A deb package (.deb file) is a software package in a specific format designed for Debian-based distributions recognized by the .deb extension. Deb packages allow installation on an Ubuntu system without an internet connection.
This article shows several ways to install and remove deb packages on Ubuntu.

Prerequisites
- A system running Ubuntu.
- Access to the terminal.
- User with sudo or root privileges.
Install deb Files Using GUI
Installing deb files through the GUI is straightforward and convenient. Below are the two most common options for installing deb packages through the user interface.
Option 1: Software Center
To install a deb package via Software Center (Ubuntu Software), follow the steps below:
Note: In Ubuntu 22.04 and older versions, the app is called Software Center. In Ubuntu 24.04, use the App Center.
1. Locate the downloaded deb package. By default, the system stores downloaded files in the Downloads directory.
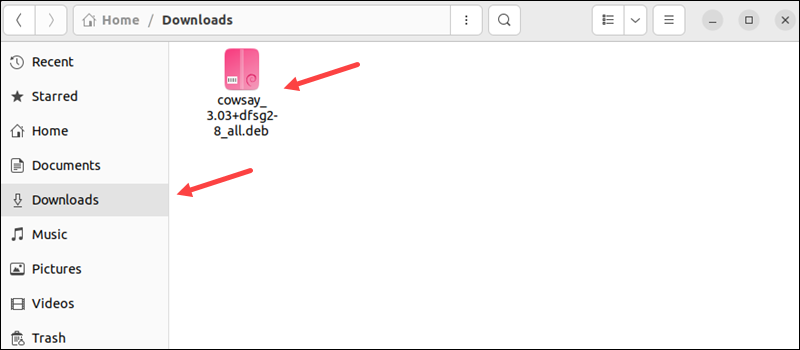
2. Right-click the deb file and choose Open with Another Application.
3. Select Software Install from the program list.
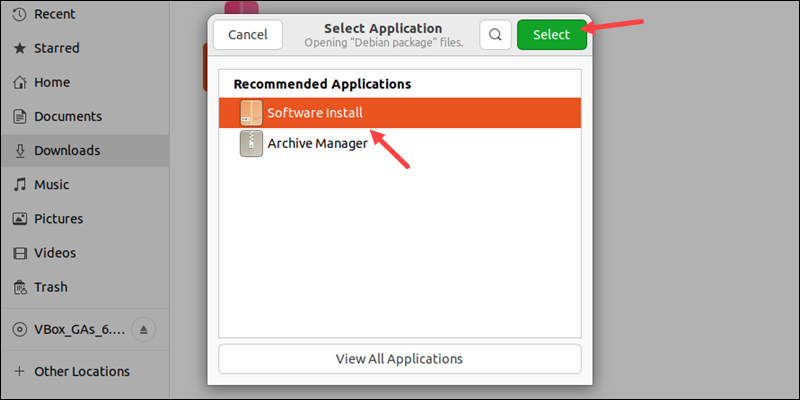
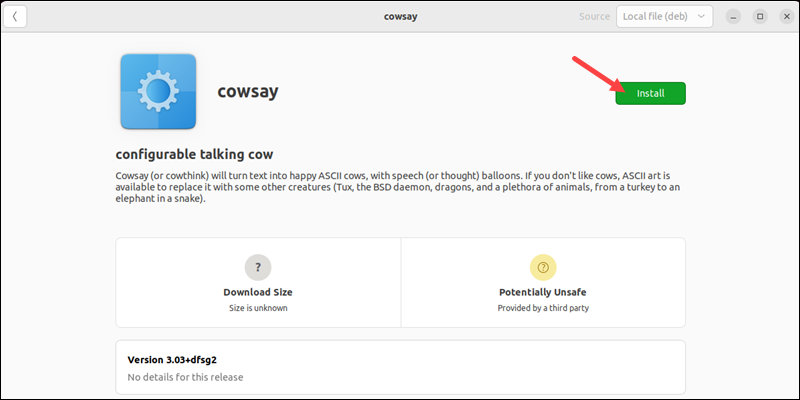
A new dialogue box opens with details about the software.
