The chkdsk command (short for Check Disk) is a Windows utility that scans disks and reports on the state of the partitions and the stored data. Use chkdsk to repair drives and recover data from the damaged drive sectors.
This tutorial shows you how to use chkdsk to detect and repair errors on your Windows drives.

Prerequisites
- Windows machine.
- User account with admin privileges.
- Access to Command Prompt or PowerShell.
Note: For the command that performs a similar function in Linux, refer to How to Use fsck Command.
chkdsk Syntax
The chkdsk command takes one or more arguments. The basic chkdsk command syntax is:
chkdsk [volume] [switches]Volumes and switches are optional. Enter the base command to start the scan:
chkdsk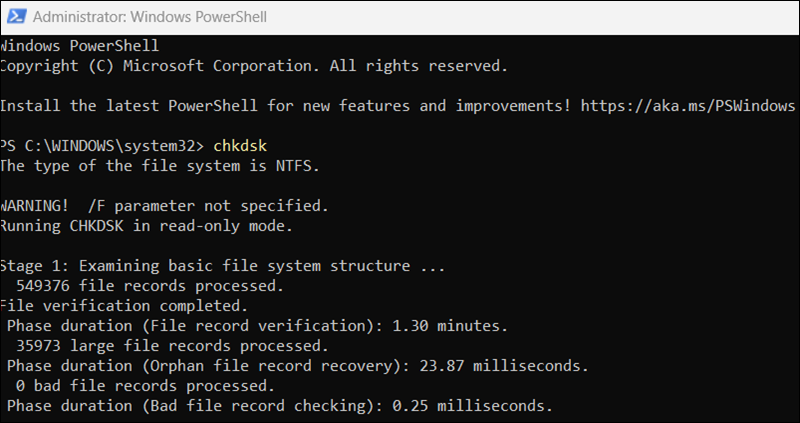
When you run chkdsk on its own, it scans the drives in read-only mode.
However, running chkdsk without the /F parameter on an active partition sometimes produces false positives, so this method of partition scanning is not recommended.
chkdsk Options
Expand and customize the chkdsk functionality by providing additional command-line arguments. The table below lists the available options.
Note: The table mentions online and offline scanning. In the chkdsk context, an online scan is performed while the volume is still mounted. An offline scan dismounts the volume to fix errors.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
[volume] | Specify a volume for chkdsk to scan. Follow the volume letter with the : symbol (e.g., C:). |
/B | Clear the list of bad clusters, rescan the drive for errors, and recover readable information. Use this switch only with NTFS partitions. |
/C | Speed up the scanning process by skipping over folder structure cycles. Use the switch only with NTFS partitions. |
/F | Fix errors on the disk. |
/forceofflinefix | Skip routine indexing checks and perform a fast drive scan. Use this switch only with NTFS partitions. |
/I | Skip routine indexing checks and perform a fast drive scan. Use the switch only with NTFS partitions. |
/L:[size] | Change the log file size. If you do not state the size, /L prints the current file size. Use the switch only with an NTFS partition. |
/offlinescanandfix | Scans and fixes the volume offline. |
/perf | Speed up the scan by using more system resources. Use the switch only with NTFS partitions alongside the /scan option. |
/R | Scan for bad sectors and recover non-corrupted information. If the /scan option is not included, chkdsk also attempts to fix the disk errors. |
/scan | Run an online scan. Use this switch only with NTFS partitions. |
/spotfix | Show the paths of all the files on the disk on FAT and FAT32 partitions. Show cleanup messages on NTFS partitions. |
/V | Show the paths of all the files on the disk on FAT and FAT32 partitions. Show cleanup messages on NTFS partitions. |
/X | Force-dismount the drive and fix any errors on the disk. |
/? | Show chkdsk help. |
How to Run chkdsk
chkdsk is a command-line interface (CLI) tool available in Windows Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell. The following steps show how to access PowerShell with administrative privileges to run the command:
1. Type PowerShell in the bottom search bar. The Windows PowerShell item appears in the list of programs.
Note: To use chkdsk in the Command Prompt, search for Command Prompt instead of PowerShell.
