Ubuntu and other Linux-based systems use client applications to manage software directly. Some software packages come preinstalled by default, while system administrators install other packages when necessary.
Depending on which package manager installed the software, there are various ways to list installed packages on Ubuntu.
This tutorial will explain how to list installed packages on an Ubuntu system.

Prerequisites
- Ubuntu system (this tutorial uses Ubuntu 22.04 and Ubuntu 24.04).
- Access to the terminal.
- The apt, dpkg, or snap package manager.
List Ubuntu Packages Using apt
By default, newer Ubuntu versions come with the apt package manager. The package manager helps conduct operations related to software packages.
List All Installed and Available Packages
Use the following command to list all installed and available packages on Ubuntu:
apt list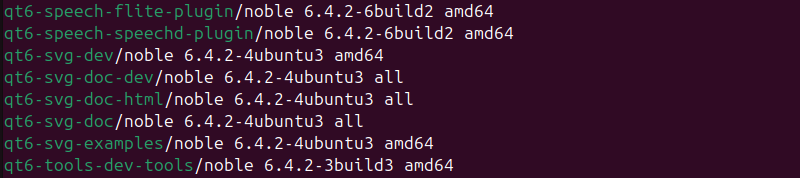
The output shows a long list of packages with the version information and the package architecture. Shorten the list by piping the less command:
apt list | lessNavigate through the list with the up or down arrow keys or space to skip to the next page. Press q to exit the viewer.
List Only Installed Packages
To list only installed packages, run:
apt list --installed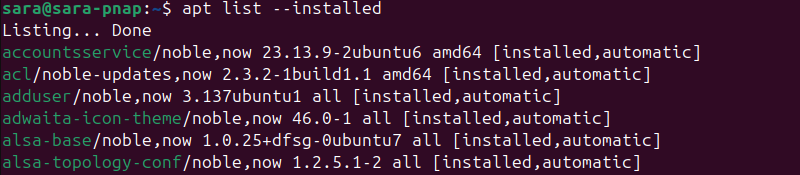
The --installed tag ensures that only installed packages appear on the list. Each installed package has one of the following tags:
[installed]. Indicates the package installed manually from the repository list.[installed, automatic]. Means the package installed automatically as a dependency for another installation.[installed, local]. Indicates the package is not from the official repository list.
List Specific Packages
There are three different ways to list a specific package:
1. Add the package name to the apt list command to fetch a specific package from the list:
apt list [package name] --installedFor example, to list the bash package, run:
apt list bash --installed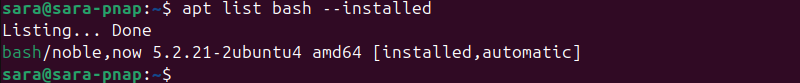
2. Combine apt list with the grep command to match a package by name:
apt list --installed | grep -i [package name]For instance, to match the bash package by name, run:
apt list --installed | grep -i bash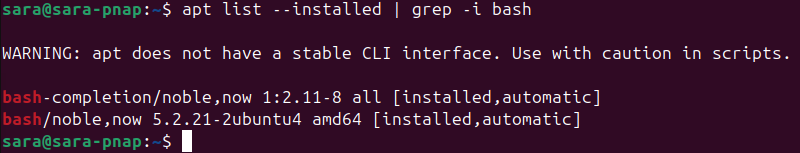
The -i tag ignores letter casing, providing a broader search.
3. Use the apt show command:
apt show [package name]For example, run the following to show bash info:
apt show bash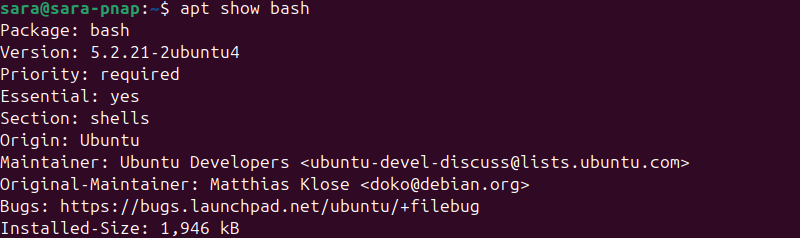
The command shows the package details, including installation information.
List Upgradable Packages
To list packages with available upgrades, run the following command:
apt list --upgradable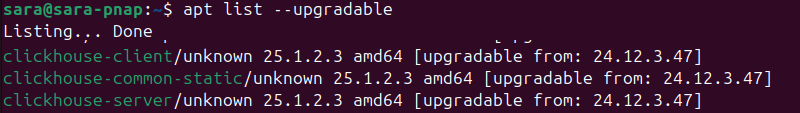
The --upgradable tag filters packages and lists only those ready for an upgrade.
Note: If you've upgraded recently, the list is empty.
Count the Number of Installed Packages
Use the apt list command with the Linux wc command to count the number of lines:
apt -qq list --installed | wc -l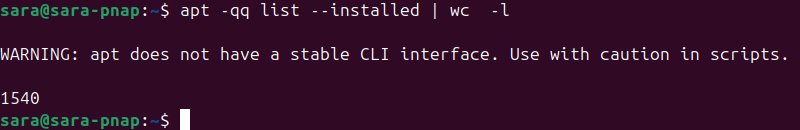
The -qq tag quiets the output. Use the marker to ensure no additional lines print to the console and enter the count number.
