Apache Hive is an enterprise data warehouse system for querying, managing, and analyzing data in the Hadoop Distributed File System.
The Hive Query Language (HiveQL) runs queries in a Hive CLI shell, while Beeline is a JDBC client that enables connecting to Hive from any environment. Hadoop can use HiveQL as a bridge to communicate with relational database management systems and execute SQL-like commands.
This guide shows how to install Apache Hive on Ubuntu 24.04.

Prerequisites
- Java installed with the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable set. - A working Hadoop installation with environment variables set.
Install Apache Hive on Ubuntu
To install Apache Hive, download the tarball and customize the configuration files and settings. Follow the steps below to install and set up Hive on Ubuntu.
Step 1: Download and Untar Hive
Begin by downloading and extracting the Hive installer:
1. Visit the Apache Hive official download page and determine which Hive version is compatible with the local Hadoop installation. To check the Hadoop version, run the following in the terminal:
hadoop version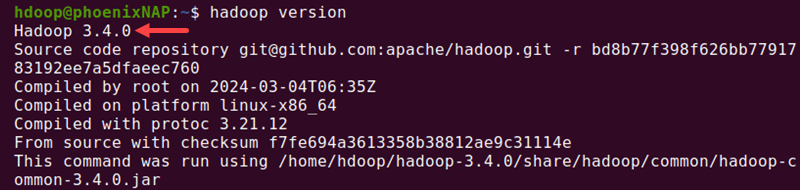
We will use Hive 4.0.0 in this guide, but the process is similar for all versions.
2. Click the Download a release now! link to access the mirrors page.
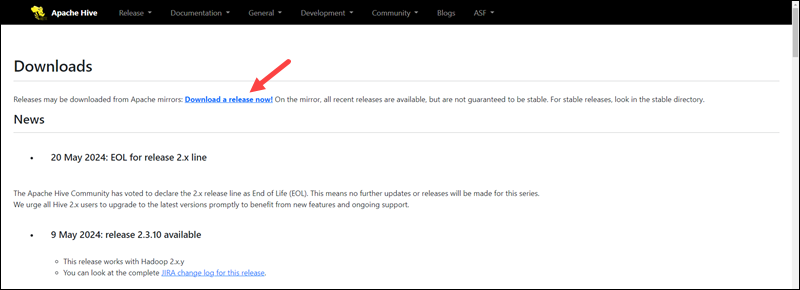
3. Choose the default mirror link.
The link leads to a downloads listing page.
