Colocations offer businesses a secure, high-performance data center environment with reliable power, cooling, and network connectivity. They reduce the costs of maintaining an on-premises facility.
Hybrid colocations further enhance that flexibility by integrating cloud services into the offer, allowing businesses to scale efficiently, improve disaster recovery, and optimize workloads between physical infrastructure and the cloud.
In this article, you will learn how hybrid colocations work, their benefits, and use cases.
What Is Hybrid Colocation?
Hybrid colocation is a service that combines traditional colocation with cloud connectivity. Businesses store their physical servers in a third-party data center where they can integrate cloud services for scalability and flexibility. This setup provides control over hardware and utilizes cloud resources for storage, computing, and networking.
Unlike standard colocation, hybrid colocation connects directly to public or private cloud providers through high-speed, low-latency links. It enables workload migration, disaster recovery, and on-demand resource scaling.
Hybrid colocation ensures high performance, security, and cost efficiency by balancing on-premises infrastructure with cloud-based solutions.
Note: Learn the difference between colocation and cloud and make the best choice for your business.
How Does Hybrid Colocation Work?
In a hybrid colocation, physical servers are kept in a third-party data center with direct connections to cloud providers. Data centers offer private, high-speed network links to platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
These connections enable businesses to move workloads between on-premises servers and the cloud with minimal latency. Organizations can store sensitive data on dedicated servers and use cloud resources for scalability.
Providers enhance hybrid colocation with software-defined networking (SDN) and cloud on-ramps to major cloud providers. SDN enables dynamic traffic routing between the physical infrastructure and cloud environments.
Hybrid Colocation Benefits
Hybrid colocation helps businesses reduce operational costs, improve redundancy, and adapt to changing IT needs. The model is ideal for organizations that need a dedicated infrastructure and cloud agility.
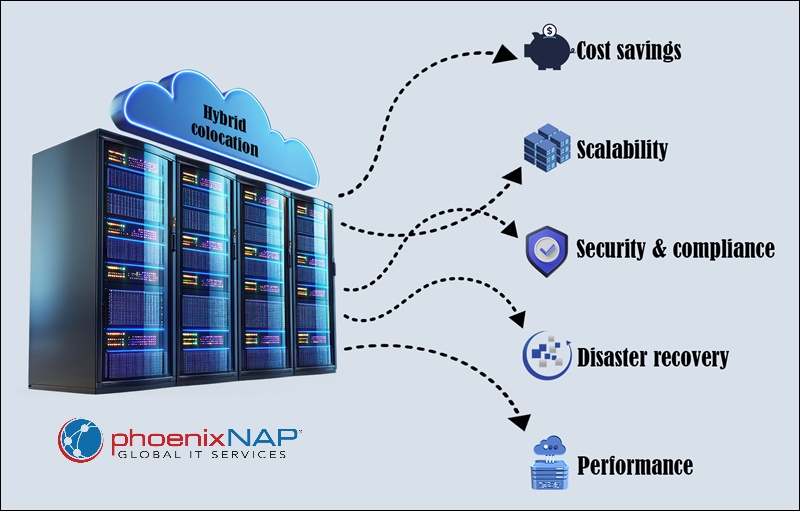
The key benefits of hybrid colocation are:
- Cost savings. There is no need to build and maintain a data center. Businesses get enterprise-level power, cooling, and security without a large investment.
- Scalability. Easily shift workloads between physical and cloud environments, using cloud resources only when needed.
- Security and compliance. Colocation facilities provide advanced physical security, including biometric access, surveillance, and on-site staff. Additionally, cybersecurity measures such as DDoS protection and zero-trust security enhance cloud-integrated environments.
- Disaster recovery. Ensures business continuity, even if cloud resources fail.
- Performance. Low-latency cloud connections improve application speed and responsiveness.
Challenges of Hybrid Colocation
Hybrid colocation comes with several challenges, primarily related to integration, security, and cost management. Combining on-premises infrastructure, colocation facilities, and cloud environments requires careful planning to ensure seamless connectivity, compliance, and performance optimization.
Below are the key challenges in hybrid colocation and their implications:
- Integration. It is a complex task to ensure seamless communication between different environments since it requires robust networking solutions and compatibility between systems.
