RPM is a package format used by Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and its derivatives, such as Rocky Linux, CentOS, or Fedora. The name comes from the RPM Package Manager (RPM), a free and open-source package management system for installing, uninstalling, and managing software packages in Linux.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install RPM packages on Ubuntu.

Prerequisites
- Ubuntu installed.
- A user account with root privileges.
- Command-line access.
Convert and Install an RPM Package on Ubuntu
Note: A converted RPM package may encounter dependency and compatibility issues. In this case, manually resolve dependencies by installing the required packages separately using Ubuntu's APT package manager.
This section outlines the steps to convert an RPM package to a DEB package and then install it. Follow the steps below to perform these actions using the alien utility.
Note: Learn the difference between APT and SNAP, two package managers for Ubuntu.
Step 1: Install alien Package
Alien is a useful tool that simplifies conversions between Red Hat's RPM, Debian's DEB, Stampede's SLP, Slackware's TSZ, and Solaris' PKG file formats. Follow the steps below to install alien:
1. Update your package repository information to get the latest program version:
sudo apt update2. Install the alien conversion utility using the command below:
sudo apt install alien -yWait for the process to finish.
Step 2: Convert RPM Files to DEB Format
After installing the alien utility, convert RPM files to the DEB format by following the steps below:
1. Download the RPM package for the software to install. Use a trusted source for the download.
2. Open the terminal and use the cd command to move to the directory where you saved the RPM file.
3. Use the syntax below to convert the RPM file and install it:
sudo alien [package_name].rpmReplace [package_name] with the full name of the package to convert. List the contents of the directory with the ls command and copy the package name for the command above. For example:
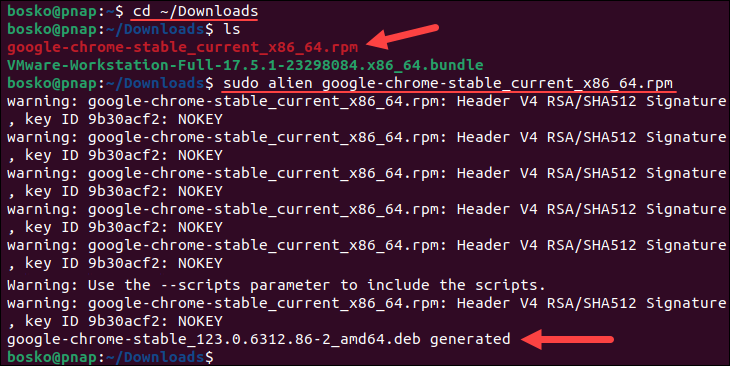
The command instructs alien to initiate the process of converting the RPM file to a DEB file. Wait for the process to complete.
Note: Log in as a user with sudo access to install packages on Ubuntu.
Step 3: Install the converted RPM package on Ubuntu
Once the conversion completes, use the following syntax to install the DEB package:
sudo dpkg -i [package_name].debReplace [package_name] with the actual name of the converted package. For example:
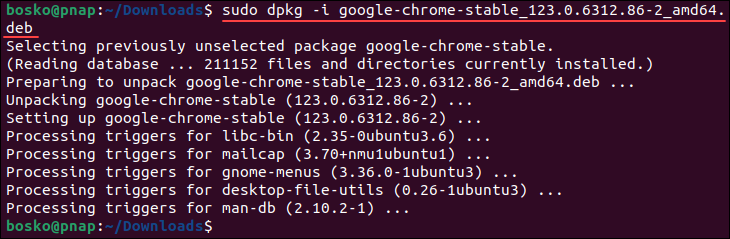
Install RPM Package Directly on Ubuntu
RPM packages can also be installed directly on Ubuntu without previously converting them. This procedure also requires the alien tool mentioned in the previous section.
Warning: This command can lead to serious compatibility issues if you attempt to run it with important system packages since RPM was not developed for Debian-based distributions.
The syntax for installing RPM packages directly is:
sudo alien -i [package_name].rpmFor example:
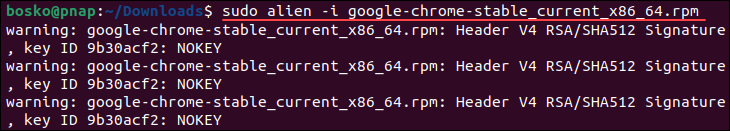
The command installs the package on the system.
Conclusion
By following the tutorial, you can install an RPM package on Ubuntu. However, be aware that installing packages not originally intended for your system can cause compatibility issues, especially when updating essential system packages. In that case, a better option would be to use Ubuntu repositories or adequate alternative packages.
Next, check out our tutorial for crucial Linux commands and download a cheat sheet, or see how to install and use winget, a Linux-style Windows package manager.