The cURL CLI tool allows sending HTTP POST requests from the terminal to a web or application server. The command is flexible and offers several options to send additional data with the request, encode the data, or send authentication credentials.
This guide will show you how to use cURL to make POST requests through practical examples.

Prerequisites
- Access to the command line/terminal.
- cURL installed.
- An application/web server to send requests.
Basic Syntax for Sending POST Requests Using cURL
To send an HTTP POST request with the curl command, use the following format:
curl -X POST -d '[data]' [URL]The command has:
-X POST. Specifies the HTTP method explicitly.-d '[data]'. Sends data along with the request.[URL]. The destination URL.
For additional options, see the following section.
Common cURL POST Request Options
Frequently used options when sending a POST request with cURL are in the table below:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-X POST--request POST | Specifies the request type as POST (optional if -d is used). |
-d '[data]'--data '[data]' | Sends the provided data in the request body of a POST request. |
--data-binary | Sends data as-is without additional processing. |
--data-urlencode '[data]' | Encodes data into the URL before sending the request. |
-H '[header]'--header '[header]' | Adds headers to the HTTP request. |
-F '[name]=[value]'--form '[name]=[value]' | Sends form data as multipart/form-data. |
-u '[user]:[password]'--user '[user]:[password]' | Includes basic authentication credentials. |
cURL POST Examples
Below are some common examples of sending POST requests using cURL for different use cases. All the requests are sent to a free public endpoint that echoes the request back for demonstration purposes.
Send Form Data
To send form data, use the -d flag and provide the data as a request body. For example:
curl -X POST -d "name=alice&[email protected]" https://httpbin.org/post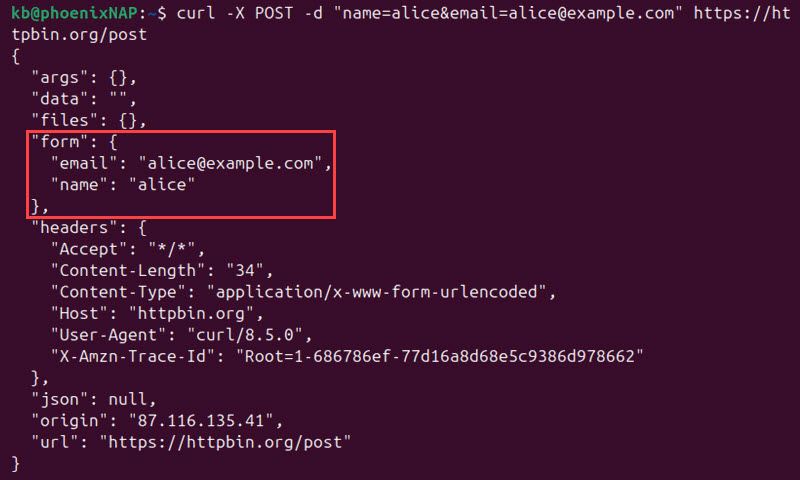
The output shows the provided data added in the form field.
Note: The request also works when omitting -X POST in this case.
Send JSON Data
The data can also be in JSON format, which is more common for HTTP requests. It requires adding a header to specify the content type along with the data:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"name": "Alice", "email": "[email protected]"}' https://httpbin.org/post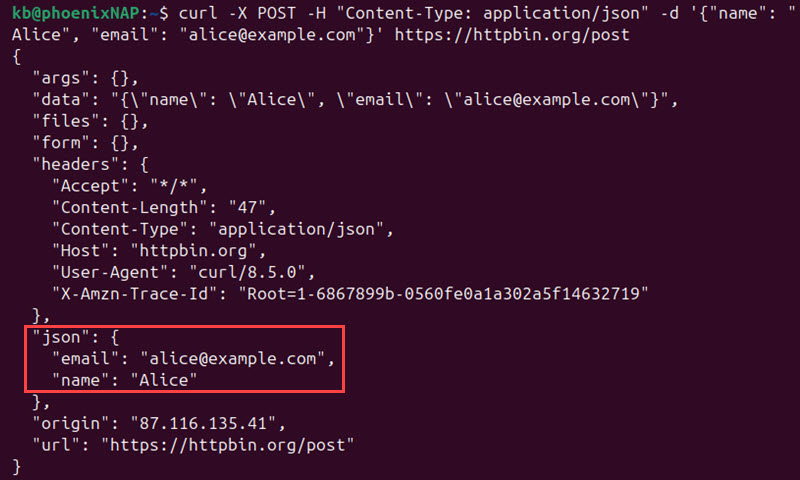
The response shows the payload in the json field.
