Git is the world's most popular version control system (VCS), and knowledge of Git has become a mandatory skill in the world of coding. Git tracks file changes and coordinates work among developers, allowing teams to collaborate on projects through centralized code management, which ensures consistency and prevents conflicts.
In this step-by-step beginner's guide, you will learn how to start using Git effectively.

What Is Git Used For?
Git is most commonly used to maintain a history of changes in a repository. It helps developers review, revert, or compare earlier versions of a project.
Git supports branching, which allows developers to work on different features or fixes in isolated environments. Teams can merge changes into the main project seamlessly, even when multiple contributors work simultaneously. Its distributed nature ensures every user has a full copy of the repository to enable offline access and reduce dependency on a central server.
In addition to code management, Git facilitates automated workflows through integration with tools like CI/CD pipelines. This streamlines processes such as testing and deployment, helping teams deliver high-quality software efficiently.
Note: Read about Git in more detail in our article on what is Git. And to learn more about git workflows, read our article on how git works.
Git Tutorial for Beginners
The steps below outline the basic things you need to know to get started using Git efficiently.
Step 1: Install Git and Create a GitHub Account
The first thing you need to do is to install Git and create a GitHub account. Follow the instructions below to install Git on your system:
- Install Git on Windows
- Install Git on Mac
- Install Git on Ubuntu
- Install Git on CentOS and Rocky
- Install Git on FreeBSD
Note: If you already have Git installed on your machine, it's best to update to the latest version available. Follow the instructions in our article on how to update Git on Windows, macOS, or Linux.
After installing Git on your machine, the next step is to create a free GitHub account. GitHub is a web-based platform for version control. Alternatives include GitLab, Bitbucket, and SourceForge.
Follow these steps:
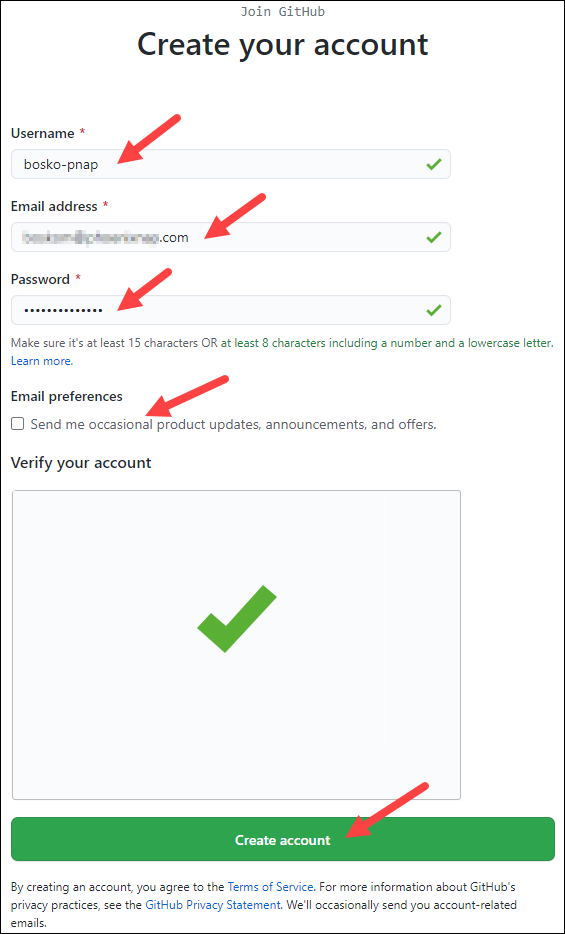
1. Visit the official account creation page: Join GitHub
2. Pick a username, enter your email address, and choose a password.
3. Opt for or opt out of receiving updates and announcements by checking/unchecking the Email preferences checkbox.
4. Verify you're not a robot by solving the Captcha puzzle.
5. Click Create account.
6. GitHub sends a launch code to the specified email address. Copy and paste the code in the designated field.
7. Optionally, enter account personalization details when asked, or Skip and click Continue.
You have now successfully created a GitHub account.
