Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) runs a Linux environment on Windows without the virtual machine (VM) overhead.
With WSL 2, the Linux subsystem runs in a lightweight VM because it is enhanced with a Linux kernel, which improves performance and compatibility with development tools such as Docker.
This guide explains the key differences between WSL and WSL2, provides steps for upgrading to WSL2, and offers common troubleshooting tips.

Prerequisites
- Windows 10 (version 1903+) or Windows 11.
- Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) installed.
- Administrator access on Windows.
- Access to the command prompt (CMD) or PowerShell.
WSL vs. WSL2: Feature Comparison
WSL and WSL2 allow users to run a Linux distribution on Windows. Version 2 introduces significant changes in the virtualization architecture and performance.
The following table shows the key differences and improvements to WSL2 when compared to WSL:
| Feature | WSL | WSL2 |
|---|---|---|
| Kernel | Emulates the kernel, leading to compatibility limitations. | Uses a Linux kernel in a lightweight VM, enabling full compatibility with Linux tools. |
| File System Performance | Integration with the Windows file system is limited. Degrades for file-heavy operations and when accessing files on the Windows file system. | Utilizes the /mnt directory to improve file system performance, especially for I/O operations. Better suited for development and data-heavy tasks. |
| Memory Usage | Lower memory usage due to not operating on a VM. | Higher memory usage due to using a lightweight VM. |
| Networking | Uses Windows networking, which is restricting in some networking scenarios. Does not support IPv6 connections. | Creates a virtualized network interface. The interface has an IP address and improves network management. Supports IPv6 connections (Windows 11 or newer). |
| Compatibility | Compatible with specific Linux distributions without advanced features. Applications that rely on kernel functionalities are incompatible due to the emulation layer. | Compatible with various Linux distributions. Applications run without adjustments, including apps that depend on kernel-specific functions. |
| Docker Support | Limited. It requires additional configuration. | Native Docker support. Enables users to run Docker containers inside WSL2. |
| Installation | Installed through Windows Features and does not require additional setup. | Requires additional setup for the Linux kernel and VM features. |
How to Upgrade WSL to WSL2
To upgrade WSL to WSL2, follow these steps:
1. Access the PowerShell or Command Prompt as an administrator.
2. Check the current WSL version for the installed subsystems with:
wsl -l -v
The first column shows installed WSL instance names, while the second shows the WSL version for each instance.
3. To upgrade an existing instance to WSL 2, run:
wsl --set-version [wsl_instance_name] 2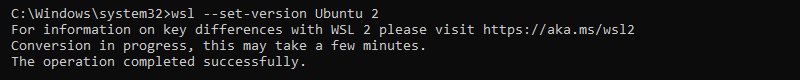
Replace [wsl_instance_name] with the installed WSL instance name.
Note: Run wsl --set-default-version 2 to use WSL2 by default. All future instances will use WSL2 automatically.
4. Confirm the change worked. Recheck the WSL version:
wsl -l -v
The WSL version changed for the stated instance to 2.
5. If the environment is running, restart the WSL environment:
wsl --shutdownShutting down the instance applies the changes. The command does not show any output.
6. Open the upgraded WSL distribution:
wsl -d [wsl_instance_name]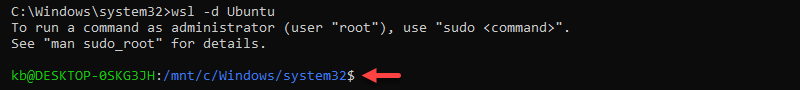
The prompt switches to the Linux terminal.
7. Test the upgrade with the uname command:
uname -r
The command shows the kernel version, confirming the upgrade was successful.
Upgrading WSL to WSL2: Common Errors & Troubleshooting
Several issues may happen when upgrading WSL to WSL2 due to incorrect setup or missing resources. Below are common errors and troubleshooting tips to resolve them.
1. "WSL 2 requires an update to its kernel component."
If the Linux kernel update for WSL2 is missing, the kernel update is missing. To resolve the error, download the latest WSL 2 kernel update from Microsoft's WSL 2 kernel update page, install it, and try upgrading again.
If the error persists, enable the Virtual Machine Platform feature. Run the following in the command prompt or PowerShell:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart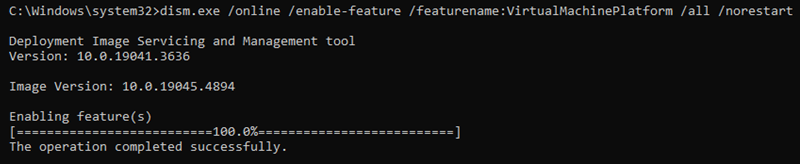
The feature is essential for WSL2 to function correctly.
2. "Invalid command line option: --set-version"
If the --set-version option shows as unavailable, the WSL program version is outdated. Update it with:
wsl --updateWait for the update to complete, and retry the command with the --set-version option.
3. "WSL 2 not supported on this device."
The minimum requirement for WSL2 is Windows 10 version 1903+ or Windows 11. To check the OS version, open the Start menu and type winver.
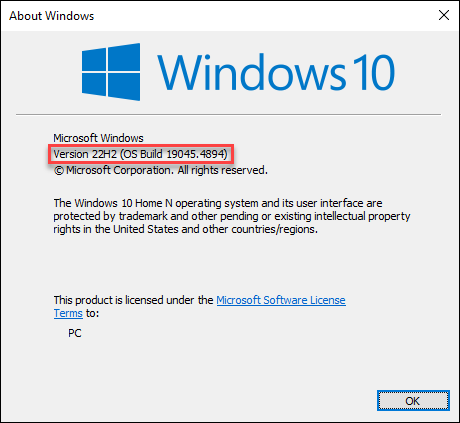
If using an unsupported version, upgrade to a newer version that supports WSL2.
4. "Virtualization is not enabled."
WSL2 requires virtualization to be enabled in the BIOS.
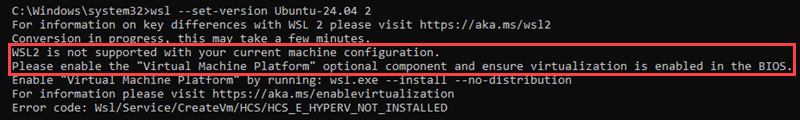
Enter the BIOS during system startup (usually by pressing F2, F12, Del, or Esc). Locate the virtualization option and enable it.
Save the changes, reboot the system, and reattempt the upgrade.
5. "Cannot Connect to the Internet in WSL2"
Networking issues may happen since WSL2 uses a virtualized network interface. Try restarting the WSL environment:
wsl --shutdownAlternatively, disable and re-enable the Virtual Machine Platform:
dism.exe /online /disable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatformdism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatformThe commands reset the WSL environment and the virtualized network interface.
6. Slow Performance or High Disk Usage
WSL 2 runs inside a lightweight VM. I/O intensive operations can slow down performance significantly. Consider adjusting the memory and CPU limits in the WSL config file (.wslconfig). For example:
[wsl2]
memory=8GB
processors=2The file is in the user's home directory (i.e., C:\Users\[username]\.wslconfig). If the file does not exist, create a new one and add the configuration. For the changes to take effect, run:
wsl --shutdownThe restart automatically applies the configuration from the config file.
Conclusion
This guide showed how to upgrade WSL to WSL2. It also provided the differences and troubleshooting steps.
Next, see how to upgrade Ubuntu on WSL.