- Network latency. Data transfer between colocation centers, on-premises infrastructure, and the cloud can introduce latency issues, which can impact performance.
- Data security and compliance. Data protection across multiple environments requires strong encryption, access controls, and adherence to various regulatory requirements (such as SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, SOX, and GLBA certifications).
- Cost management. Networking, security, and data transfer fees can build up expenses, so budget planning is essential to overcome this challenge.
- Operational complexity. Skilled personnel and advanced tools are required to manage hybrid infrastructure, as well as monitor and optimize performance.
- Data sovereignty. Organizations must navigate jurisdictional regulations regarding where data is stored and how it is accessed.
- Monitoring & governance. Effective supervision is necessary to prevent inefficiencies, downtime, and security vulnerabilities.
To overcome these challenges, businesses must carefully plan, invest in automation and monitoring tools, collaborate with experienced service providers, and implement best practices for security, performance optimization, and cost control.
Hybrid Colocation Use Cases
Hybrid colocation is ideal for organizations that require high performance, enhanced security, and cost-effective scalability without sacrificing control over critical workloads.
Below are the key use cases where hybrid colocation offers significant advantages:
- Disaster recovery and business continuity. Hybrid colocation supports disaster recovery by allowing businesses to maintain failover sites in geographically separated data centers, ensuring redundancy and minimal downtime in case of failures.
- High-performance computing (HPC). Hybrid colocation supports industries like finance, healthcare, and AI-driven applications that require low-latency, high-processing power infrastructure.
- Regulatory compliance. Organizations can store sensitive data in a secure, controlled colocation environment and leverage cloud scalability for less regulated workloads.
- Edge computing and latency reduction. Businesses can deploy infrastructure closer to end users for improved speed and responsiveness. This makes hybrid colocation suitable for gaming, IoT, and real-time analytics.
- Hybrid cloud strategy. Hybrid colocation connects private infrastructure with the public cloud, which optimizes workloads for cost, performance, and security.
- Cost optimization. Balances the predictable costs of colocation with the flexibility of cloud services. It prevents unnecessary cloud expenses and maintains control over critical systems.
- Data sovereignty and localization. Hybrid colocation keeps data in specific geographic locations to comply with jurisdictional laws but also leverages hybrid architecture for scalability.
Considerations for Building Hybrid Colocation Solution
Building a hybrid colocation solution requires careful planning to ensure seamless integration, optimal performance, and cost efficiency. It is crucial to evaluate key factors to create a well-balanced hybrid environment.
Below are the critical considerations when building a hybrid colocation:
- Infrastructure compatibility. Ensure that colocation hardware and networking equipment align with existing on-premises and cloud environments for smooth integration.
- Network connectivity. Establish low-latency, high-bandwidth connections between colocation, on-premises, and cloud environments using direct interconnects or SD-WAN solutions.
- Security & compliance. Implement robust security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and access controls. Adhere to industry regulations and data protection laws.
- Scalability & flexibility. Choose a colocation provider that offers scalable infrastructure and flexible contracts to accommodate future growth and evolving workloads.
- Performance optimization. Monitor latency, bandwidth, and resource utilization to ensure high availability and efficient workload distribution across hybrid environments.
- Cost management. Plan for expenses related to colocation, network interconnects, cloud integration, and ongoing operational costs to avoid budget overruns.
- Monitoring and management tools. Deploy centralized monitoring and automation tools to gain real-time visibility into infrastructure health, security, and performance.
- Provider reliability and support. Assess colocation providers based on uptime guarantees, service-level agreements (SLAs), and available technical support to minimize downtime risks.
Address these considerations to build a robust and efficient hybrid colocation strategy that balances performance, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Note: Check out phoenixNAP's colocation solutions that provide secure, high-performance infrastructure with direct cloud on-ramps, compliance-driven security, and scalable options.
Conclusion
This article explained how hybrid colocation works, its benefits, challenges, and use cases. Hybrid colocation offers the best of both worlds: control over infrastructure with the flexibility of the cloud.
Next, learn about data center tiers or find out more about colocation data center types and benefits.