Step 2: Create a Local Git Repository
After the installation, the next step is to create a local Git repository. To create a Git repository, follow the steps below:
1. Open a Git Bash terminal and move to the directory where you want to keep the project on your local machine. For example:
cd ~/Desktop
mkdir myproject
cd myproject/In this example, we changed the directory to Desktop and created a subdirectory called myproject.
2. Create a Git repository in the selected folder by running the git init command. The syntax is:
git init [repository-name]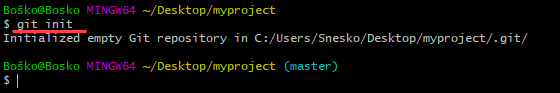
Now, you have successfully created a local Git repository.
Step 3: Create a New Repository on GitHub
GitHub allows you to keep track of your code when you are working with a team and need to modify the project's code collaboratively.
Follow these steps to create a new repository on GitHub:
1. Log in and browse to the GitHub home page.
2. Find and click the New repository option under the + sign next to your profile picture in the top right corner.
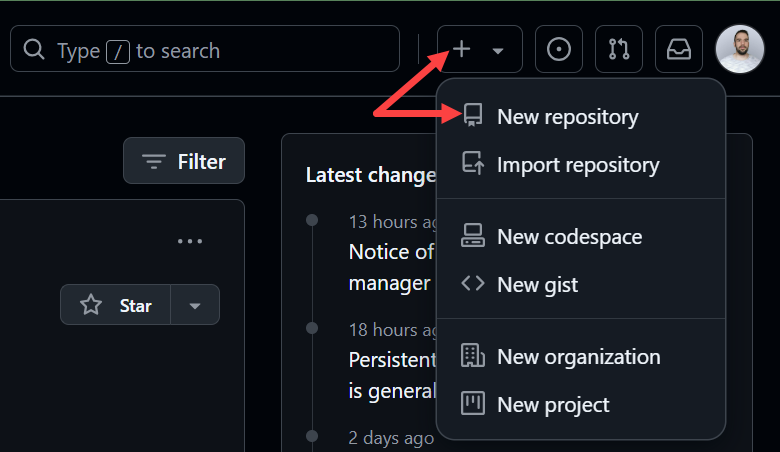
3. Enter a name for your repository, provide a brief description, and choose a privacy setting.
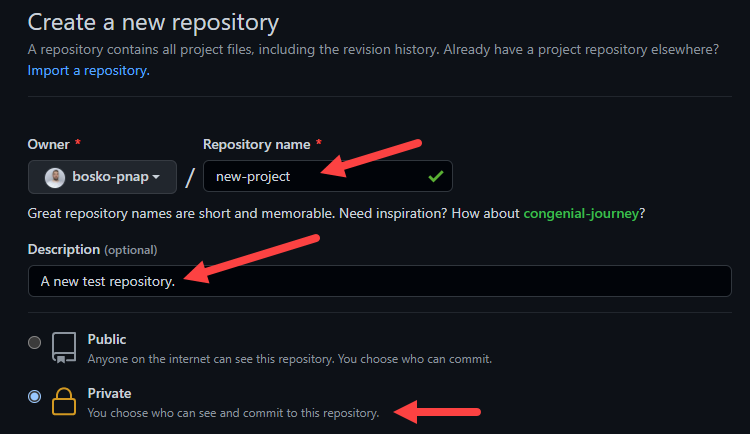
4. Click the Create repository button.
GitHub allows you to add an existing repo you have created locally. To push a local repository from your machine to GitHub, use the following syntax:
git remote add origin https://github.com/[your-username]/[repository-name.git]
git push -u origin masterFor example:
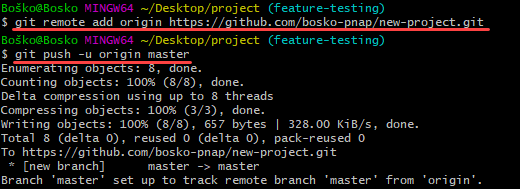
Note: For more info, read our guide on how to push Git tags to a remote repository.
