | A legacy version of the net command. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
netcfg | Install various network components. | Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
netsh | Configure and manage network settings and components. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
netdom | Join a computer to a domain or manage domain trusts. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
nfsadmin | Manage Network File System (NFS) server and client services. | Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008 |
nltest | Perform network administrative tasks and verify trust relationships. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
ocsetup | Install, list, or uninstall optional components in Windows. | Windows Vista, Windows 7 |
openfiles | View and disconnect files and folders opened by network users. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
pagefileconfig | Set up or display pagefile settings. | Windows XP, Windows Vista |
pathping | Combine the ping and traceroute commands for network path information. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
pause | Pause the execution of a batch file until you press a key. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
perfmon | Open the Performance Monitor utility. GUI only | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
pkgmgr | Install, configure, or uninstall Windows packages. | Windows Vista, Windows 7 |
pnpunattend | Install device drivers automatically. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
pnputil | Manage various device drivers. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
popd | Restore the previous value of the current directory saved by pushd. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
print | Print a text file. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
pushd | Save the current directory and then change it. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
pwlauncher | Turn on Windows To Go startup options. | Windows 8, Windows 10 |
qappsrv | Display all Remote Desktop Session Host servers on the network. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
qprocess | Show information about processes on a system. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
query | Display information about servers, sessions, or processes. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
quser | Display information about user sessions on a Remote Desktop Session Host server. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
qwinsta | Display information about sessions on a Remote Desktop Session Host server. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
rasautou | Manage automatic dialing for RAS connections. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 |
rasdial | Connect to a remote network. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
rdpsign | Digitally sign Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) files. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
reagentc | Set up the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE). | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
recover | Recover readable information from a damaged disk. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
reg | Manage the Windows Registry. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
regedit | Access the Windows Registry Editor. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
regini | Modify the Windows Registry. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
register-cimprovider | Register a Common Information Model (CIM) provider with Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI). | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
regsvr32 | Register OLE controls and DLLs. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
relog | Extract performance counter data from a log file. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
rem | Add comments within batch files or scripts. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
repair-bde | Recover data from a damaged BitLocker-encrypted drive. | Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
replace | Replace files. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
reset | Reset a session in a Remote Desktop environment. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
rmdir | Remove a directory. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
rmtshare | Manage shared resources remotely. | Windows 2000, Windows XP |
rpcinfo | Show RPC information. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
rpcping | Test remote procedure call (RPC) connectivity. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
runas | Run a program as another user. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
rwinsta | Reset the session subsystem hardware and software to default. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
sc | Manage services from the command line. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
scconfig | Configure service startup types and service recovery options. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
sdbinst | Install and uninstall application compatibility databases. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
secedit | Analyze and configure system security settings. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
setlocal | Begin localization of environment changes in a batch file. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
setspn | Manage Service Principal Names (SPN) for Active Directory. | Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
setx | Create or modify environment variables in the user or system environment. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
shadow | Monitor and control a Remote Desktop session. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
shift | Reposition replaceable parameters in a batch file. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
showmount | Display mounted remote NFS file systems. | Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008 |
sigverif | Verify the integrity of system files. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
subst | Associate a path with a drive letter. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
sxstrace | Trace issues with side-by-side assemblies. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
tcmsetup | Set up Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) clients. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
tpmvscmgr | Manage Trusted Platform Module (TPM) virtual smart cards. | Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
tracerpt | Process logs or real-time trace data. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
tscon | Connect a user to a session on a Remote Desktop Session Host server. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
tsdiscon | Disconnect a Remote Desktop Services session. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
tskill | Terminate a process by its process ID or name. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
typeperf | Write performance data to the command window or a log file. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
tzutil | Display or set the system time zone. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
umount | Unmount network file systems. | Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008 |
unlodctr | Unload Performance Monitor counter names and explain text for an extensible counter. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
vaultcmd | Manage credentials in the Windows Vault. | Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
verify | Check if files are written correctly to a disk. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
vssadmin | Set up Volume Shadow Copy services. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
w32tm | Configure Windows Time service settings. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
waitfor | Send or wait for a signal on a system. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
wbadmin | Manage backup and restore operations. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
wecutil | Manage subscriptions to Windows Event Collector (WEC). | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
wevtutil | Manage Windows Event Log. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
winmgmt | Manage the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) service. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
winrm | Manage Windows Remote Management. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
winrs | Initiate remote commands on a remote computer. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
wmic | Command-line interface for Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI). | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
wsmanhttpconfig | Configure Windows Remote Management (WinRM) and HTTP settings. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
xwizard | Access the Windows Experience Wizard for performance and reliability testing. | Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 |
Deprecated and Obsolete CMD Commands
Over the years, many CMD commands have been replaced with modern alternatives, and some do not work in the latest Windows releases. However, older industrial machines, medical devices, ATMs, or even gaming enthusiasts may still operate machines that run on MS-DOS, Windows 95, and other obsolete systems.