4. Click on the Install button to proceed.
5. Enter the user's password when prompted and press Enter to authenticate.
6. Wait for the installation to complete. When finished, the software is ready to use.
Option 2: GDebi GUI
GDebi is a simple tool for installing local deb packages. The program also identifies all the required dependencies and automatically downloads and installs them using the apt package manager. GDebi is available both as a command-line and GUI tool.
Note: GDebi does not come on Ubuntu by default. To install it, run sudo apt install gdebi -y.
To install a deb package using the GDebi GUI, follow these steps:
1. Open the file manager and locate the deb file.
2. Right-click on the deb file and choose Open With GDebi Package Installer.
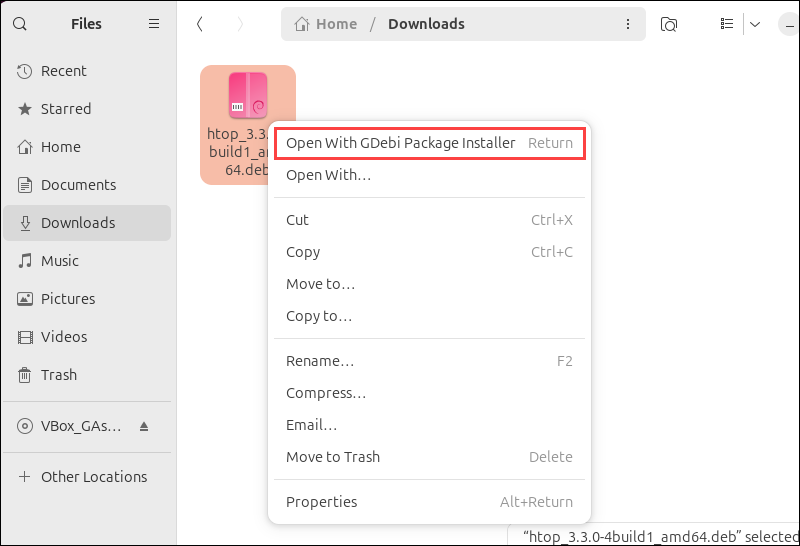
3. The installer loads the deb package and shows the software description. Click Install Package to start the installation.
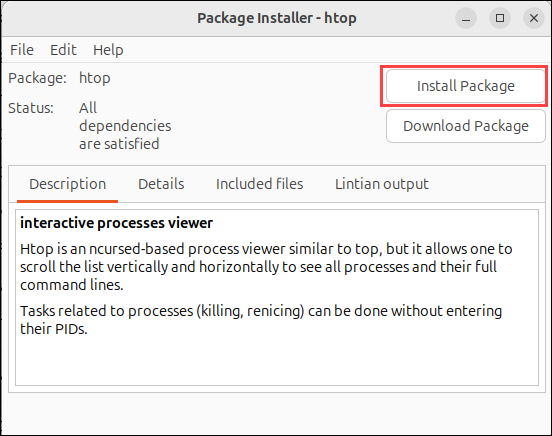
4. Provide the user password when prompted and press Enter.
5. Wait for the installation to complete. Once done, the software is ready to use.
Install deb Files using the Terminal
The Ubuntu terminal enables installing packages using different package managers and commands. Below are a few options for installing deb packages using terminal commands.
Option 1: dpkg Command
<strong>dpkg</strong> a is a package manager for installing, removing, and building packages.
To install a deb package using the dpkg command, run the following command:
sudo dpkg -i [package path]For example, to install the htop package, run:
sudo dpkg -i ~/Downloads/htop_3.3.0-4build1_amd64.deb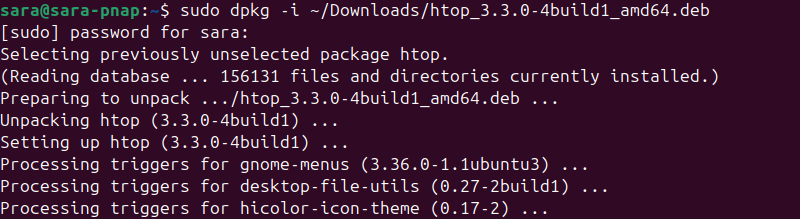
Provide the password and wait for the installation to complete. If a package relies on unavailable dependencies, the dpkg command returns an error. Download any dependencies manually.
