The Linux distribution ecosystem offers various options, ranging from beginner-friendly operating systems to complex, use-case-oriented designs. While all the distros share the standard Linux kernel, they differ in many other aspects, such as the choice of a package management system, software repositories, and desktop environment.
This article compares Kali Linux and Ubuntu, two popular distributions catering to different use cases.
What Is Ubuntu?
Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux operating system for desktops, servers, and cloud computing created and maintained by Canonical, Ltd. The desktop version comes in many official "flavors," separate editions with different desktop environments, settings, and defaults.
The main Ubuntu edition comes with a GNOME desktop environment:
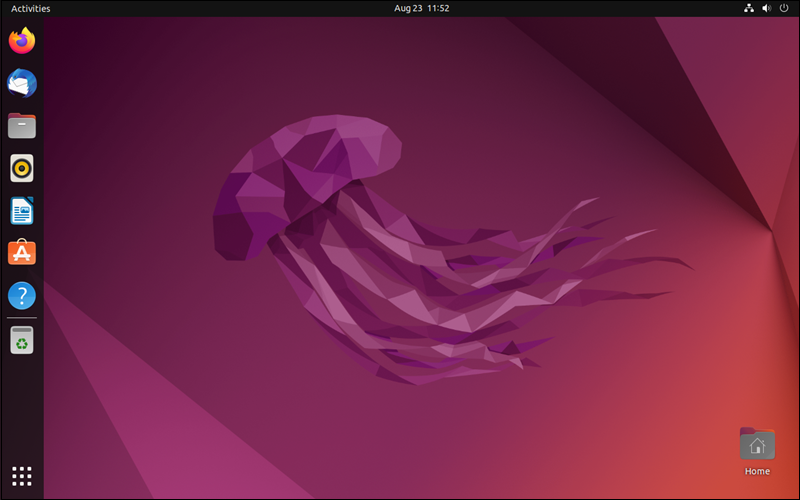
Ubuntu aims to provide a user-friendly, reliable, and accessible Linux environment for everyday use. The distribution has a large community of developers that contribute to its code base and provide support through documentation and online resources.
Ubuntu Features: Overview
As a distribution meant primarily for general consumption, Ubuntu Desktop focuses on features that make everyday tasks easier. Below is the list of the most essential characteristics of Ubuntu:
- User-friendly interface. Ubuntu GNOME desktop is customized to improve the user experience further and make navigation around the system more accessible for less tech-savvy people.
- Pre-installed applications. Ubuntu comes pre-loaded with many applications for everyday tasks, including Firefox internet browser, Thunderbird mail client, LibreOffice office suite, Rhythmbox audio player, Shotwell photo organizer, and more.
- Snap packages. Similar to other packaging solutions such as flatpaks and AppImages, snaps are self-contained software packages that bundle the application with all its dependencies for easier distribution and installation. Ubuntu offers an extensive collection of snaps through its Software Center but can also be installed using the terminal.
- Stability. While Ubuntu publishes a new release twice a year, those who need a stable and robust platform can opt for Long-Term Support (LTS) releases. LTS versions of Ubuntu come out once in two years, and Canonical supports them for ten years, twice as long as the regular releases.
- Hardware support. As a mature and widespread distribution, Ubuntu supports a wide range of computer components and peripherals.
Note: Learn how to install GNOME in Arch Linux.
What Is Kali Linux?
Kali Linux is a Debian-based distribution for penetration testing funded and maintained by Offensive Security. As a platform for cyber-security professionals, Kali Linux is in the same category with distributions such as Parrot OS, Wifislax, and BlackArch.
The OS features an XFCE desktop environment known for its stability and lightweight operation:

Kali Linux is frequently utilized for assessing the security of computer systems, software, and networks. Security experts also use it for malware analysis and simulation of social engineering attacks, such as phishing, credential harvesting, and wireless attacks.
Kali Linux Features: Overview
Given its highly specialized nature, the stand-out traits of Kali Linux primarily focus on the cyber-security use case. The following are the essential features of Kali Linux:
- Extensive collection of security applications. With over 600 tools available, Kali enables cyber-security professionals to perform penetration testing, digital forensics, incident response, wireless security assessments, reverse engineering of binaries, and more.
- Custom kernel and patches. The custom Kali Linux kernel supports advanced security and networking features, while patches enable better performance and hardware support.
- Live environment. Users can boot Kali Linux from a USB drive or DVD, making it easy to perform security tests without affecting the host system.
- Reporting and documentation. Kali offers tools for report generation to facilitate documenting the security tests and communication with clients.
- Rolling updates. The rolling-release nature of Kali Linux allows its users to receive constant updates and access the latest software versions.
Kali Linux vs. Ubuntu: Comparison
Although both systems are Debian-based Linux distributions, Kali and Ubuntu are very different platforms. The table below provides the most relevant points of comparison.
| Kali Linux | Ubuntu | |
|---|---|---|
| Based on | Debian Testing | Debian Unstable |
| Kernel | Customized Kali Linux kernel | Ubuntu Kernel |
| Initial release | March 13, 2013 | October 20, 2004 |
| Release cycle | Rolling release | Two releases per year, LTS releases once in two years |
| Use cases | Penetration testing and malware analysis | General use |
| Default environment | XFCE | GNOME (plus many others via other flavors) |
| ARM support | Yes | Only the server edition |
| Pre-installed apps | More than 600 penetration testing apps, such as Metasploit, Hydra, Nmap, Responder, etc. | Office suite, media players, image editing, and other general-purpose apps |
| Default terminal app | qterminal | GNOME terminal |
| Default shell | ZSH | Bash |
| Ease of use | For penetration testing professionals | For general users |
| Support | Extensive Documentation. Official support on Kali Linux Community Support Channels, Kali Linux Forum, Discord, etc. | Extensive documentation. Commercial support provided by Canonical, free support on Ubuntu forums, Ask Ubuntu website, etc. |
Kali Linux vs. Ubuntu: How to Choose
Given the clear-cut differences between Kali and Ubuntu, deciding which OS to use boils down to a single factor. Consider your use case and follow the advice below:
- Choose Kali Linux if you are a cyber-security expert or enthusiast who plans to use the computer for security testing.
- Choose Ubuntu if you want to use your computer to perform everyday tasks. These tasks include document editing, audio and video streaming, photo editing, coding, etc.
Conclusion
After reading this comparison article, you should know more about two popular Linux distros, Kali Linux and Ubuntu. The article presented both systems and provided advice on choosing the one that is right for you.
Next, read about 25 Best Kali Linux Tools for cyber-security professionals.