Businesses of all sizes are turning to cloud computing to enhance operational efficiency, scalability, and agility. Choosing the right cloud provider significantly impacts an organization’s success.
In today’s market, organizations have many options, each with its own unique features and pricing. It is little wonder that finding the ideal cloud provider can be daunting.
In this article, we will examine the essential factors to consider when choosing a cloud services provider so that you can find one that aligns perfectly with your business objectives.
How to Choose a Cloud Service Provider?
Every organization looking to migrate to the cloud needs to research the various options available and consider the following factors:
1. Service Offerings
In this first step, you need to determine whether the cloud provider offers the specific services and tools your organization needs. The cloud services typically include:
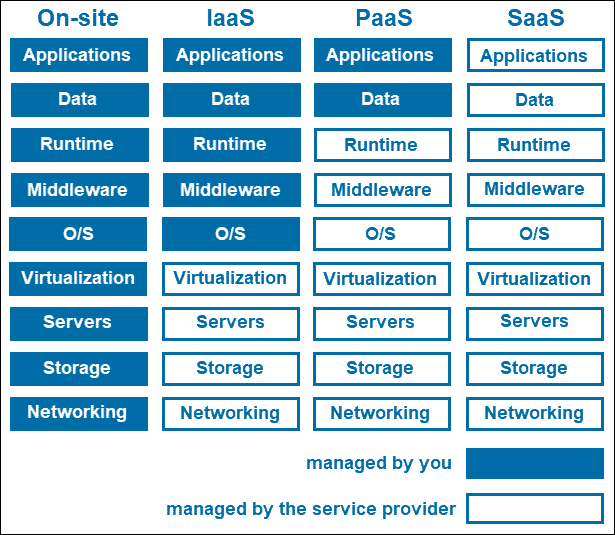
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Includes servers, virtual machines, storage, networks, and other resources. Users provision and manage these resources on demand, eliminating the need for physical hardware.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS). Includes the hardware and software needed to develop and deploy applications. It is useful for application developers as it streamlines the development process by removing the need to manage infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS). Includes software that is hosted and managed by the CSP, which clients access via web browsers without the need for installation or maintenance.
For the ultimate comparison between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, read our article.
2. Scalability
Scalability means that the cloud provider can maintain performance while experiencing changes in the size or volume of workloads. Ensure the cloud provider can scale up or down resources to meet your needs easily and without significant disruptions or cost spikes. Cloud providers scale resources in the following ways:
- Vertical scaling. The capacity of individual resources, such as processing power, memory, or storage, is adjusted to accommodate fluctuating traffic or resource-intensive tasks.
- Horizontal scaling. Also called “scaling out”, this involves adding more instances or resources for efficient workload distribution.
- Global scaling. Businesses with a global presence need a cloud provider that can scale resources across data centers in different geographic regions.
3. Performance
Assess the provider's track record to determine whether services are reliable and of high quality. Here are some of the performance factors to consider:
- Uptime and availability. Check the SLA (service level agreement) to determine the guaranteed percentage of time services are available.
- Network performance. Assess the provider’s network infrastructure, as data transfer and communication between applications and users depend on the speed and reliability of the network.
- Response times. Ensure the provider makes your applications available with minimal latency.
- Compute performance. Choose the instance types that match your computational requirements, as CPU, GPU, and memory capabilities directly affect the processing speed of your applications.
- Storage performance. Cloud providers offer various storage options, so consider your needs to find the right balance of storage performance and cost.
4. Data Center Locations
The location of the cloud provider’s data centers is a critical consideration, as this can have an impact on the performance, compliance, and resilience of your services and applications. Smaller distances between your users and the data center decrease latency and improve response times. Furthermore, global businesses must contend with regional regulations, such as GDPR in Europe, which mandates that data is stored in data centers within a certain jurisdiction. Another benefit of geographically dispersed data centers is that disaster recovery and business continuity are greatly enhanced as data can be replicated across multiple data centers.
