Pip (Python Installs Packages) is a popular Python package manager application. It retrieves packages from PyPI, a large repository of community-contributed Python packages, and includes the dependencies and libraries needed for each package.
Pip also facilitates Python package installation and removal, making it one of the most popular Python package managers.
In this tutorial, you will learn to install Pip on Debian 12.

Prerequisites
- Debian 12 operating system.
- Access to the terminal.
- An account with root privileges.
Note: Debian does not create a root account by default if the user does not specify a root password during installation. If you don't have a root account, refer to our guide How to Create a Sudo User on Debian.
Installing Pip on Debian 12
You can install Pip on Debian using one of the two methods:
- Via the apt package manager. We recommend installing Pip from the official Debian repository. The benefits of installing Pip using
aptare easier package management, simplified updates, and installation consistency across systems. - Via a Pip installation script. This method lets you install bleeding-edge Pip versions not available in official repositories. However, updating the app later is more complex.
In this tutorial, we will install Pip3, designed for Python 3. Debian 12 ships with Python 3, as Python 2 is deprecated. It is important that the Pip version aligns with your Python version to avoid compatibility issues.
Check if Python 3 is installed on your system by running:
python3 --version
The output states the Python version installed on your system.
If it doesn't, install Python by running:
sudo apt install python3After installing Python, move on to the sections below and choose the Pip installation method you prefer.
Note: See how to install Python on Rocky Linux, CentOS 7, CentOS 8, Ubuntu, or Windows 10.
Method 1: Debian APT Repository
Follow the steps below to install Pip from the official Debian apt repository:
1. Update the package repository to ensure the latest version is installed. Run the command below:
sudo apt update2. Install the Pip package for Python:
sudo apt install python3-pip -yThe -y flag automatically answers Yes to any prompts during the installation. If you want to review what packages will be installed, omit the -y flag.
3. Verify the installation by checking the Pip version:
pip3 --version
Method 2: Pip Installation Script (get-pip.py)
The second method involves downloading the get-pip.py script using the command line and curl command. The script allows you to install the latest Pip version, which may not be available in Debian's repository. Follow the steps below:
1. Run the following command to download the script:
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py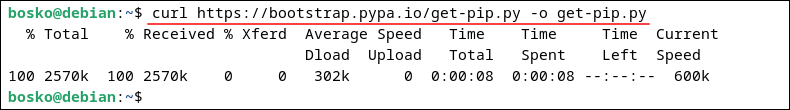
The command downloads the get-pip.py script and saves it in your current working directory.
Note: To check what your current working directory is, use the pwd command.
2. Run the script to initiate the Pip installation. We will run the script through Python:
sudo python3 get-pip.py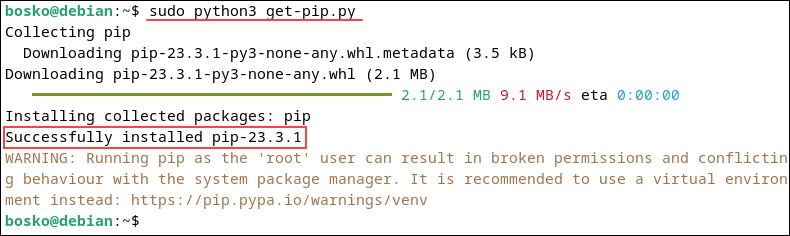
The command installs Pip3 on your Debian system.
3. Validate the installation by checking the program version:
pip3 --versionUsing Pip on Debian 12
Pip allows you to install, remove, update, and manage Python packages. This section shows some basic operations for using Pip on Debian 12.
Install Python Packages
The syntax for installing Python packages is:
pip install [package_name]For example, to install Numpy, run the command below:
pip install numpy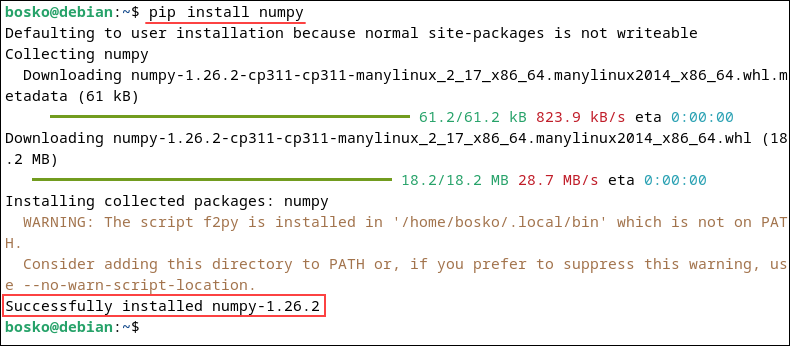
The command installs the package and all its dependencies.