2. Select Run as Administrator in the pane on the right side.
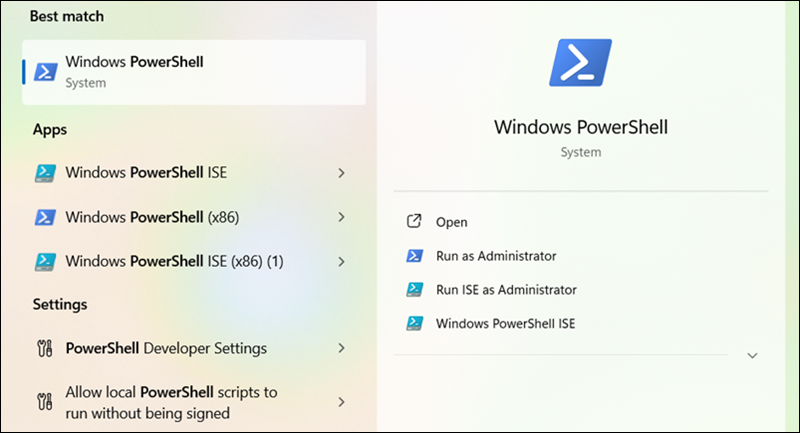
The PowerShell window opens.
chkdsk Examples
Combining the available switches with the chkdsk command helps narrow the scan target and perform custom scans. The following are examples of using the chkdsk command.
Check Disk without Fixing Errors
If you want to scan the drive without making any fixes, use:
chkdsk C: /scan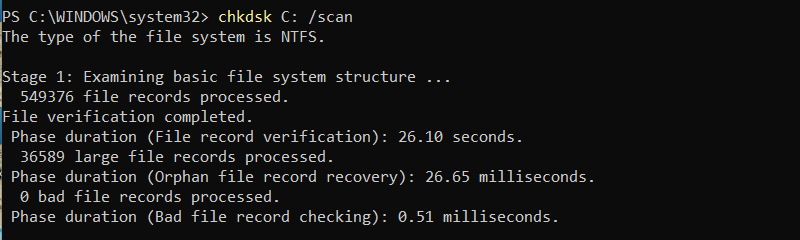
This command scans for errors but does not attempt to fix them. It's useful for diagnostics without making changes.
Scan for Bad Sectors
Scan the C: drive for bad sectors and recover the readable information. Run the following:
chkdsk C: /RIf chkdsk cannot lock the drive, it displays the following message.
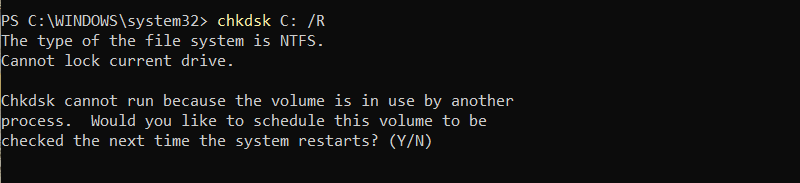
Type Y and press Enter. Then, restart the computer to complete the scan.
Check Disk and Fix Errors
Check and fix file system errors on the C: drive with:
chkdsk C: /F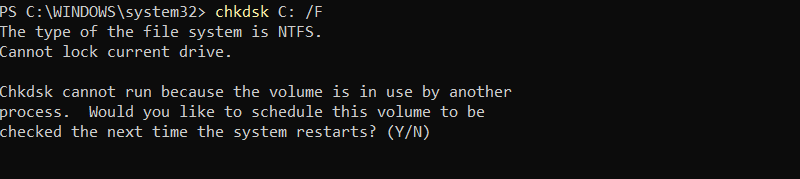
The command checks the file system for errors, such as issues with file or directory entries. If it finds any file system errors, it automatically fixes them.
The command cannot run on the C: drive while Windows is actively using it because the C: drive is the system drive used by the operating system.
Windows asks if you want to schedule the check to run during the next restart. Type Y and press Enter to schedule the check for the next reboot.
