Managing containerized microservice applications using Kubernetes is a popular method for deployment automation. Kubernetes helps manage and coordinate thousands of containers at production scale. Furthermore, employing Kubernetes in production allows for easy horizontal scaling.
However, a significant obstacle to Kubernetes adoption in production is its steep learning curve. If a small DevOps-oriented company does not have engineers who have already worked with Kubernetes, the overall cost of staff training may prove to be an obstacle.
This article will compare Portainer and Rancher, two platforms designed to simplify the Kubernetes experience without sacrificing essential functionalities.
Portainer vs. Rancher: Definitions
Portainer and Rancher are both self-hosted control planes for Kubernetes management, providing a GUI for easy access to Kubernetes features. The sections below provide more information about both solutions.
What is Portainer?
Portainer is a container management tool designed to facilitate working with containerized applications. With Portainer, users manage multiple Docker container environments from a single web UI.
While Portainer was primarily designed for Docker, its latest versions support orchestration platforms such as Docker Swarm, Azure ACI, and Kubernetes. Portainer's server-agent architecture allows for its simple integration into a Kubernetes cluster.
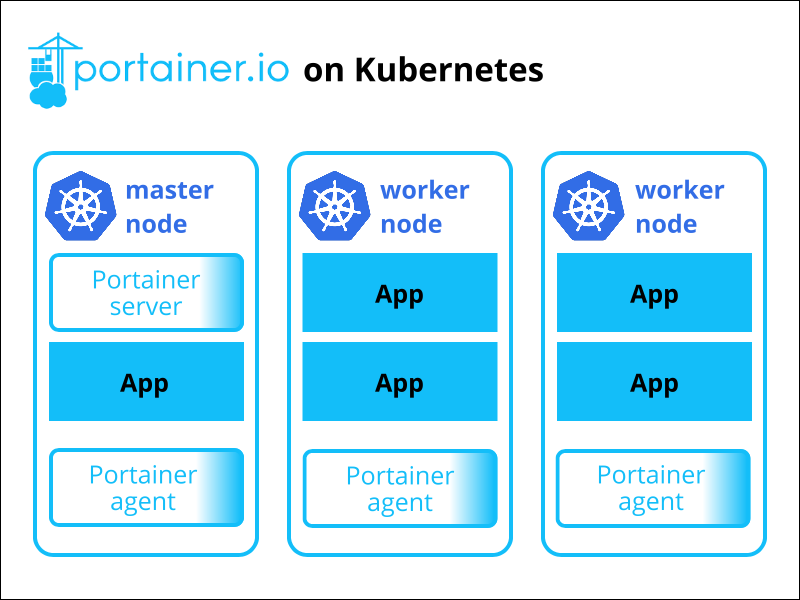
The diagram above illustrates how Portainer integrates with Kubernetes. The server instance resides on the Kubernetes master node. Furthermore, each cluster node has an agent instance that enables Portainer to control it.
Portainer comes in two editions:
- Portainer Community Edition is free and open-source.
- Portainer Business Edition is a license-based paid solution for enterprise users. It offers up to 5 free nodes.
What is Rancher?
Rancher is an open-source platform for container management, exclusively focused on supporting Kubernetes. The platform allows users access to Kubernetes’ native tools while providing additional infrastructure services such as load balancing, networking, storage, and security.
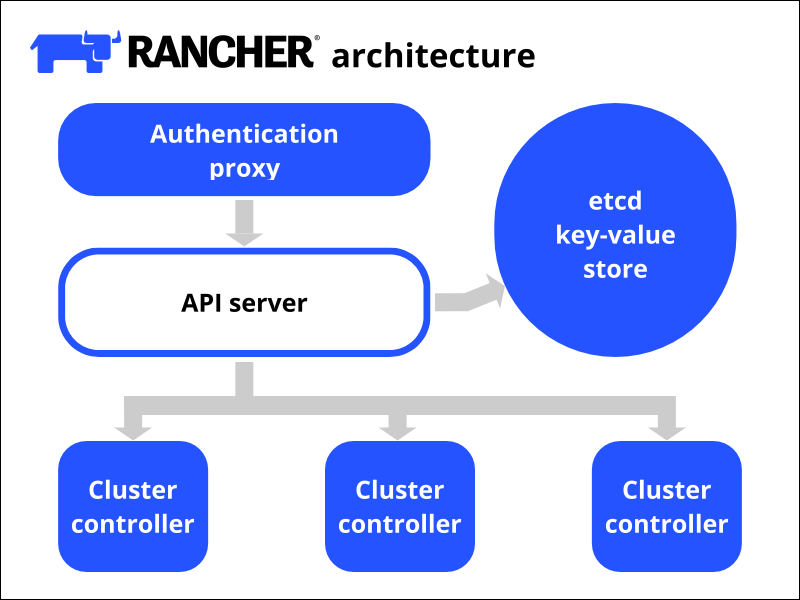
Rancher consists of the authentication proxy that receives input from a GUI, CLI, or API and forwards it to the API server. The server communicates with the etcd key-value store and issues instructions to cluster controllers. Lastly, the controllers connect to downstream clusters. The diagram below shows a simple overview of Rancher's architecture.