Option 2: apt Package Manager
The apt command runs the apt package manager software. To install a deb package using the apt command, run:
sudo apt install [package path]To install the htop package, run:
sudo apt install ~/Downloads/htop_3.3.0-4build1_amd64.deb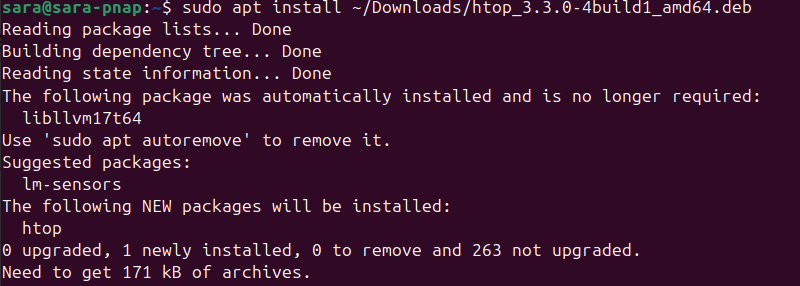
Provide the user's password if prompted. The package manager also locates and installs any dependencies automatically.
Option 3: GDebi Package Installer
The GDebi tool also works as a command-line tool for package installation. To install a deb package with GDebi in the command line, run the following in the terminal:
sudo gdebi [package path]Install htop with:
sudo gdebi ~/Downloads/htop_3.3.0-4build1_amd64.deb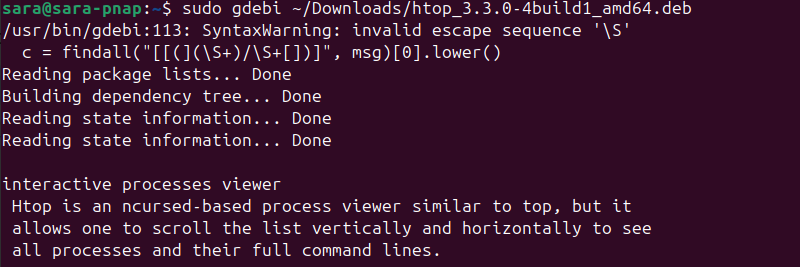
How to Remove deb Packages
There are several different ways to remove a previously installed deb package. The removal method depends on how the package was initially installed.
Below are examples of several options for removing deb packages from the system.
Option 1: App Center
To remove a deb package using the App Center, do the following:
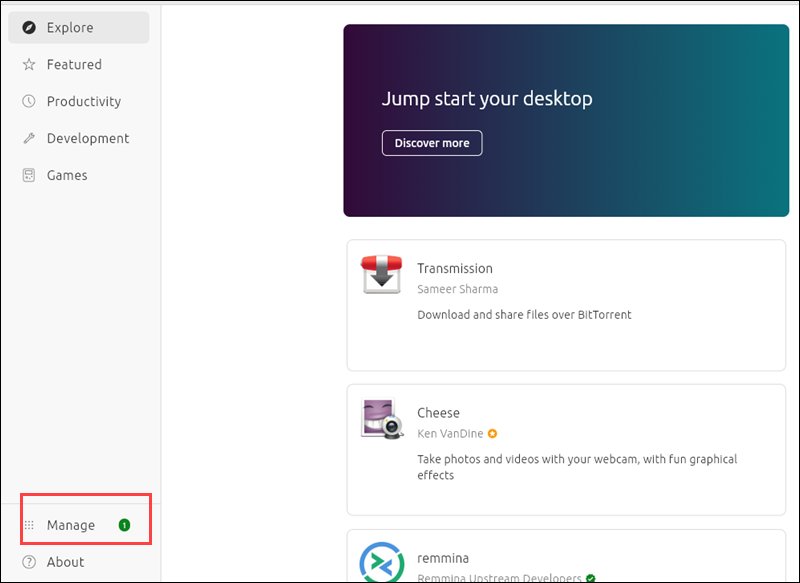
1. Open the App Center application.

