Cloud Computing is one of the most implemented methods for developing and delivering enterprise applications currently. It is also the most opted solution for the ever-expanding needs of SMEs and large-scale enterprises alike.
As businesses grow and their process technologies improve, there is a growing trend towards companies migrating to the cloud. This process of moving services and applications to the cloud is the basic definition of Cloud Migration. The enthusiasm that companies have towards cloud migration is evident in the massive amounts of money and resources they dedicate to improving their operations.
In this article, we will introduce Cloud Migration processes and different ways of adapting to your organizational structure.

What Is Cloud Computing?
Before tackling the question of “What is Cloud Migration?” let’s define Cloud Computing.
Cloud Computing is an enhanced IT service model that provides services over the Internet. Scalable and virtual resources, such as servers, data storage, networking, and software, are examples of these services. Cloud computing can also mean running workloads in a provider’s powerful data centers and on servers for a price.
Cloud Computing is considered one of the cutting-edge technologies of the 21st century. Its innovative ability to provide relatively inexpensive and convenient networking and processing resources has fueled wide-ranging adaptation in the computing world.
The Cloud Migration process is an inevitable outcome of Cloud Computing. It has revolutionized the business world by facilitating easy access to data and software through any IoT (internet-connected) device. Moreover, it facilitates parts of the SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle), such as development and testing, without considering physical infrastructure.
What Is Cloud Migration?
Cloud Migration is simply the adoption of cloud computing. It is the process of transferring data, application code, and other technology-related business processes from an on-premise or legacy infrastructure to the cloud environment.
Cloud Migration is a phenomenal transformation in the business information system domain as it provides adequate services for the growing needs of businesses. However, moving data to the cloud requires preparation and planning to determine the best approach.
The other use case for Cloud Migration is cloud-to-cloud transfer.
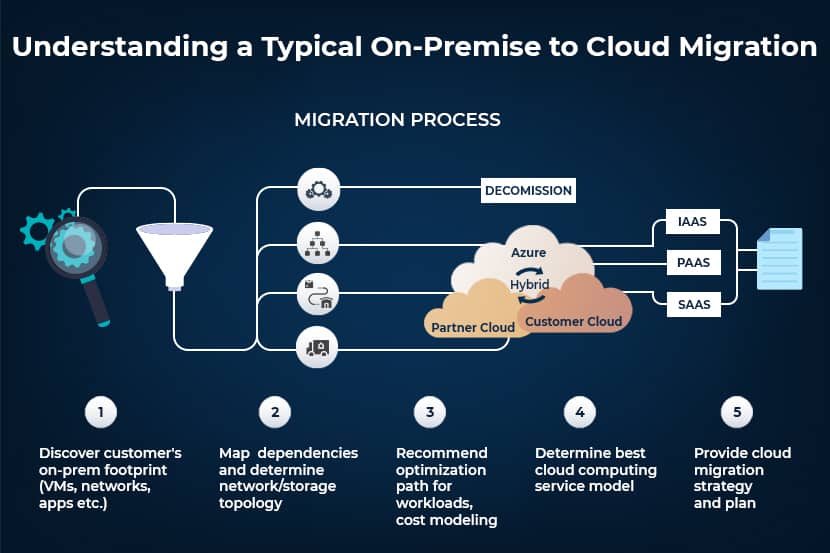
Types of Cloud Migration
The process of Cloud Migration creates a great deal of concern in the business and corporate world who have to prepare for many contingencies that come along with it. The type and degree of migration may differ from one organization to another. While certain organizations may opt for a complete migration, some may do so in part, while others remain on-premises. Some process-heavy organizations may require more than one cloud service.
In addition to the degree of adoption, other parameters categorize Cloud Migration. These are some of the more commonly seen use cases.
Lift and Shift
This process involves moving software from on-premise resources to the cloud without any changes in the application or the process used before. It is the fastest type of cloud migration available and involves fewer work disruptions since it involves only infrastructure, information, and security teams. Furthermore, it is more cost-effective compared to other methods available.