Portainer vs. Rancher: Features
Features of both Portainer and Rancher aim to simplify the experience of working with native tools for container management and orchestration. However, the platforms differ in several aspects.
Below is a table that compares the most important feature differences.
| Feature | Portainer | Rancher |
|---|---|---|
| Dashboard/GUI | Cross-platform, web UI. | Cross-platform, web UI and desktop application. |
| Cluster Building | Portainer’s Business Edition supports cluster building on popular cloud provider KaaS. | Rancher Kubernetes Engine (RKE) and Rancher UI provide cluster creation and node provisioning tools. |
| Cluster Management | Requires a working k8s cluster. Allows defining cluster policies, managing nodes, taints, etc. | Facilitates the use of the native containerization platform management tools. |
| Centralized Identity Management | Supports the OAuth authentication standard. | Supports the SAML authentication standard. |
| Templates | JSON and Compose YAML for Docker and YAML for Kubernetes. | YAML and JSON for Kubernetes. |
| Ease of Use | Aimed at beginners in deployment automation. | Requires intermediate skills in k8s cluster management. |
| Business Model | Features the free Community Edition (CE) and the paid Business Edition (BE) that comes with up to 5 free nodes. | Free and open source. |
| Support | The CE is community-supported, while the BE features professional support from the company. | Online resources. Paying customers receive enterprise-level support. |
The sections below go into more detail on the key features of Portainer and Rancher.
Dashboard/GUI
Portainer dashboard is designed to offer a simplified version of the native Kubernetes dashboard. Since it does not require previous knowledge of Kubernetes CLI commands, Portainer's GUI is a good solution for DevOps beginners and those who deploy 3rd-party container-based applications.
Rancher features two dashboards for Kubernetes management. The Cluster Manager lets users create, manage, configure, and monitor Kubernetes clusters.
Rancher Cluster Dashboard facilitates app deployment and management in the cluster. It features cluster resource consumption stats and tools for deploying and orchestrating containers.
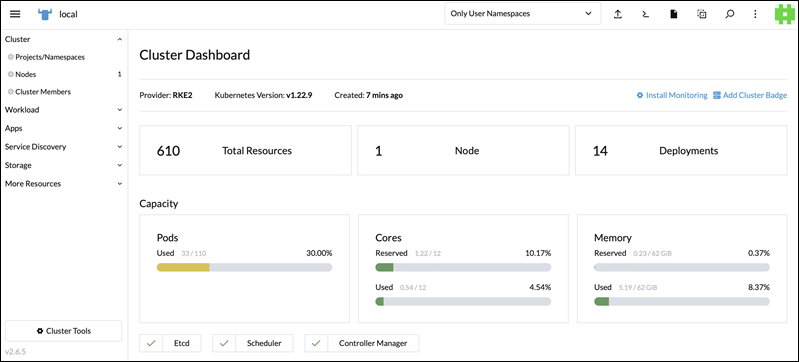
Note: As of Rancher 2.6, the solution provides a single dashboard for all Kubernetes cluster management tasks.
Cluster Building
Portainer Business Edition provides cluster building functionalities on popular cloud provider KaaS offerings, such as Amazon EKS, Azure AKS, and Google GKE. However, it is primarily a management controller that does not feature its own Kubernetes distribution, so it does not support self-managed Kubernetes clusters out-of-the-box.
Rancher comes bundled with RKE (Rancher Kubernetes Engine), a CNCF certified k8s distribution running within Docker containers. Its own distribution enables Rancher to offer the full range of cluster building and node management options. Users can deploy Rancher-controlled clusters on-premises or by employing an IaaS solution. Clusters and nodes can also be deployed at host providers (phoenixNAP Rancher deployment solution, AKS, EKS, GKE, etc.) using cluster and node drivers.