Step 4: Check Repository Status
Git notifies you when you add or modify files in the directory that contains the Git repository. However, it does not track the file unless instructed. Git saves the changes only for the files it tracks, so you need to let Git know you want to track changes for a specific file.
You can check for untracked files with:
git status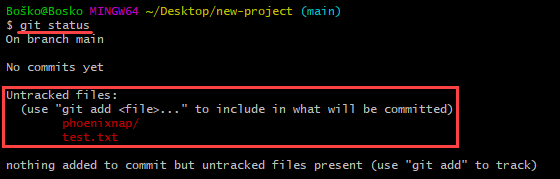
Git informs you if you have any untracked files. Refer to the section below to see how to track files.
Step 5: Add a File to Staging Environment
Add a file to the staging environment in Git to mark it for inclusion in the next commit. The staging area acts as an intermediate space where Git tracks changes you want to commit and allows you to prepare and review updates before finalizing them.
This process gives you control over which modifications become part of the project history, even if the working directory contains other untracked or unrelated changes.
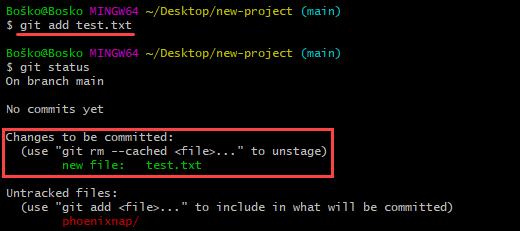
The syntax to add a file to the staging environment is:
git add [filename]Replace [filename] with the name of the file(s) that you want to add to the staging environment. For example:
To add more files, separate the file names with a space. For example:
git add file1.txt file2.txt file3.txtTo stage all files in the current directory, use the command below:
git add .Note: If you have unnecessary files in your repository, you can remove untracked files in Git to improve efficiency and organization.
Step 6: Unstage Files on Git
Working with Git usually involves adding all the files to your index to prepare them for a commit. If you want to remove some files from the index before committing, you have to unstage the files in Git.
One way to unstage files on Git is to run the git reset command. The syntax is:
git reset [commit] -- [file_path][commit]refers to the target commit. If omitted, it defaults toHEAD(the current commit).- Replace
[file_path]with the path to the file you want to unstage.
For example:

Note: You can also use the rm command to unstage files on Git.
The syntax is:
git rm --cached [file-name]Step 7: Create a Commit
After adding the specified files to the staging environment, instruct Git to package the files into a commit using the git commit command. Git then stores that file version. You can review the stored version at any given time.
The syntax to create a commit is:
git commit -m "Notes about the commit"Use the -m flag to add a message at the end of the commit to state whether it's a new feature, a bug fix, or anything else. Commits remain in the repository, which are rarely deleted, so an explanation of what you changed helps you and other developers working on the project keep track of all the changes.
For example:
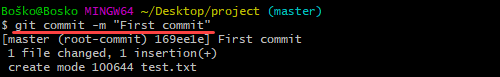
Step 8: Undo Last Commit
Important: Git allows users to revert the last commit. However, other developers could have already retrieved the updated project, and deleting updates from one system could cause conflicts for other team members.
Use the revert and reset commands to undo changes and revert to a previous commit.
To undo a published commit, use the following syntax:
git revert [hash]A hash is a code that identifies each commit. Obtain a commit hash by running:
git logFor example:
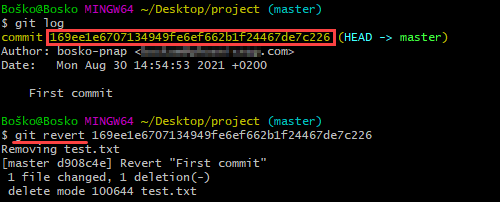
In this example, we first ran the git log command to obtain the commit hash, and then we reverted the last commit by running git revert with the commit hash we obtained.