The only downside to this method is that it does not fully leverage the performance and cloud versatility advantages, as it only involves moving the application to a new location. Therefore, it’s more suitable for companies with regular peak schedules and that follow market trends. Consider it as a first step in the adoption of the Cloud Migration process.
The Shift to SaaS
This method involves outsourcing one or more preferred applications to a specialized cloud service provider. Through this model, businesses can offload less business-critical processes and focus more on their core applications. This setup will enable them to become more streamlined and competitive.
While this method provides the ability to personalize your application, it sometimes can cause problems in the support model provided by the SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) platform. It’s risky enough that you could lose some competitive edge in your industry. This method is more suitable for non-customer-facing applications and routine functionalities such as email and payroll.
Legacy Application Refactoring
Cloud migration processes enable companies to fully replicate their legacy applications on the cloud platform through refactoring. In this way, you can allow legacy applications to function and concurrently build new applications to replace the old ones on the cloud.
Refactoring lets you prioritize business processes by moving less critical ones to the cloud first. This method is cost-effective, improves response time, and helps in prioritizing updates for better interactions.
Re-platforming
Re-platforming is a cloud migration process that involves replacing the application code to make it cloud-native. This process is the most resource-intensive type of migration, as it requires extensive planning.
Completely rewriting business processes can also be quite costly. Nonetheless, this migration method offers total flexibility and brings you all the benefits of the cloud to their fullest extent.
The Cloud Migration Process
This process is how an organization achieves Cloud Migration. These cloud migration steps depend entirely on the specific resource that the organization is planning to move to the cloud and the type of migration performed.
Here are the five main stages of the process:
Step 1. Create a Cloud Migration Strategy
This step is the most important part of the process. It’s where you create your cloud migration plan and identify the specifics of the migration. You will need to understand the data, technical, financial, resource, and security requirements and decide on the necessary operations for the migration.
Expert consultation is also recommended during this stage to ensure successful planning. Identifying potential risks and failure points is another important part of this stage of the process. Mitigation actions or plans for resolutions will also need to be put in place to ensure business continuity.
Step 2. Selecting a Cloud Deployment Model
While part of this stage is related to the first one, you must choose the best-suited cloud deployment model considering both the organization and the resources at hand. A single or multi-cloud solution will need to be planned based on the types of resources that are required. If you are a small or medium-scale organization with minimal resources, the public cloud is the recommended option.
If your organization uses a SaaS application but needs extra layers like security for application data, a Hybrid Cloud architecture will be better suited to your needs. Private Cloud solutions are ideal for handling sensitive data and situations where full system control is crucial.
Step 3. Selecting your Service Model
In this stage, you can determine the various service models required for each of your business operations. The available service models are IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service), PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service), and SaaS (Software-as-a-Service). The difference in choices relates to the type of migration planned, as each one requires a different type of service.
Step 4. Define KPIs
Defining KPIs will ensure that you can monitor the migrated application within the cloud environment. These KPIs may include system performance, user experience, and infrastructure availability.
Step 5. Moving to the Cloud
You can adopt many different methods to move data from your infrastructure to the cloud. This move may be using the public Internet, a private network connection, or offline data transfer. Once all data and processes are moved and the migration is complete, make sure that all requirements are fulfilled based on the pre-defined KPIs.
What Is Cloud Migration Strategy?
A cloud migration strategy is the process of planning and preparation an organization conducts to move its data from on-premises to the cloud.
Cloud migration offers numerous advantages and business solutions, but transitioning to a cloud platform can be a challenging process. You must take into consideration several factors before initiating the migration process. And you may likely face many challenges both during the strategy development stage and during the actual migration process.

To address the above issues and ensure a smooth migration process, develop cloud migration strategies that consider all factors, including risk evaluation, disaster management, and in-depth business and technology analysis.
