Package managers download and install the main binary package and its dependencies. Once the application is no longer needed, it is advisable to remove it, as its packages can take up storage space and hinder performance.
This guide shows you how to remove packages in Ubuntu using the command line or GUI.

Prerequisites
- Ubuntu installed (this tutorial uses Ubuntu 22.04).
- Command-line access.
- A user account with sudo privileges.
Uninstall Packages in Ubuntu via CLI
The default Ubuntu command-line application management tools are APT, DPKG, and Snap. Each utility provides methods for uninstalling and removing software from the system.
Read the sections below for instructions on uninstalling packages using the Ubuntu CLI.
Option 1: Uninstall Ubuntu Packages with APT
The APT package manager offers several ways to remove unwanted packages. The most common way to uninstall an app with APT is to use the apt remove command:
sudo apt remove [package]For instance, to remove the curl tool from Ubuntu, type the following command:
sudo apt remove curl -yAdding the -y argument to the command auto-approves all queries during uninstallation.
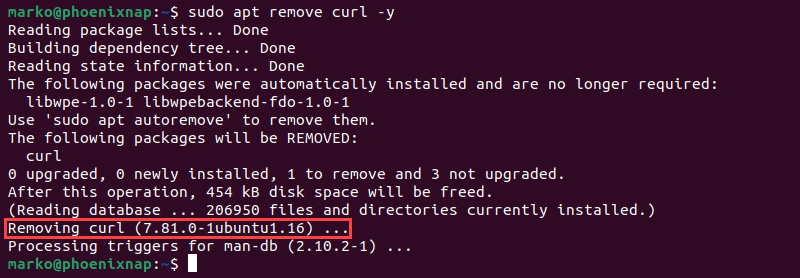
The apt remove command uninstalls the application but does not remove configuration files. To clear packages from the system completely, use apt purge. The purge option deletes packages and removes all dependencies:
sudo apt purge [package]For instance, delete curl and its configuration files by typing:
sudo apt purge curl -yRemove the outdated packages' cache by using the apt clean utility. To clear the cache from an Ubuntu system, run:
sudo apt cleanThe command prints no output.
Option 2: Uninstall Ubuntu Packages with DPKG
The DPKG utility is a low-level packaging tool on Debian-based systems such as Ubuntu. To use DPKG to remove a package, enter the following command:
sudo dpkg -r [package]For instance, to remove curl, run:
sudo dpkg -r curl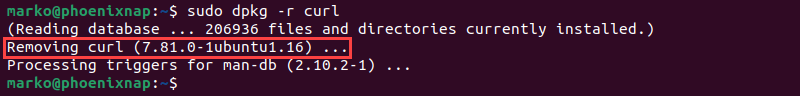
Adding the -P option tells DPKG to remove the package and all its dependencies:
sudo dpkg -P [package]For example, purge curl with:
sudo dpkg -P curlThe command removes the package, all its dependencies, and any configuration files from the system.
Option 3: Uninstall Ubuntu Packages with Snap
Snap is a popular software package and deployment system designed for application management on Ubuntu. Uninstalling snaps on Ubuntu is straightforward because the utility bundles all dependencies into a single package.
To remove snap packages with the snap command, follow the steps below:
1. List all installed snaps with:
snap list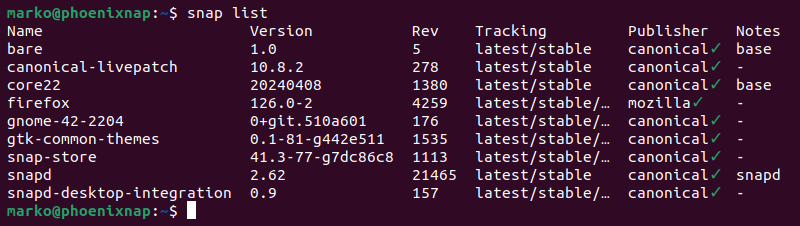
2. Note the name of the package to delete.
3. To delete an installed snap, execute:
sudo snap remove [package]The snap remove command completely deletes the software from the system, including config files and all associated user data. For example, remove the Firefox snap by executing the following command:
sudo snap remove firefoxThe output confirms that the package has been removed.