Note: If you wish to undo a commit to update the commit message, there is a better way to do it. Learn all the ways you can change a Git commit message.
Another useful thing to know is how to restore a Git repository if you accidentally deleted it or forcefully pushed a new commit before fetching the latest version.
Step 9: Create a New Branch
The first branch in a Git repository is called master or main, and it is the primary branch in a project.
To create a new Git branch means to create a copy of the project from a specific point in time. Branches in Git allow users to make new features without applying the changes to the main branch while the feature is in development.
The common method for creating a new branch is to use the syntax below:
git branch [new_branch_name]For example:

In this example, we create a new branch named new-feature.
Note: Learn about different Git branching strategies.
Step 10: Switch Branches
Having several branches of a Git project provides a test environment for developers to track progress without affecting the production version of an application. Git allows you to switch between branches with the checkout command. The syntax is:
git checkout [branch_name]Replace [branch_name] with the branch name you want to access.
For example:
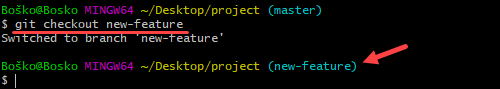
Step 11: Rename a Local or Remote Git Branch
In Git, you can rename a local or remote Git branch.
The syntax for changing a local Git branch name is:
git branch -m new-nameFor example:
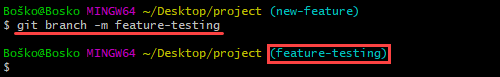
In this example, we changed the local branch name from new-feature to feature-testing.
Since there is no direct way to rename a remote Git branch, you must first delete the old branch name and then push the new branch name to the remote repository. The syntax is:
git push origin --delete [old_branch_name]After you delete the old branch, push the branch with the new name to the remote repository:
git push origin -u [new_branch_name]Note: Make sure to read our tutorial if you want to find out more on how to push a branch to a remote repository.
Step 12: Delete a Local or Remote Git Branch
You may decide to delete a local or remote Git branch after you merge the changes with the master branch or if the branches become corrupted.
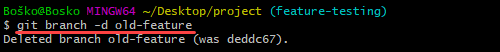
Deleting a local branch doesn't affect a remote branch. To delete a local Git branch, run:
git branch -d [branch_name]Use the following syntax to delete a remote Git branch:
git push [remote_repository] --delete [branch_name]Replace [remote_repository] with the name of your remote repository - usually origin.
In this example, we deleted a local Git branch:
Step 13: Set Upstream Branch
Sending something upstream in Git means that you are sending it back to the repository owner.
Use the git set upstream command to choose the flow direction of your current local branch. The command also allows you to change the default remote branch.
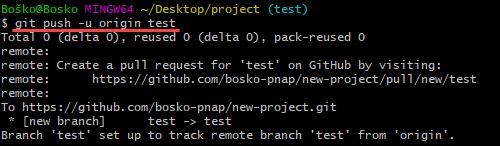
Our tutorial on Git upstream and setting an upstream branch deals with the different methods for setting an upstream branch and gives a detailed explanation.
Step 14: Remove a Git Remote
A Git remote is a connection to a repository hosted on a remote server – GitHub, BitBucket, GitLab, or any other remote location. Over time, the remote repository may move to another host, or a team member may stop working on the project. The remote in question is then no longer needed.
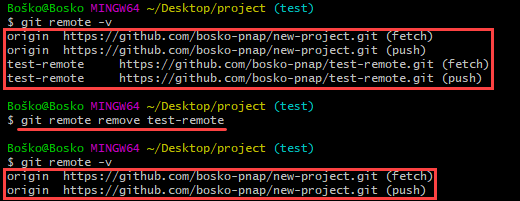
There are several ways to remove a Git remote. One of the ways is to use the syntax below:
git remote remove [remote name]In the following example, running git remote -v shows the available remote repositories, origin and test-remote. After removing test-remote and rerunning git remote -v to list available remotes, we see that the only available remote is origin.