2. Click Manage.
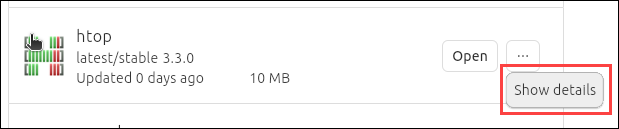
3. Locate the software you want to remove. Click the three dots and then Show details.
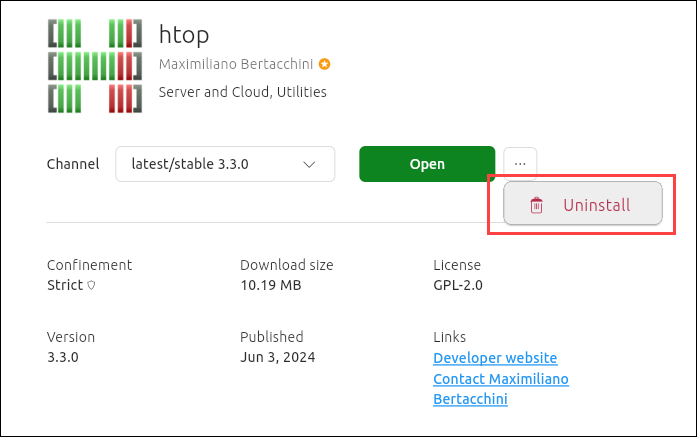
4. Click the three dots again and then Uninstall.
Option 2: GDebi GUI
To uninstall software with Gdebi, do the following:
1. Locate the package file on the system.
2. Right-click the file and select Open With GDebi Package Installer.
3. Click Remove Package to uninstall the software.
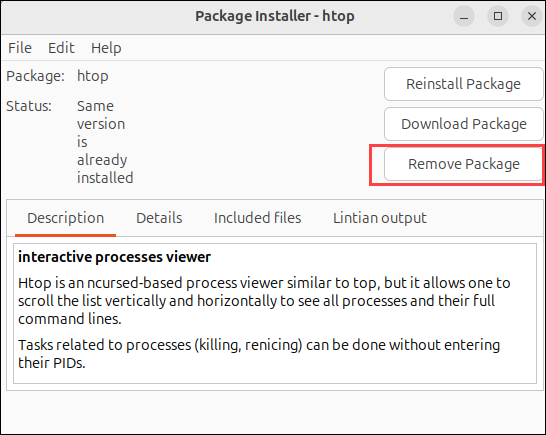
4. Provide the user's password and wait for the uninstall process to complete.
Option 3: dpkg Command
To remove packages installed with dpkg, use the following command in the terminal:
sudo dpkg -r [software name]To remove htop, run:
sudo dpkg -r htop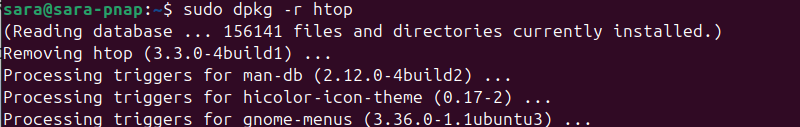
Use the official package name (not the .deb file name) in the command.
Option 4: apt Package Manager
To uninstall a package using the apt command, run the following:
sudo apt remove [software name]Remove htop with:
sudo apt remove htop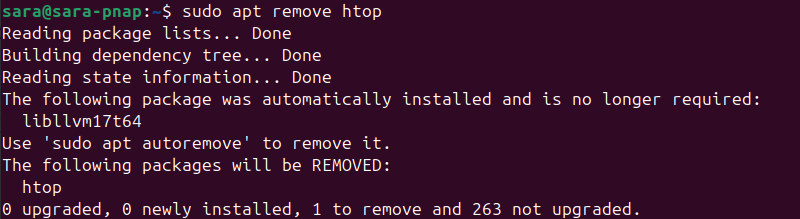
Press Y to confirm the removal.
The method works if the initial installation was through the Ubuntu software center or the apt package manager.
Conclusion
This article explained several ways to install local software packages (.deb) on Ubuntu. It also elaborated on methods for removing .deb packages.
Next, see different ways to list installed packages on Ubuntu.