Option 4: Uninstall Ubuntu Packages with Flatpak
Flatpak is a software deployment utility that aims to provide a unified way to install Linux software. Follow the steps below to remove Flatpak packages from the system:
1. Enter this command to list all Flatpak apps and their IDs:
flatpak list --app2. Note the ID of the app you want to uninstall.
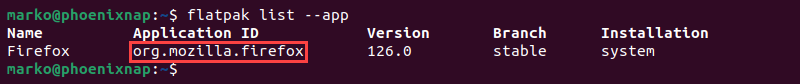
3. Uninstall the app by typing:
sudo flatpak uninstall [app-id]For example, to remove the Firefox flatpak, enter the following command:
sudo flatpak uninstall org.mozilla.firefox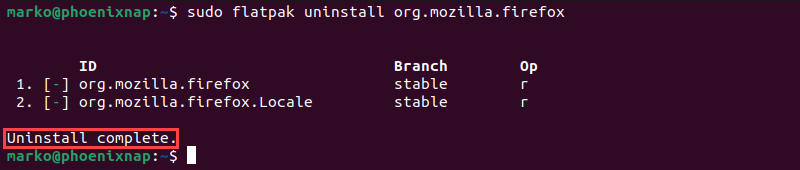
4. Unused runtime libraries accumulate over time. To delete unused runtimes, use the --unused option:
flatpak uninstall --unused5. If you wish to delete all Flatpak apps, use:
flatpak uninstall --allNote: Learn about the differences between Flatpak, Snap, and AppImage.
Option 5: Uninstall Ubuntu Packages with ppa-purge
Third-party repositories allow users to access applications that are unavailable in the default system repositories. The ppa-purge utility allows users to uninstall all packages from a single repository and remove the repository itself.
Note: If ppa-purge is unavailable on the system, install it by typing: sudo apt install ppa-purge.
Use the following syntax for the ppa-purge command:
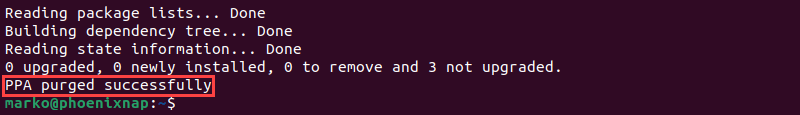
sudo ppa-purge [ppa]Replace [ppa] with the repository name. For example:
sudo ppa-purge ppa:ubuntu-mozilla-daily/ppaThe output confirms the operation's success.
Option 6: Remove Ubuntu Packages with rm
Application binaries are located in multiple locations across the system, e.g., /usr/bin, /usr/sbin, and /usr/local/bin. To manually remove a binary, use the rm command:
sudo rm -rf [path-to-binary]/[binary]For example, to remove test-app located in /usr/local/bin, type:
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/bin/test-appWarning: Manually removing packages may result in broken installations and compromise the system's stability.
Option 7: Remove Dependencies with autoremove
Sometimes, unnecessary dependencies remain on the system from previous installations. To get rid of unused packages and free up space, run the following:
sudo apt autoremove -y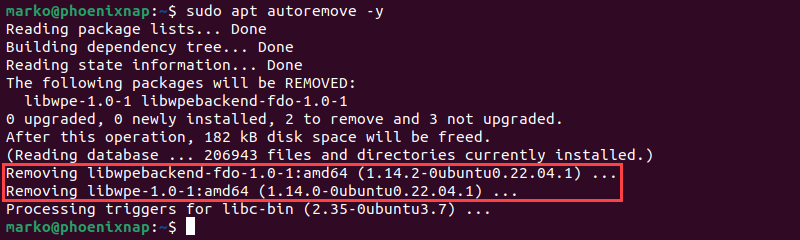
The command removes all orphaned or unused dependencies.