Get free advice in our Cloud Migration Checklist for an in-depth understanding of how to get started.
Benefits of Cloud Migration
Businesses tend to spend a significant amount on software development and deployment. But cloud migration offers a variety of methods to choose from, and they can be used to access SaaS at a much lower cost while safely storing and sharing data.
Cloud migration benefits include:
Cost Saving
Maintaining and managing a physical data center can be costly. But cloud migration allows curtailing operational expenses since cloud service providers like SaaS or even PaaS takes care of maintenance and upgrades of these data centers for a minimal upfront cost.
In addition to the direct cost savings of not maintaining your own data centers, cloud migration offers indirect cost savings by eliminating the need for a dedicated technical team. Another benefit is that most licensing requirements are taken care of by the service provider.
Flexibility
Cloud migration facilitates upward or downward business expansions based on its needs. Small-scale businesses can easily scale up their processes into new territories, and large-scale businesses can expand their services to an international audience through cloud migration.
This flexibility is possible through horizontal expansion via globally distributed data centers and the integration of hybrid cloud computing solutions, including AI, Machine Learning (ML), and image processing.
It also enables users to access data and services easily from anywhere and on any device. Companies can also outsource certain functionalities to service providers, allowing them to focus more on their core processes.
Quality Performance
Cloud migration enables better interactions and communications within business communities by increasing data visibility. It also facilitates quick decision-making since it reduces the time spent on infrastructure. Organizations can extend their ability to integrate different cloud-based solutions with other enterprise systems and solutions. This capability, in turn, ensures the quality and performance of the systems.
Automatic Updates
Updating systems can be a tedious task, especially for large-scale companies, as they can require prolonged analysis. With Cloud migration, companies no longer need to worry about this as the infrastructure is off-premises, and cloud service providers are likely to take care of automatic updates. Ready-to-go software updates are part of most cloud computing plans and are available at a fraction of the cost of usual licensing fees.
Enhanced Security
Many studies have proven that data stored in a cloud environment is more secure compared to data in on-premise data centers. Cloud vendors are experts in data security proactively secure data by updating their mechanisms regularly. Moreover, the cloud provides enhanced control over data accessibility and availability, ensuring that only authorized users can access the data.
Ensuring Business Continuity
Businesses often need to set up additional resources for disaster recovery. Cloud migration offers intelligent and cost-effective disaster management solutions. It ensures that applications are functional and available even during and after critical incidents, ensuring business continuity.
Cloud service providers take serious care of their data centers and ensure that they are protected both virtually and physically. This security, combined with the availability of geographically dispersed locations, enables the convenient setup of robust Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity plans.
Note: Learn more about Cloud Workload Analysis, a paramount step in your cloud migration.
Cloud Migration Tools and Services
Many commercially available tools assist in the planning and execution of a cloud migration strategy. Some well-known cloud migration services include Google, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure. They provide services for public cloud data transfer, private networks, and offline transactions.
They also come with tools to plan and track the progress of the migration process, completed by collecting the system’s on-premise data, such as system dependencies. Some examples of migration services include Google Cloud Data Transfer Service, AWS Migration Hub, AWS Snowball, and Azure Migrate. Additionally, there are third-party vendors like Racemi, RiverMeadow, and CloudVelox. When choosing a tool, consider factors like functionality, compatibility, and price.
Migration tools can be categorized into three main types as follows:
- Open Source – These are free or low-cost tools that can be easily customized.
- Batch Processing Tools – These tools are used to process large amounts of data at regular intervals.
- Cloud-based Tools – These are task-specific tools that bind data and the cloud with connectors and toolsets.
Is Moving To The Cloud Right For Your Business?
Taking all this into account, you can now finally decide if Cloud Migration is an option for your organization. If so, the next decision will be which migration model to adopt and how to plan the migration process. Each migration is unique, so your plan will also need to be tailor-made. Discover the benefits of cloud computing for business with our cloud services.