Force Offline Fixes for NTFS C Partition
Run an online scan of the NTFS-formatted C: partition but force chkdsk to perform all the fixes offline:
chkdsk C: /scan /forceofflinefix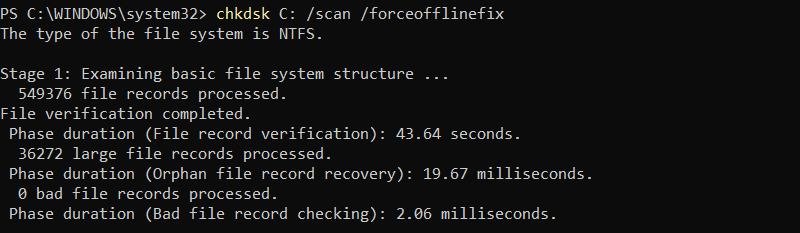
The output shows the scan stages.
If the scan finds any errors, they are repaired after the drive is dismounted. If there are no errors, chkdsk displays a report:
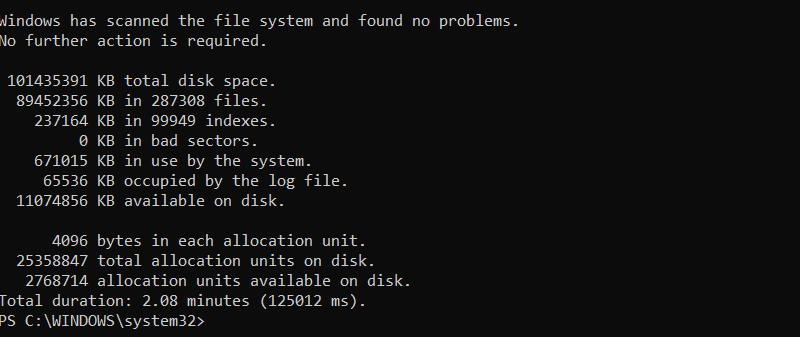
Scan and Fix Drive Using Maximum Resources
Scan and fix drive D: bad sectors online, using the maximum allowed amount of system resources. Run the following:
chkdsk D: /R /scan /perf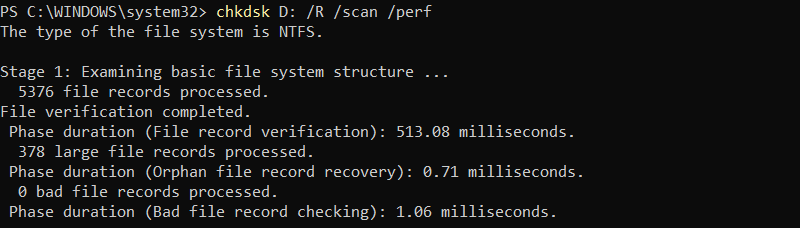
Scan Drive for Errors with Forced Dismount
Scan for disk errors on the drive D: and force the drive to dismount if necessary. Run the following:
chkdsk D: /X Note: If the D: drive is in use, forcing a dismount could cause loss of unsaved data or potential file corruption.
Scan Drive and Ignore Bad Sector Records
Perform an online scan of the C: drive to reevaluate previously marked bad clusters and update the error records without requiring a reboot:
chkdsk C: /B /scan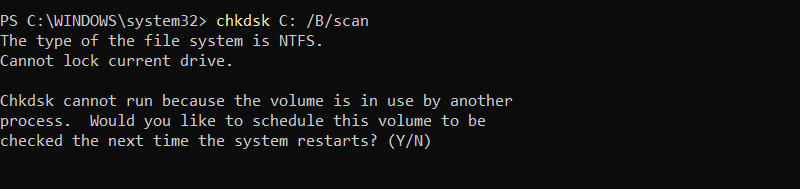
The command returns an error because the C: drive is the system drive and is currently in use by the operating system and running processes. chkdsk cannot obtain exclusive access, so it needs to scan and update certain parts of the file system.
The command can run during the next system restart when the operating system isn't loaded.
Conclusion
This tutorial presented the chkdsk command, a Windows CLI utility for scanning and repairing disks. It explained how to scan for and recover bad sectors, and to fix disk errors on your Windows system.
Next, learn more about data corruption and how to prevent it.