Kali Linux is one of the best operating systems for penetration testing. It is a Debian-based Linux distribution with a large user community.
The OS has a rolling release model, with new releases coming out approximately four times a year. Updating the system regularly improves overall security and speeds up system performance.
In this article, you will learn how to update Kali Linux.
Prerequisites
- A system running Kali Linux (it is best to install Kali as a VM).
- Access to a terminal window/command line (Ctrl+Alt+T).
- A user account with root privileges.
Do I Need to Update Kali Linux?
Regular updates are crucial for maintaining any Linux system, especially those used for security-related tasks like Kali Linux. Regular updates ensure that security vulnerabilities are patched, protecting the system from potential exploits and cyber-attacks.
Updates also provide the latest features and improvements and enhance user experience and functionality. Additionally, bug fixes included in updates address issues that could cause system crashes or malfunctions and ensure the system runs smoothly.
Ignoring important updates can leave systems exposed to threats and hinder optimal performance, so the best practice is to perform regular updates on your system.
How to Update Kali Linux?
Kali Linux uses the Debian Package management system, which allows you to update and upgrade using the apt or apt-get command. Follow the steps outlined below to update and upgrade Kali.
Step 1: Check the Source List Files
When downloading updates using the APT package manager, ensure the system connects to the correct remote repository. The /etc/apt/source.list configuration file contains the URLs from which Kali installs packages and applications.
Open the root terminal emulator and run the following command to open the configuration files to check the source list:
cat /etc/apt/source.listThe output should display the following URL:
deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main contrib non-free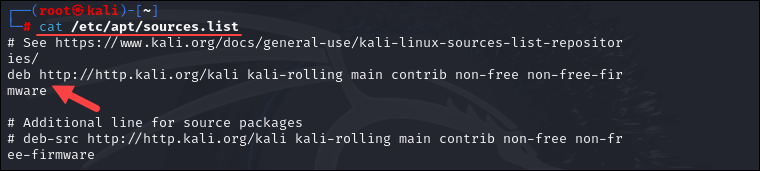
If the URL is not there, paste it and save the file.
Step 2: Update Package Repository Information
Before installing the latest software, you must update the package repository information to ensure you download the newest package versions. Run the following command to get the latest package lists:
apt update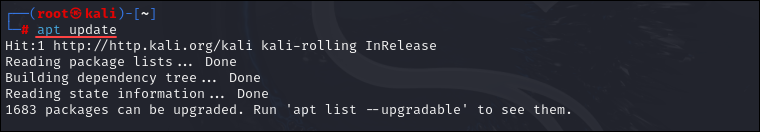
The output states the number of upgradable packages.
Step 3: Upgrade the System
Next, you can run the upgrade, which installs the latest packages and patches for Kali Linux. There are three commands you can use to upgrade Kali:
apt upgrade -yThe apt upgrade command downloads and updates packages without deleting anything previously installed on your Kali Linux system. However, note that if a new version of a package requires additional dependencies or removing existing ones, apt upgrade will hold back such packages.
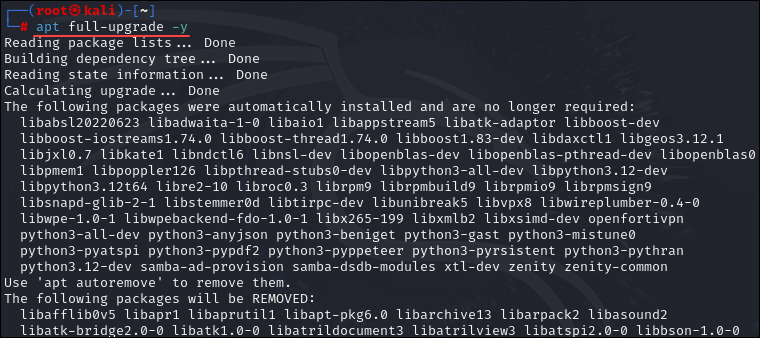
apt full-upgrade -yThe apt full-upgrade command downloads and updates packages. However, it also removes already installed packages if needed. This command is useful for more significant updates where new dependencies might be needed, or obsolete packages should be removed to ensure the system is fully upgraded. This is the preferred command for upgrading Kali.
apt dist-upgrade -yThe apt dist-upgrade command does the same as a regular upgrade while intelligently handling changing dependencies, removing obsolete packages, and adding new ones.
Once you decide how to upgrade, type in the command and press Enter. For this tutorial, we will use apt full-upgrade -y:
Note: Instead of running each command separately, you can update Kali Linux using a single command:
apt update && apt full-upgrade -yStep 4: Remove Unnecessary Packages
Remove obsolete packages after the upgrade to free up disk space by running the command below:
apt autoremove
Confirm the removal with y and Enter and the package manager automatically removes unnecessary packages. After rebooting, your system will be upgraded to the latest version.
Note: Learn how Kali Linux compares to Ubuntu.
How Often to Update Kali Linux?
You should update Kali Linux regularly to ensure the system remains secure and up-to-date with the latest features and tools. Check for updates at least once a week, as frequent updates can quickly address newly discovered vulnerabilities and incorporate the latest enhancements.
For users who rely heavily on Kali Linux for security testing and professional use, updating even more frequently, such as daily or every few days, ensures the environment is always in top shape. Regular updates prevent the accumulation of too many changes at once, making the update process smoother and less time-consuming.
Conclusion
Upgrading your Kali Linux system is crucial to ensure the latest security patches and features are installed. After reading this article, you should know how to update and upgrade your Kali Linux system using the apt package manager.
Next, check out our list of 25 best Kali Linux tools.