5. Security
Robust security is a paramount factor when selecting a cloud provider, as it ensures your data, applications, and infrastructure are protected from threats and vulnerabilities. Here are some of the security concerns to consider:
- Physical security. Your cloud provider facilities should be protected with stringent physical access controls, including security personnel, surveillance cameras, biometric authentication, and other measures.
- Identity and access management (IAM). Robust IAM solutions, such as multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and least-privilege access (implemented by the cloud provider), allow you to maintain strict control over who can access your resources.
- Data encryption. Ensure that your cloud provider follows standard encryption practices and protects your data both at rest and in transit.
- DDoS protection. Many cloud providers offer protection from distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks by filtering malicious traffic and absorbing sudden traffic spikes.
- Security monitoring. Cloud providers offer cloud security monitoring tools that help you detect and respond to security incidents in real time.
- Data privacy. Cloud providers offer features and tools that align with privacy regulations, including anonymization and data masking, and the ability to restrict data processing according to user preferences.
While it is essential to carefully assess the security capabilities of the cloud provider, organizations need to understand that cloud security is based on the shared responsibility model and that they must also perform due diligence to ensure the safety and integrity of their data and applications.
6. Compliance
For organizations operating in highly regulated industries or that handle sensitive data, compliance is a critical factor when choosing a cloud provider. Here are some of the compliance criteria to take into account:
- Industry-specific regulations. Organizations must find a cloud provider that offers solutions tailored to their specific industry, e.g., HIPAA for healthcare and PCI DSS for finance.
- Security and compliance certifications. Determine if the cloud provider has undergone specific security audits and assessments and obtained relevant certifications, such as SOC2, ISO 27001, FedRAMP, and others.
- Regional regulations. Organizations operating in certain regions must comply with local or regional regulations, such as GDPR in Europe.
- Auditing and monitoring tools. Find out whether the cloud provider offers tools that help you track and document compliance-related activities by creating logs, reports, and alerts.
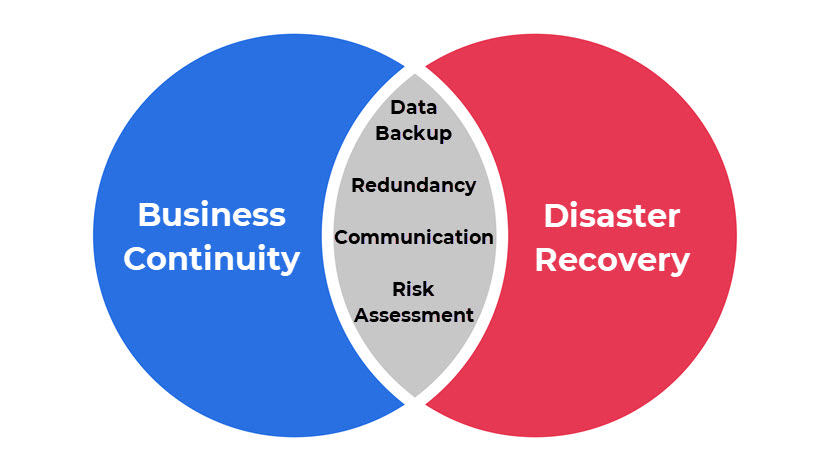
7. Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Business continuity depends on your ability to withstand and recover from disasters, whether they come in the form of natural events or malicious activity. When choosing a provider, thoroughly evaluate their data backup and disaster recovery capabilities to ensure the safety and availability of your data and applications. Here are some factors to consider:
- Data backup options. Providers typically offer different data backup options, including full, differential, and incremental backups, so it is necessary to assess the methods available and determine how they meet your data protection needs.
- Data security. Check that the cloud provider adequately protects your backed-up data with encryption and access controls to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Data retention policies. Find out how long backed-up data is retained, as this information is crucial for compliance and your ability to recover data.
- RTO and RPO. Examine the recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO) that the cloud provider offers. These metrics determine the time it takes to recover from an adverse event and the acceptable data loss, respectively.
- Automation. Automated backup and recovery simplify the process of creating and restoring backups, reducing the risk of human error.