The following table lists deprecated and obsolete CMD commands:
| Command | Description | Status | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
append | Control the path used to search for files in MS-DOS applications. | Deprecated | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
at | Schedule commands and programs to run on a computer at a specified time. | Deprecated and replaced by schtasks in later Windows versions. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 |
atmadm | Display information about asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) connections. | Deprecated | Windows 2000, Windows XP |
bitsadmin | Manage Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) jobs. | Deprecated and replaced by PowerShell cmdlets like Start-BitsTransfer. | Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 |
bootcfg | Configure boot file settings (boot.ini). | Deprecated and replaced by bcedit in modern systems. | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 |
break | Enable or disable the CTRL+C feature to interrupt running scripts or commands. | Deprecated but retained for backward compatibility. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
cacls | Modify access control lists (ACLs) of files. | Deprecated in favor of icacls. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
cmdstp | Stop a command processor started with the /k option. | Deprecated | Windows XP |
command | Start a new command interpreter instance in MS-DOS. | Obsolete. Replaced by cmd. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
ctty | Change the terminal device used to control MS-DOS. | Obsolete and no longer supported due to modern terminal management. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
dblspace | Compress drives to increase disk space. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
debug | Start the Debug tool to test and edit programs. | Deprecated | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP |
deltree | Delete an entire directory, including subdirectories. | Deprecated | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
diskcomp | Compare the contents of two floppy disks. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
diskcopy | Copy the contents of one floppy disk to another. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
dosshell | Open the DOS Shell graphical interface. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
dosx | Load the DOS Protected Mode Interface. | Obsolete | MS-DOS |
drvspace | Compress drive to increase disk space. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
edit | Start the MS-DOS text Editor. | Deprecated | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows XP |
edlin | Create and edit text files in MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
emm386 | Enable or disable EMM386 expanded memory support in MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
eventtriggers | Configure event triggers to send notifications. | Deprecated and replaced by Task Scheduler. | Windows XP, Windows Vista |
exe2bin | Convert .exe files to binary format. | Obsolete | MS-DOS |
extrac32 | Extract CAB files (Windows Cabinet files). | Deprecated | Windows XP, Windows Vista |
extract | Extract files from a compressed file. | Obsolete | Windows 95, Windows 98 |
fasthelp | Help for MS-DOS commands. | Obsolete. The help command offers similar functionality. | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
fastopen | Improve the performance of frequently used applications. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
fdisk | Partition and configure hard drives. | Deprecated and replaced by diskpart. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
forcedos | Start a program in MS-DOS compatibility mode. | Obsolete | Windows 95, Windows 98 |
graphics | Load a program that prints graphics screens. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
graftabl | Display extended character sets in graphics mode. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
interlnk | Connect two computers via serial or parallel ports. | Obsolete | MS-DOS |
intersvr | Start the Interlnk server to share files over serial or parallel ports. | Obsolete | MS-DOS |
ipxroute | Manage IPX routing tables for Novell networks. | Obsolete | Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT |
kb16 | Use a specific keyboard layout for MS-DOS. | Deprecated | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
keyb | Configure the keyboard layout for MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
lh | Load a program into upper memory. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
loadfix | Load a program above the first 64K of memory to avoid conflicts. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
loadhigh | Load a program into upper memory. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
lock | Lock a drive to allow direct disk access. | Deprecated | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
mem | Display memory usage statistics. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
memmaker | Optimize memory usage. | Obsolete due to modern automatic memory management. | MS-DOS |
msav | Start Microsoft AntiVirus. | Obsolete | MS-DOS |
msbackup | Create or restore backups in MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
mscdex | CD-ROM access in MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
msd | Start Microsoft Diagnostics. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
nlsfunc | Load country-specific information for the MS-DOS program. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
ntbackup | Back up and restore files. | Deprecated and replaced by Windows Backup and Restore. | Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows XP |
ntsd | Start the NT Symbolic Debugger. | Obsolete | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 |
pentnt | Detect floating-point division errors in Intel Pentium chips. | Obsolete | Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT |
power | Turn power management on or off in MS-DOS. | Obsolete and replaced by the powercfg command on modern systems. | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
qbasic | Start the QBasic programming environment. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
rcp | Copy files to and from devices using the rshd daemon. | Obsolete and deprecated as it does not encrypt connections. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8 |
recimg | Create a custom recovery image for Windows. | Deprecated | Windows 8 |
restore | Restore files backed up with the backup command. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
rexec | Execute commands on remote computers using the Rexec service. | Obsolete due to security concerns. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8 |
rsh | Run commands on remote computers running the RSH (Remote Shell) service. | Obsolete due to security concerns. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8 |
rsm | Manage removable storage media from the command line. | Deprecated | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 |
scandisk | Check and repair file system errors on a disk. | Deprecated and replaced with the chkdsk command. | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
scanreg | Scan and back up the Windows Registry. | Obsolete | Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows Me |
setever | Set the version number that MS-DOS reports to a program. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
share | Install file-sharing and locking capabilities in MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
smartdrv | Enable disk caching to improve performance in MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
sys | Copy system files to a disk and make it bootable. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
tftp | Transfer files to and from a remote computer using TFTP. | Deprecated due to security concerns. | Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 |
tlntadmn | Manage a Telnet server. | Deprecated | Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 |
tsshutdn | Restart or shut down a Terminal Services server. | Depreacted | Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003 |
undelete | Recover deleted files in MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
unformat | Recover a disk that was accidentally formatted. | Obsolete | MS-DOS, Windows 95 |
unlock | Unlock a drive to allow direct disk access. | Deprecated | MS-DOS, Windows 95, Windows 98 |
vsafe | Enable antivirus protection in MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS |
winstat | Display system statistics in MS-DOS. | Obsolete | MS-DOS |
Conclusion
After reading this comprehensive guide, you have a solid overview of nearly 300 Windows CMD commands and can perform a wide range of system tasks.
You can use CMD commands to set up cron jobs in Windows and automate repetitive everyday tasks.


