PHP is a programming language often used to automate server tasks. It is part of the LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) stack, a software bundle used for running internet servers and services. PHP handles dynamic content, database requests, and processing and displaying data.
This step-by-step guide shows how to install PHP on CentOS or Rocky Linux.

Prerequisites
- A user account with root privileges.
- Access to a terminal window.
- A third-party software repository, detailed below.
How to Install PHP with Apache on CentOS and Rocky Linux
CentOS and Rocky Linux use the same package manager, dnf (or its predecessor, yum, in older CentOS versions). Since Rocky Linux is a community-supported rebuild of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), just like CentOS was, their package management and software installation steps are identical.
Note: Learn about the CentOS EOL and see how it differs from Rocky Linux.
Follow the steps below to install PHP on your preferred distribution.
Step 1: Choose PHP Version to Install
The latest stable PHP version at the time this article was written was PHP 8.3. However, some software repositories default to older versions of the software.
While older releases provide high stability and reliability, newer releases may include more features but are often more experimental and could cause system instability. If you cannot decide which version is right for you, version 8.3 is a great place to start.
Step 2: Enable Additional Software Repositories
By default, the yum/dnf package managers do not include access to the repositories that store the PHP packages. Therefore, you need to enable access to these software packages:
1. Ensure your system is updated:
sudo dnf update -y2. Enable the epel-release (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository with the command below:
sudo dnf install epel-release -y3. Finally, add the Remi software repository that provides the latest PHP versions:
sudo dnf install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-9.rpmStep 3: Install PHP
After completing the steps above, you can install PHP:
1. Run the following command to reset the module, which removes any custom PHP module stream selection:
sudo dnf module reset php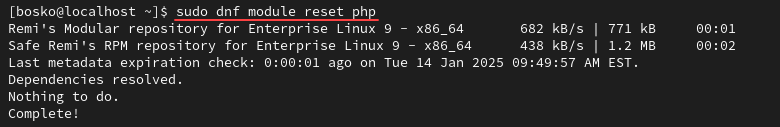
2. Enable the PHP version you want to install with:
sudo dnf module install php:remi-8.3 -y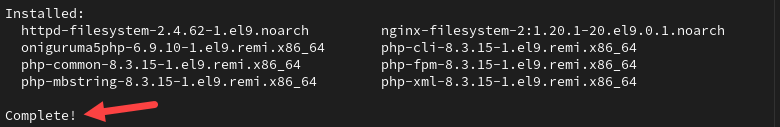
The command installs many modules and add-ons that help PHP integrate with your local server configuration.
Step 4: PHP Modules
The installation in the previous step included more than just the base PHP package. Many of these are modules that provide basic functionality to PHP. Installing this set helps ensure that the PHP installation meets your usage expectations.
Like many other Linux applications, you can enhance your system's PHP functionality using modules.
To search for available modules and generate a list of modules, run the following command:
sudo dnf search php | more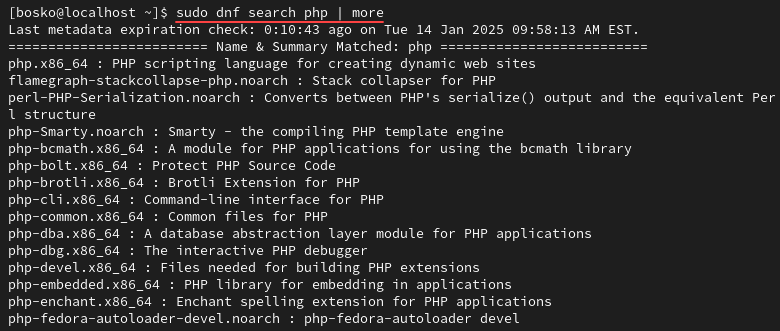
To install a module from the list, use the syntax below:
sudo dnf install [module_name]Step 5: Verify PHP Version
Finally, verify your installation was successful. Check your PHP version with the command:
php -v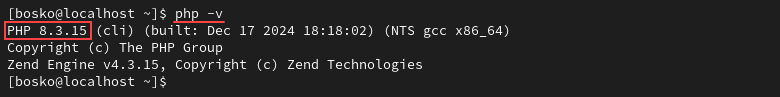
Conclusion
Installing PHP on CentOS or Rocky Linux is fairly straightforward. PHP helps developers create dynamic and interactive web applications, powers popular platforms like WordPress, and seamlessly integrates with databases like MySQL.
Next, see how to install phpMyAdmin on CentOS or Rocky Linux.