Send Data From File
To send data from a file using cURL, create a file and add some values:
echo '{"name":"Alice"}' > data.jsonThen send a POST request and add @ before the file name:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" --data-binary @data.json https://httpbin.org/post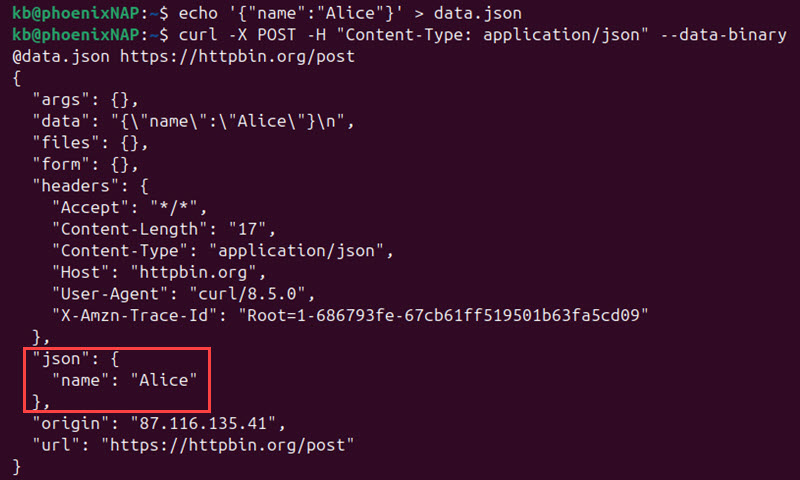
Use this format when posting a file, JSON payload, or any other content where the data should not be modified.
Using Custom Headers
Send a POST request with authorization headers and provide a custom value, such as a token. For example:
curl -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer example_token" -d "name=Alice" https://httpbin.org/post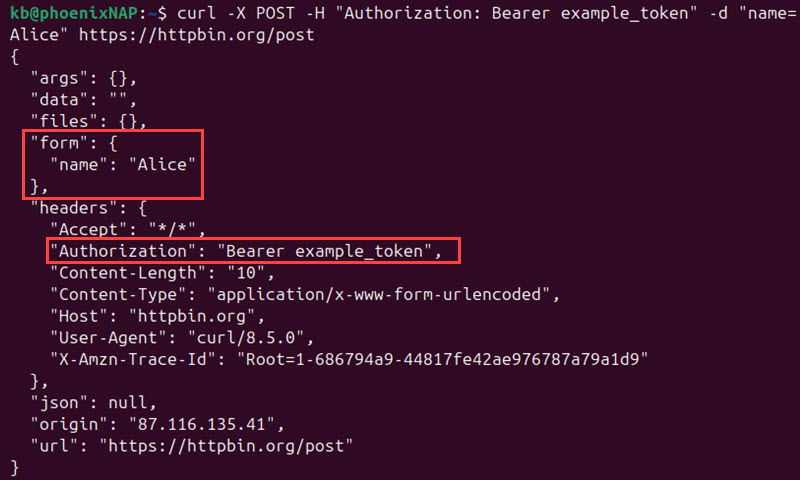
The header section shows the example token, while the form section contains the passed data.
Using Basic Authentication
To use basic authorization through a curl POST request, provide the username and password with the -u option:
curl -u alice:secret -X POST -d "name=Alice" https://httpbin.org/post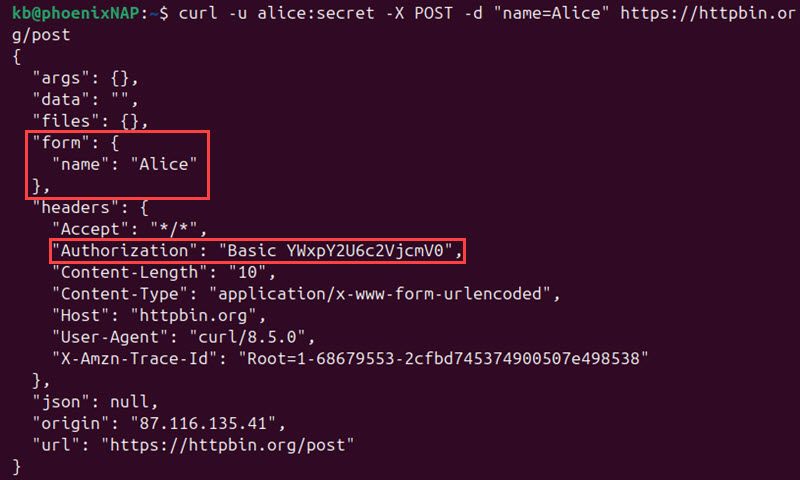
The user data in the authorization section is shown as basic encrypted authentication.
Conclusion
This guide explained how to send a cURL POST HTTP request. We also showed how different options work to send different data formats, headers, and authorization information.
Next, see how to send a cURL DELETE request, or learn how to show and send HTTP headers with cURL.