- Data redundancy. Check that the cloud provider offers built-in redundancy features across different geographical locations to enhance the safety and availability of your data and services.
8. Cost and Pricing Structure
The cost of cloud services directly impacts the financial feasibility of an organization’s cloud adoption. Cloud providers typically offer different pricing models for their services and also provide detailed cost breakdowns for various available resources. Here are some essential considerations regarding cloud costs:
- Pricing model. These are often divided into three types. The pay-as-you-go model charges you based on the actual resources you use. The subscription-based model provides fixed costs for monthly or yearly commitments. If your workloads have predictable resource demands, you can benefit from reserved instances, which come with cost savings on long-term commitments.
- Data transfer costs. Check data transfer costs, which include fees for data ingress and egress. Consider how the volume of data transfer will impact your overall cloud costs.
- Resource costs. Various cloud resources come with different prices, and cloud providers offer different resources and storage, each with its own pricing structure. Choose the instance types and storage classes that match your use and budget.
- Billing transparency. Make sure that the cloud provider sends clear and detailed billing statements.
9. Support
The support your cloud provider offers directly impacts your ability to address issues, maintain operational efficiency, and ensure the reliability of your cloud-based applications and services. Providers often have different levels of support, each coming with varying response times, availability, and types of customer care.
Cloud support comes in various forms, including:
- Customer support agents.
- Documentation, including knowledge bases, FAQs, and user guides.
- Community support provided by user communities and forums.
- Dedicated account managers.
10. Vendor Lock-in
Vendor lock-in occurs when an organization becomes so dependent on a specific cloud provider’s services that migrating to an alternative provider becomes difficult and costly. This situation arises when organizations build applications and services that are tightly integrated with the proprietary technologies, APIs, and toolsets unique to the cloud provider’s platform. Other elements that contribute to vendor lock-in include long-term contracts and licensing agreements, as well as the high costs associated with migrating to another cloud provider.
To mitigate vendor lock-in, organizations can adopt a multi-cloud strategy, using different cloud providers for different workloads and services. Container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes and infrastructure provisioning tools like Terraform also help to abstract infrastructure, making it easier to migrate between providers.
11. Networking and Connectivity
Networking and connectivity directly impact the performance, availability, and security of your services. When choosing a cloud provider, evaluate the following criteria:
- Network infrastructure. A wide and robust geographic presence reduces latency and provides redundancy.
- Private network connections. Find out whether the cloud provider offers private network connections that enable dedicated, low-latency links between your on-premises infrastructure and the provider’s network.
- Bandwidth and throughput. Depending on your workloads, you may need high-speed connections to support data-intensive applications and real-time communication.
- IPv6 support. If your organization requires IPv6 compatibility for its growing number of connected devices, make sure the cloud provider supports this networking protocol.
- Load balancing. Load balancing services distribute traffic across multiple instances and servers, improving scalability, fault tolerance, and performance.
- Redundancy and high availability. Check the cloud provider’s redundant network connections and failover mechanisms in the event of network outages or hardware failure.
12. Integration and Compatibility
Integration is a critical factor determining how well your cloud provider’s services harmonize with your existing infrastructure. Integration refers to the ability of systems, applications, and services to connect and interoperate. When choosing a cloud provider, it is essential to establish whether their offerings can integrate with your existing tech stack, including your organization’s on-prem systems, databases, development frameworks, and third-party applications. Robust APIs and SDKs will enable you to create custom integrations and streamline workflows.
13. Monitoring and Analytics
Look for a cloud provider that offers monitoring and analytics tools and services to help you gain insight into the performance, security, and health of your cloud-based applications. Monitoring and analytics are important factors when selecting a cloud provider for the following reasons:
- Visibility. The ability to observe resource utilization, response times, error rates, and other metrics in real time is essential for delivering a great user experience.
- Cost optimization. Tools that track resource consumption and usage patterns help identify cost optimization opportunities.
- Scaling. Monitoring ensures that resources are automatically scaled to accommodate fluctuating demands, optimizing resource allocation.