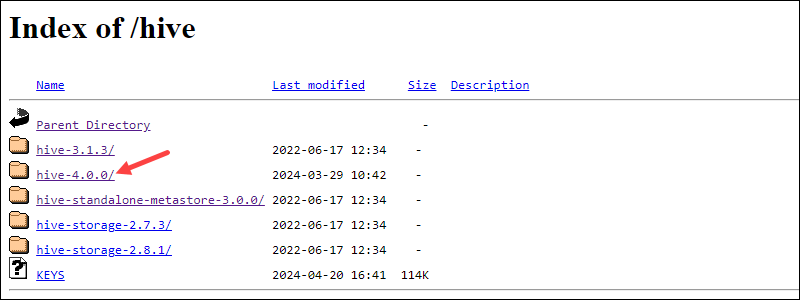
4. Open the directory for the desired Hive version.
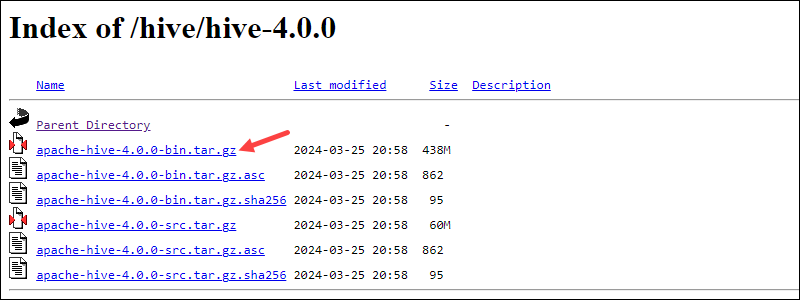
5. Select the bin.tar.gz file to begin the download.
Alternatively, copy the URL and use the wget command to download the file:
wget https://downloads.apache.org/hive/hive-4.0.0/apache-hive-4.0.0-bin.tar.gz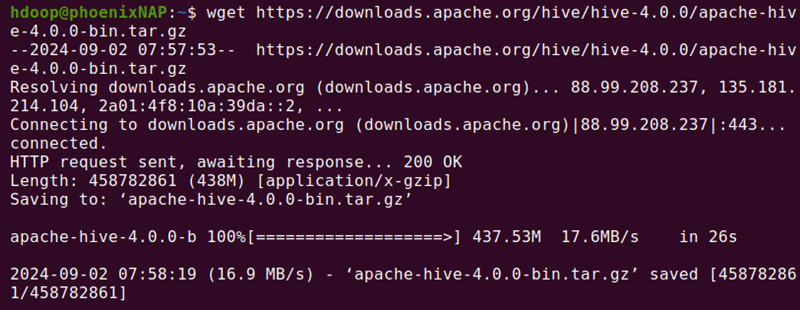
6. When the download completes, extract the tar.gz archive by providing the command with the exact file name:
tar xzf apache-hive-4.0.0-bin.tar.gz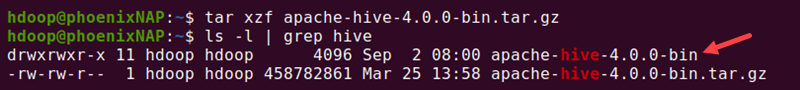
The Hive files are in the apache-hive-4.0.0-bin directory.
Step 2: Configure Hive Environment Variables (.bashrc)
Set the HIVE_HOME environment variable to direct the client shell to the apache-hive-4.0.0-bin directory, and add it to PATH:
1. Edit the .bashrc shell configuration file using a text editor (we will use nano):
nano .bashrc2. Append the following Hive environment variables to the .bashrc file and ensure you provide the correct Hive program version:
export HIVE_HOME="/home/hdoop/apache-hive-4.0.0-bin"
export PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin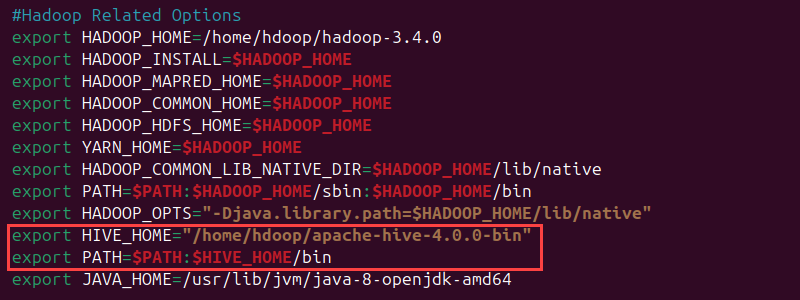
The Hadoop environment variables are in the same file.
3. Save and exit the .bashrc file.
4. Apply the changes to the current environment:
source ~/.bashrcThe variables are immediately available in the current shell session.
Step 3: Edit core-site.xml File
Adjust the settings in the core-site.xml file, which is part of the Hadoop configuration:
1. Open the core-site.xml file in a text editor:
nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/core-site.xmlChange the path if the file is in a different location or if the Hadoop version differs.
2. Paste the following lines in the file:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.db_user.groups</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.db_user.hosts</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.server.hosts</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.server.groups</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
</configuration>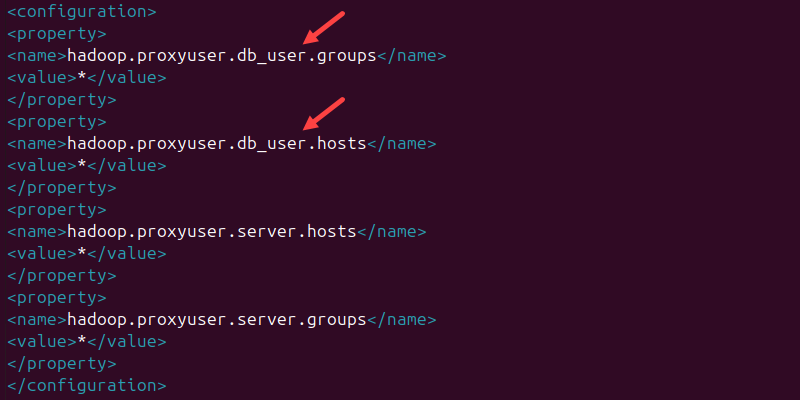
The db_user is the username used to connect to the database.