Step 15: Git Merge
Git merge unifies multiple commit sequences into a single commit. It can combine two branches and integrate the independent development lines into a single branch.
After merging two branches, Git updates the current branch to reflect the merge, but the target branch is not affected. That means you have to use the git branch -d command to delete the obsolete target branch.
For example, you may want to merge a new feature branch into the master (main) branch. Follow the steps below:
1. Run the git status command to ensure that HEAD is pointing to the correct merge-receiving (master) branch. If it is not, run git checkout master to switch to the master branch.
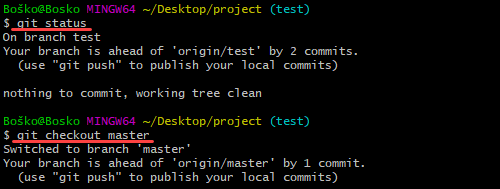
2. Run git fetch to pull the latest remote commits and git pull to ensure the main branch has the latest updates.
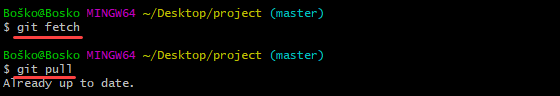
3. Merge the branches with the syntax below:
git merge [target_branch]Replace [target_branch] with the name of the branch you want to merge into the receiving branch. For example:
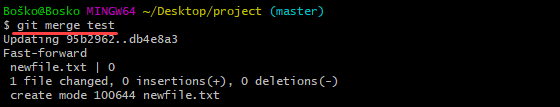
Step 16: Resolve Merge Conflicts
Merge conflicts usually occur when multiple developers work on the same code of a project or when they work with several development branches. Git merge warns the user about these conflicts.
Although most merge conflicts resolve automatically, there are cases when Git merge cannot resolve an issue.
Our detailed guide on resolving merge conflicts in Git offers tips for preventing merge conflicts, as well as ways to resolve existing merge conflicts.
Step 17: Create a Pull Request
Create a pull request (PR) to inform a repository owner that they should review the changes you have made to their code. Then, the owner can approve the pull request and merge the changes into the main repository.
If you are the co-owner or owner of a repository, you don't have to create pull requests to merge your changes. However, you can still do it to keep track of your feature updates and history.
For this guide, we will create a readme file for our repository locally and make a pull request on GitHub to illustrate the process.
Follow the steps below:
1. In Git Bash, create an empty readme file:
touch readme.md2. Create and switch to a new branch on which to modify the file:
git checkout -b create-readme-file3. Open the readme file in a text editor and add the text you want it to contain. In this example, we will use the Nano text editor to modify the file within the command line window:
nano readme.md
Note: Check out our list of best Linux text editors.
4. Save the file and start tracking it with:
git add readme.md5. Create a new commit:
git commit -m "Added a readme file"6. Push the changes to GitHub:
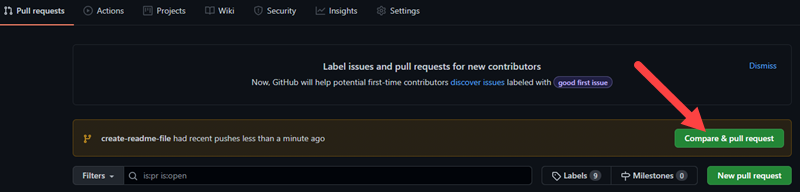
git push origin create-readme-file7. Log in to your GitHub page. There is now a Create pull request option in your repository with the branch name we created in the command line. Click the Compare & pull request button.