Uninstall Packages in Ubuntu via GUI
Ubuntu users who prefer managing packages via a graphical interface can use the Ubuntu Software Center, the default GUI. Another popular option is Synaptic Package Manager, which offers more granular control over packages.
The following sections provide instructions for uninstalling packages in Ubuntu using the GUI.
Option 1: Uninstall Packages with Ubuntu Software Manager
The default software manager for Ubuntu GUI users is Ubuntu Software Center. To uninstall a package using this utility, proceed with the following steps:
1. Open Ubuntu Software Center.

2. Select the Installed tab.
3. Scroll down the list of programs and find the one to uninstall.
4. Click the Uninstall button next to the program.
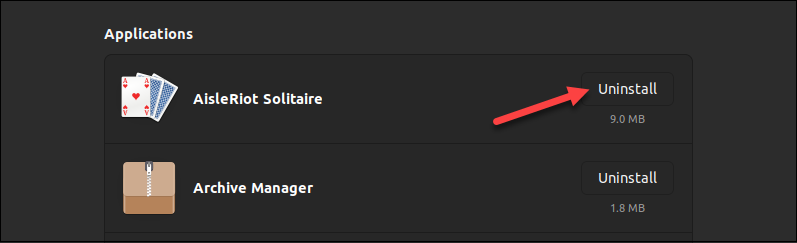
5. Type the password to confirm and wait for the uninstallation to finish.
Option 2: Use the Synaptic Package Manager
Many Ubuntu users prefer the Synaptic Package Manager for its robust architecture and feature-rich interface. To uninstall packages using Synaptic, launch the tool and follow the steps below:
1. Select the Status button on the left side of the screen.
2. Choose Installed from the menu options.
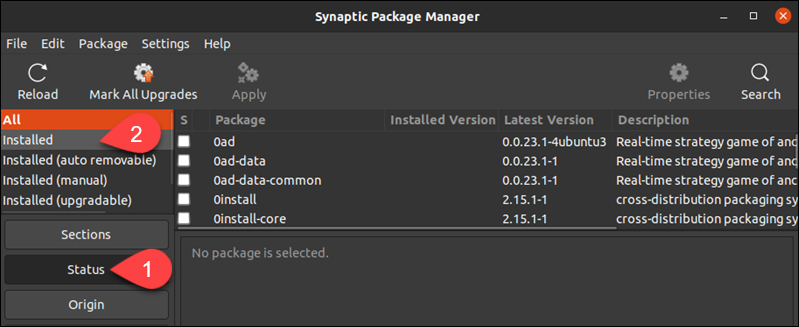
3. Highlight the application you want to remove from the list of packages.
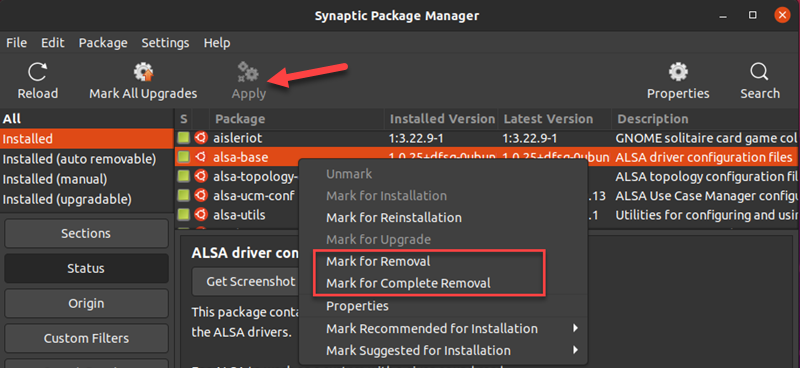
4. Right-click the application.
5. Select Mark for Removal. Alternatively, select Mark for Complete Removal to delete the standard configuration files along with the software package.
6. Click Apply.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you should be ready to uninstall or remove packages in Ubuntu. The guide provided detailed instructions for removing the package using both the command line and the GUI.
Next, learn how to list all installed packages in Ubuntu.