3. Save the file and close nano.
Step 4: Create Hive Directories in HDFS
Create two separate directories to store data in the HDFS layer:
- /tmp - Stores the intermediate results of Hive processes.
- /user/hive/warehouse - Stores the Hive tables.
Create /tmp Directory
The directory is within the HDFS storage layer. It will contain the intermediate data that Hive sends to HDFS. Follow the steps below:
1. Create a /tmp directory:
hadoop fs -mkdir /tmp2. Add write and execute permissions to group members with:
hadoop fs -chmod g+w /tmp3. Check the permissions with:
hadoop fs -ls /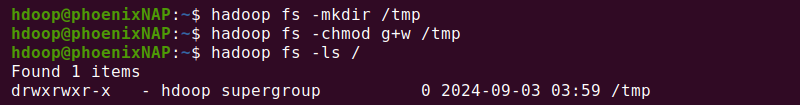
The output confirms that group users now have write permissions.
Create /user/hive/warehouse Directory
Create the warehouse subdirectory within the /user/hive/ parent directory:
1. Create the directories one by one. Start with the /user directory:
hadoop fs -mkdir /user2. Make the /user/hive directory:
hadoop fs -mkdir /user/hive3. Create the /user/hive/warehouse directory:
hadoop fs -mkdir /user/hive/warehouse4. Add write and execute permissions to group members:
hadoop fs -chmod g+w /user/hive/warehouse5. Check if the permissions applied correctly:
hadoop fs -ls /user/hive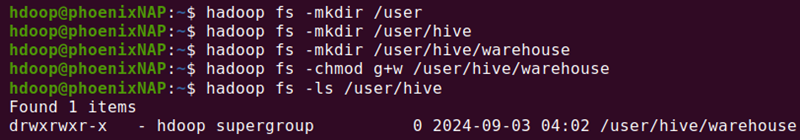
The output confirms that the group has write permissions.
Step 5: Configure hive-site.xml File (Optional)
Apache Hive distributions contain template configuration files by default. The template files are located within the Hive conf directory and outline default Hive settings:
1. Navigate to the /conf directory in the Hive installation:
cd $HIVE_HOME/conf2. List the files contained in the folder using the ls command:
ls -l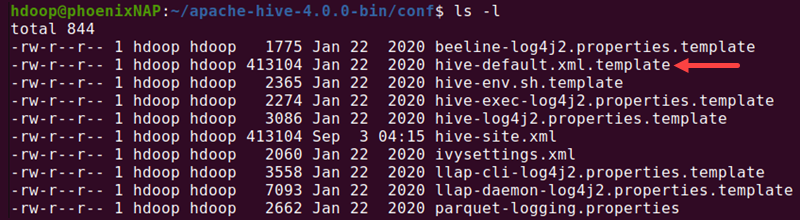
Locate the hive-default.xml.template file.
3. Create a copy of the file and change its extension using the cp command:
cp hive-default.xml.template hive-site.xml4. Open the hive-site.xml file using nano:
nano hive-site.xml5. Configure the system to use the local storage.
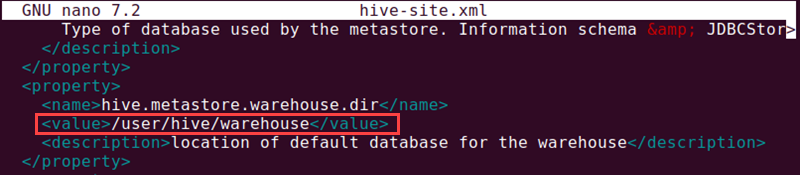
Set the hive.metastore.warehouse.dir parameter value to the Hive warehouse directory (/user/hive/warehouse).
6. Save the file and close nano.
Step 6: Initiate Derby Database
Apache Hive uses the Derby database to store metadata. Initiate the Derby database from the Hive bin directory:
1. Navigate to the Hive base directory:
cd $HIVE_HOME2. Use the schematool command from the /bin directory:
bin/schematool -dbType derby -initSchema
The process takes a few moments to complete.
Note: Derby is the default metadata store for Hive. In the hive-site.xml file, specify the database type in the hive.metastore.warehouse.db.type parameter to use a different database solution, such as Postgres or MySQL.