- Machine learning and predictive analytics. These advanced technologies can forecast resource needs, detect anomalies, and provide proactive recommendations for performance and cost optimization.
- Alerts and notifications. Timely alerts are essential for quick responses to security incidents or performance deviations. Check whether you can customize metrics and dashboards to tailor your monitoring to your organization’s specific needs and workflows.
- DevSecOps integration. Monitoring and analytics can be integrated into DevSecOps pipelines to provide teams with real-time insights into the health and security of applications and infrastructure.
14. Business Health
Evaluating the financial stability, reputation, and long-term viability of the cloud provider is essential when going through the selection process. You need a partner with a proven history of adapting to the dynamic technology landscape.
A financially stable provider is more likely to invest in infrastructure, security, and innovative technologies that ensure long-term success. It is also beneficial to investigate a provider's reputation with customers by reading case studies, customer reviews, and industry analyst reports. Additionally, by looking into the provider’s ecosystem and network of partners, software vendors, and third-party integrations, you will ensure that your organization finds compatible services and solutions.
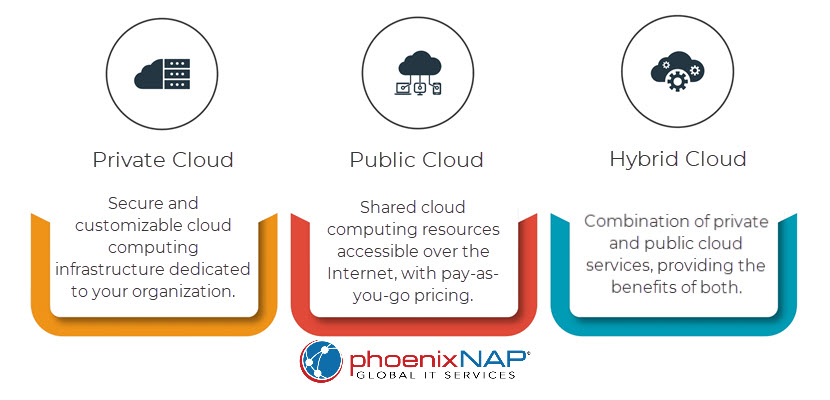
Should You Use Multiple Cloud Providers?
Using multiple cloud providers, a strategy known as multi-cloud, is an option, depending on your organization’s goals, needs, and resources. While multi-cloud offers important benefits, it also introduces complexities that need to be carefully managed.
Here is a quick rundown of the advantages and downsides of going down the multi-cloud road:
Advantages:
- Reduced vendor lock-in.
- Optimized cost management.
- Increased redundancy and resilience.
- Geographic reach.
- Ability to choose best-of-breed services.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity in managing resources.
- Difficulty maintaining security and compliance standards.
- Challenging to ensure interoperability.
- High data transfer costs between different providers.
- Cost overheads stemming from complex cost management across providers.
- Complicated and time-consuming vendor relationships.
For an in-depth guide on how to successfully implement a multi-cloud strategy, read our blog article.
Is It Easy to Switch Cloud Providers?
Migrating from one cloud provider to another can be a complex and challenging process. The ease of switching between cloud providers depends on several factors, including the organization’s specific workloads (stateful or stateless), the complexity of data transfer, the extent of vendor-specific dependencies, and the cost of data transfer, infrastructure provisioning, and reconfiguration.
Moving to an alternative cloud provider requires careful planning and a thorough assessment of your existing environment, your data transfer requirements, and compatibility challenges. Consider a phased or incremental approach to migration and continually monitor the performance of your applications and infrastructure in the new environment.

Future-Proof Your Cloud Strategy: Choose the Right Cloud Provider
To select the right cloud provider, consider the factors that are critical to the services you offer, your security and compliance standards, budgeting constraints, and projected business growth. The cloud is a dynamic environment, so regularly assess your choice of cloud provider to ensure that it stays aligned with your evolving requirements and remains attuned to industry trends.