List Ubuntu Packages Using dpkg
The dpkg package manager is included in earlier Ubuntu versions when apt is unavailable.
To list installed Ubuntu packages using the dpkg command, run:
dpkg --get-selections | grep -w "install"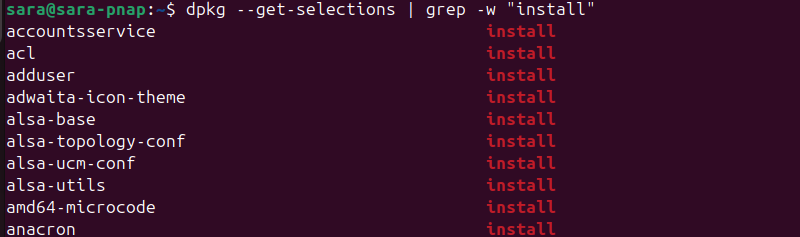
Alternatively, use the dpkg-query tool:
dpkg-query -l | grep ii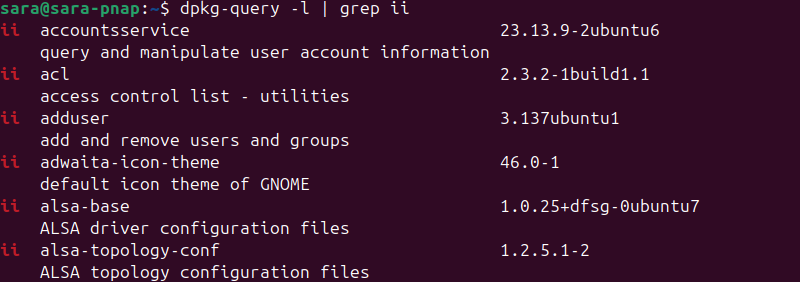
In both cases, the output shows a long list of installed packages.
Create a List of all Installed Packages
To save the installed package names into a text file, use the following command:
dpkg --get-selections | grep -w "install" | cut -f1 > packages_list.txtNext, use the head command to see the first ten entries in the file:
head packages_list.txt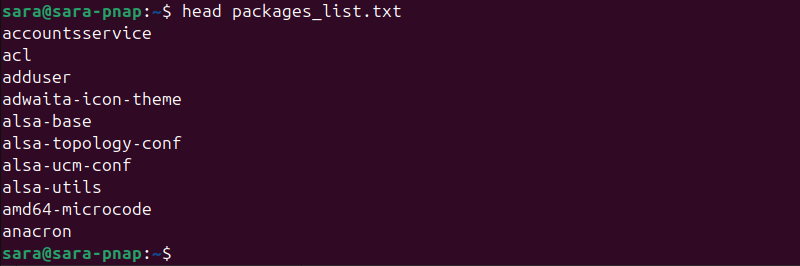
Count the Number of Installed Packages
Use the wc command to count the lines from the list of installed packages:
dpkg --get-selections | grep -w "install" | wc -l
The -l tag counts the number of lines from the dpkg --get-selections output.
List Installed Packages Sorted by Date and Time
The dpkg logs store the date and time for package installations. To fetch all the information from log files, use the following command:
zgrep "installed" /var/log/dpkg.log*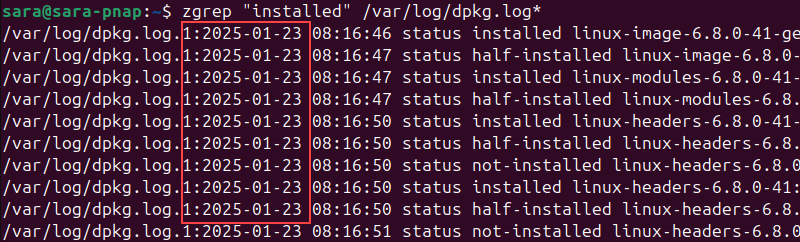
The output shows the exact timestamp for installed packages. The logs are archived and deleted after a specific time, so the list is not comprehensive.
List Installed Snap Packages
Snap is an alternative package manager system. The previous commands do not show packages installed through Snap.
To list installed Snap packages, run:
snap list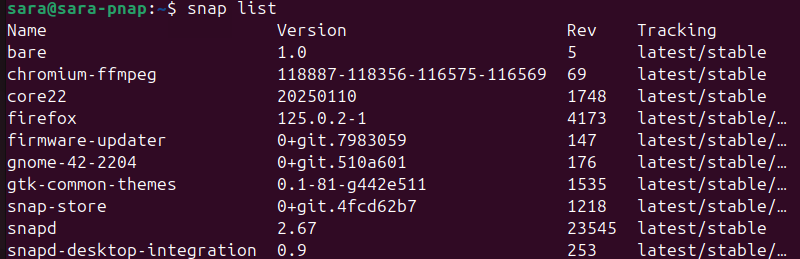
Note: Learn about the differences between the Snap packaging system and the apt package manager in Snap vs. Apt.
Conclusion
This guide explained how to list installed packages on Ubuntu and other Debian-based systems using various commands. Keeping track of installed packages helps with system maintenance, troubleshooting, and software management.
If there is a problem with the installed packages, read our article on fixing broken packages in Ubuntu.