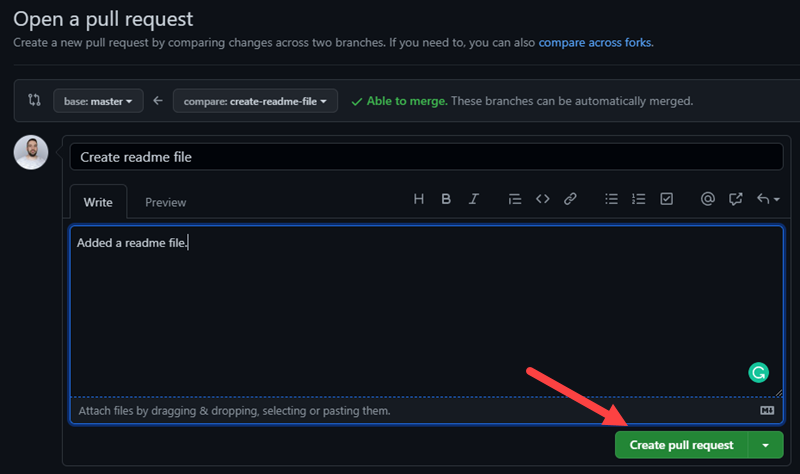
8. GitHub states if you can merge the branches and apply the changes. Optionally, add a comment about your pull request and click Create pull request.
Now, the repository owner can review the changes and accept or reject them.
You can accept the changes in the Pull requests tab on GitHub. When you merge the branches, delete the obsolete branch with the Delete branch button to keep the repository clean.
Note: Learn how to use git blame, a command that allows users to see who last modified each line of a file and when
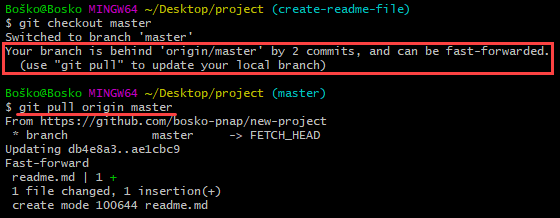
Step 18: Synchronize Changes on GitHub and Locally
When you merge changes on GitHub, they don't appear automatically in your local repository. You must pull the changes to your local repository to see the updates.
Synchronize your local repository with GitHub with:
git pull origin masterThe command updates your local repository to match the one on GitHub and states the changes.
In the following example, we first switch to our master branch and Git warns us that we should update our local repository:
Basic Git Commands You Should Be Using
This section is a summary of the key Git commands discussed in the article. The table below provides a quick reference to their purpose and syntax, which you can use as a handy cheat sheet while working on your projects:
| Command | Purpose | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
git init | Initializes a new Git repository in the current directory. | git init [repository-name] |
git status | Displays the working directory and staging area status. | git status |
git add | Stages files to include in the next commit. | git add [filename] or git add . |
git reset | Unstages files and moves them from the staging area back to the working directory. | git reset [commit] -- [file_path] |
git commit | Saves changes to the repository with a descriptive message. | git commit -m "Commit message" |
git branch | Creates, lists, or deletes branches. | git branch [branch_name] |
git checkout | Switches between branches or restores files. | git checkout [branch_name] |
git merge | Combines changes from different branches into one. | git merge [branch_name] |
git remote | Manages connections to remote repositories. | git remote add [remote_name] [URL] |
git push | Uploads local repository content to a remote repository. | git push [remote_name] [branch_name] |
git pull | Fetches and integrates changes from a remote repository. | git pull [remote_name] [branch_name] |
git log | Shows the commit history of the repository. | git log |
git revert | Reverts a specific commit by creating a new commit. | git revert [commit_hash] |
git rm --cached | Removes files from the staging area but keeps them in the working directory. | git rm --cached [file-name] |
git push --delete | Deletes a branch on a remote repository. | git push [remote_name] --delete [branch_name] |
git branch -m | Renames a local branch. | git branch -m [new_branch_name] |
git set-upstream | Sets a default remote branch for push/pull operations. | git branch --set-upstream-to=[remote_name]/[branch_name] |
Conclusion
You now know the basic and some more advanced Git functions. Feel free to test them out to make sure you understand how they work.
Next, download our Git commands cheat sheet to have all Git commands in one place for future use and learn how to use GitHub.