Note: phoenixNAP BMC Rancher solution lets you seamlessly deploy Rancher-controlled Kubernetes clusters on powerful and flexible BMC instances.
Cluster Management
Through the secure Portainer agent, Portainer allows its users to define cluster policies and manage multiple clusters (regardless of whether they come from a single provider or multiple providers). Advanced node and taint management are also supported.
Rancher allows users access to native cluster management tools - the CLI-based kubectl tool and the kubeconfig file. The platform provides many additional management features, such as:
- Cluster members management
- Upgrading clusters
- Node, persistent volume, and storage class management
- Project, namespace, and workload management
- App catalogs
Centralized Identity Management
The default settings of a Kubernetes cluster do not include centralized identity and access management. The only account available on a fresh k8s installation is the service account for the cluster administrator. Adding more accounts requires advanced Kubernetes administration skills.
Portainer facilitates the process of user account creation and RBAC setup. Users select the roles they need and apply them across multiple clusters. Portainer also integrates with external authentication and logging systems.
Rancher features centralized user authentication, allowing users to define a single set of credentials for authenticating across clusters hosted with multiple providers. Like Portainer, setting up RBAC in Rancher is a simple process. Global permissions and cluster and project roles determine the permissions given to users. Rancher implements global permissions and roles on top of Kubernetes RBAC, which means Kubernetes itself enforces those permissions.
Ease of Use
Portainer aims to appeal to non-experts by featuring a simple interface that is still capable of performing advanced functions. Originally designed to simplify the use of Docker containers, Portainer applies the same philosophy to Kubernetes. Expert users can utilize Portainer's capabilities to pre-configure cluster settings and prepare the cluster for less experienced users.
Rancher also simplifies many aspects of Kubernetes cluster management. However, beginners can expect a steep learning curve for mastering all of its functions. For example, many Rancher features still require knowledge of the Kubernetes CLI.
Business Model
Portainer comes in two flavors:
- Portainer Community Edition (CE) is a free and open-source version of the platform.
- Portainer Business Edition (BE) is aimed at larger enterprises. It is closed source and requires licensing. However, it offers additional automation, security, and audit features. Customers can obtain the first five nodes on Portainer Business Edition for free.
Rancher is entirely free and open source.
Support
Portainer CE is community-supported. On the Portainer's website, users can access a library of resources and tutorials or join the Discord and Slack channels for additional support. By joining the community, users receive monthly updates from the Portainer team and get access to AMA sessions and special events. Portainer BE comes with full support from the company.
Rancher's website contains a comprehensive list of help resources - quick start guides, tutorials, FAQs, etc. Rancher community features forums where users can find answers to specific problems and a Slack channel for more direct interaction. Rancher also offers a paid enterprise-level support plan.
Portainer vs. Rancher: How to Choose?
Choose Portainer if:
- You plan to deploy containers with limited resources. With its lightweight design, Portainer runs well on systems with limited resources.
- You don't have time or the expertise to deal with complex Kubernetes deployments. Portainer provides an easy to use Kubernetes GUI that eliminates the need to manually work with the Kubernetes API. Admins don't have to write YAML manifests, use the Kubernetes CLI and API, or learn Helm and kubectl commands thanks to Portainer.
- You are a beginner user. Portainer's interface is uncluttered and intuitive, and the available support options are designed with beginners in mind.
- You want to focus on apps and containers. Unlike Rancher, Portainer does not deal with infrastructure. Instead, it focuses on providing the optimal interface for containerized app deployment and management. Portainer provides deep visibility into the state of each container.
- You want to run Docker Swarm. Portainer provides native support for Docker Swarm, while Rancher does not.
Chose Rancher if:
- You are deploying in a medium/big environment. Rancher excels in complex self-managed Kubernetes deployments - multiple teams simultaneously working on various projects will benefit from Rancher's approach to Kubernetes namespaces.
- You manage multiple Kubernetes clusters in different environments. The operational and security challenges related to multiple cluster management across environments are largely mitigated by Rancher's centralized identity management and well-designed UI.
- You are developing a containerized app. Rancher offers native integrations with popular tools such as Jenkins, Istio, Grafana, Prometheus, Fleet, and other. It provides developers a CI/CD environment for deploying containerized apps.
Note: You might also want to check out our comparison article Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm.
Conclusion
The article compared two popular container management solutions - Rancher and Portainer. It presented the essential features of both tools and provided advice on choosing the right tool for specific usage cases.
To learn more about the benefits of container orchestration, read What is Container Orchestration.