Launch Hive Client Shell on Ubuntu
Start HiveServer2 and connect to the Beeline CLI to interact with Hive:
1. Run the following command to launch HiveServer2:
bin/hiveserver2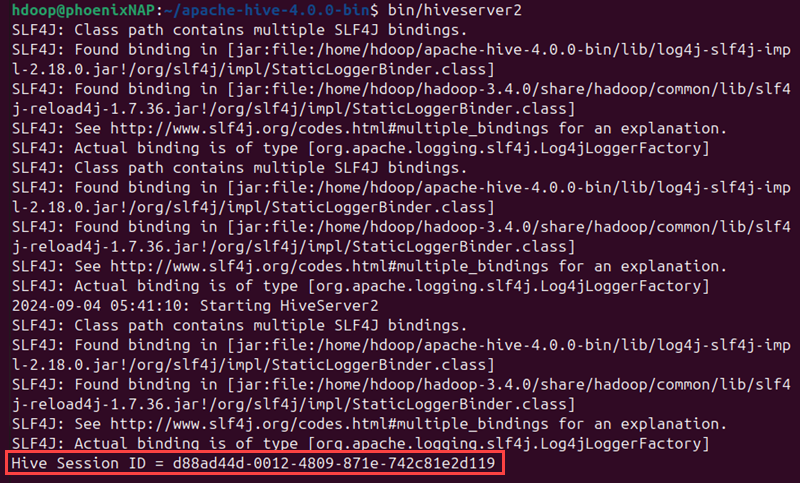
Wait for the server to start and show the Hive Session ID.
2. In another terminal tab, switch to the Hadoop user using the su command:
su - hdoopProvide the user's password when prompted.
3. Navigate to the Hive base directory:
cd $HIVE_HOME4. Connect to the Beeline client:
bin/beeline -n db_user -u jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000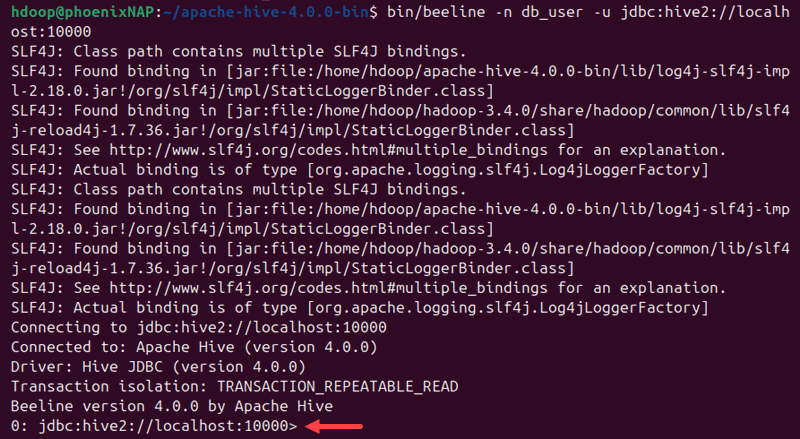
Replace the db_user with the one provided in the core-site.xml file in Step 4. The command connects to Hive via Beeline.
5. Test the connection with:
show databases;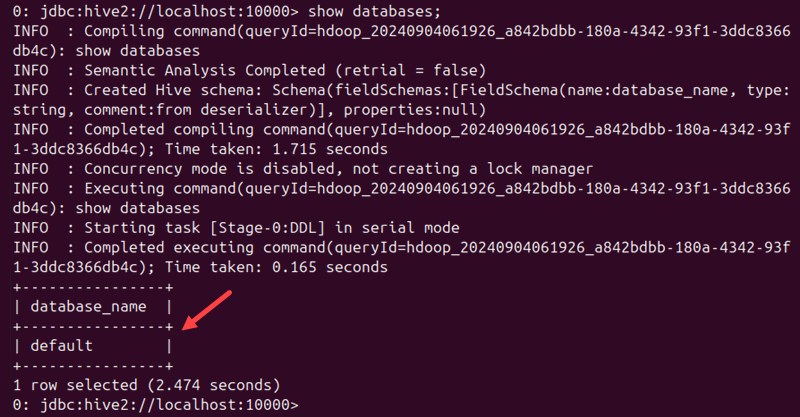
The command shows a table with the default database in the Hive warehouse, indicating the installation is successful.
Conclusion
You have successfully installed and configured Hive on Ubuntu 24.04. Use HiveQL to query and manage your Hadoop distributed storage and perform SQL-like tasks.
Next, see how to create an external table in Hive.