List Installed Packages
List all the installed Python packages by running the command below:
pip list
The command outputs a list of the installed Python packages.
Download Python Packages
Pip allows users to download Python packages, which can later be installed on another machine or without an Internet connection.
The syntax for downloading a Python package is:
pip download [package_name]For example, to download the tensorflow package, an open-source library for machine learning, run:
pip download tensorflow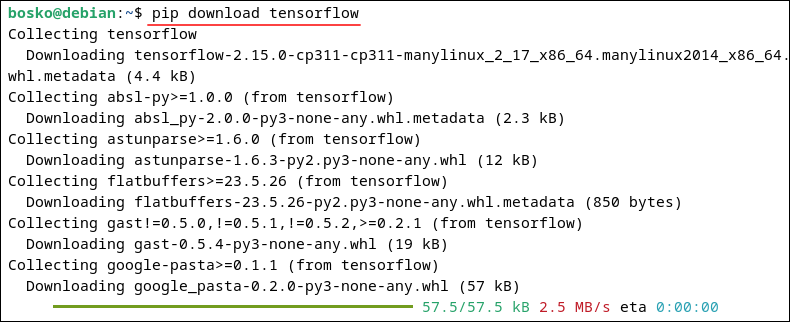
The command downloads the package and all its dependencies, allowing you to install it later.
Show Python Package
To obtain information about a specific Python package, utilize the show option. The syntax is:
pip show [package_name]For example, to display information about the numpy package, run:
pip show numpy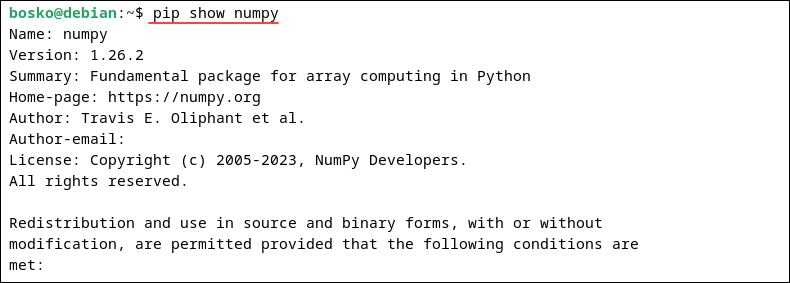
The output shows the package version, description, author information, and other details about the package contained in the repository.
Uninstall Python Package
To uninstall a Python package from your system, use the syntax below:
pip uninstall [package_name]For example, to uninstall numpy, run:
pip uninstall numpy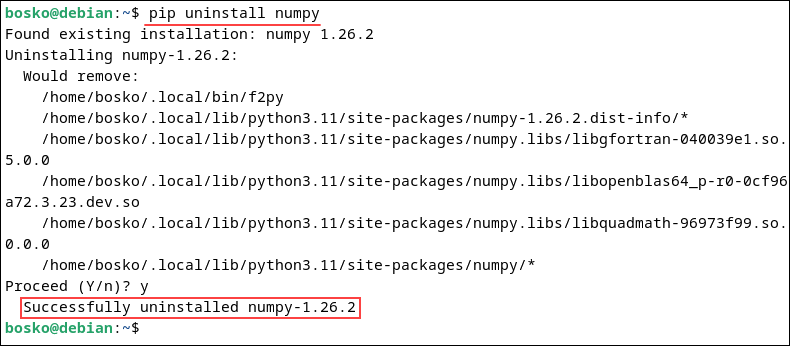
When prompted, press y to confirm the uninstall, then press Enter to proceed. The command removes the package and its dependencies from your system.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to install and use the Pip package manager on Debian 12 with practical examples.
Next, see how to install Pip on Debian 9, 10, and 11 if you use an older version of Debian.