Remote Desktop allows you to control and use another computer remotely via a graphical interface.
Users who prefer a point-and-click interface or are unfamiliar with command-line operations can enable this feature on an Ubuntu host machine to allow remote access and control from a client machine.
Learn how to enable Remote Desktop on Ubuntu and connect from a remote Linux device.

Prerequisites
- A host system running Ubuntu 22.04.
- A client system running Linux.
- A user account with sudo privileges.
- Access to a terminal window/command line.
How to Enable Remote Desktop on Ubuntu
Before accessing a remote Ubuntu system, you must enable Desktop Sharing on the host machine.
To enable screen sharing in Ubuntu:
1. Open the System Menu in the top right corner of the Ubuntu desktop GUI.
2. Click Settings.
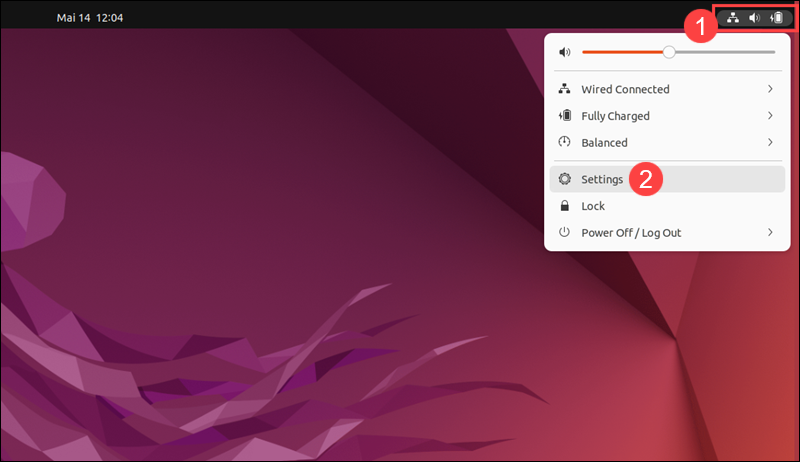
3. Select Sharing.
4. Activate Sharing by toggling the switch to the On position.
5. Click Remote Desktop.
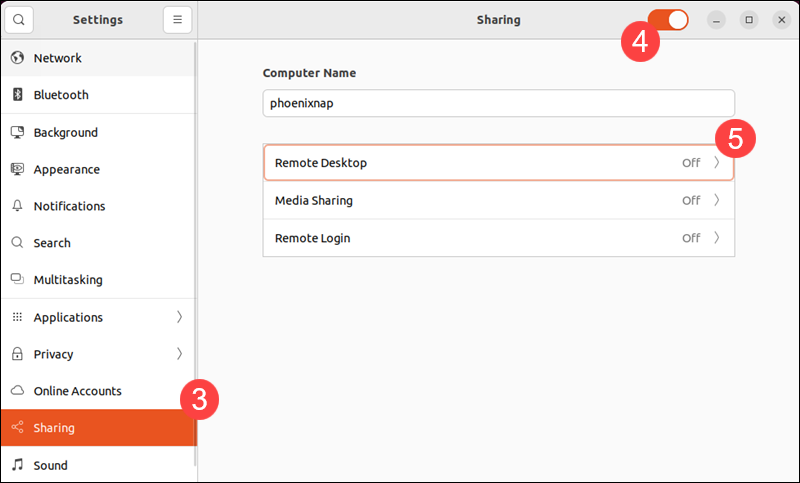
6. Enable Remote Desktop and Remote Control.
Note: The Enable Legacy VNC Protocol option allows Ubuntu to communicate with clients using an older version of the VNC protocol. Modern VNC clients like TigerVNC, RealVNC, and Remmina use more secure, updated protocol versions.
7. Enter a User Name and Password to authenticate connections to the host system.
8. Close the Remote Desktop settings window.
9. (Optional) Turn on Media Sharing in the Sharing menu if you plan to share images, music, or pictures.
Client systems with the correct credentials can now establish a connection and remotely control the Ubuntu host machine.
Note: Implement Best Practices For Securing Remote Access to enhance security and prevent common mistakes.
How to Remote Control Ubuntu via VNC
Linux offers numerous desktop clients that streamline VNC and RDP connections to remote systems. The Remmina client supports several protocols, including VNC, and is pre-installed on Ubuntu systems.
It can also be installed on other Linux distributions to facilitate a connection with a remote Ubuntu host. To install Remmina, open a terminal window and use the command specific to your distribution. The following commands install Remmina along with its VNC and RDP plugins.
| Distribution | Installation Command |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | sudo apt install remmina remmina-plugin-rdp remmina-plugin-vnc |
| Fedora | sudo dnf install remmina remmina-plugins-vnc remmina-plugins-rdp |
| Debian | sudo apt install remmina remmina-plugin-rdp remmina-plugin-vnc |
| Arch Linux | sudo pacman -S remmina freerdp remmina-plugin-vnc |
| openSUSE | sudo zypper install remmina remmina-plugin-rdp remmina-plugin-vnc |
| Rocky Linux | sudo dnf install remmina remmina-plugins-vnc remmina-plugins-rdp |
To connect from a Linux client system to a remote Ubuntu host using Remmina, follow the steps in the sections below.
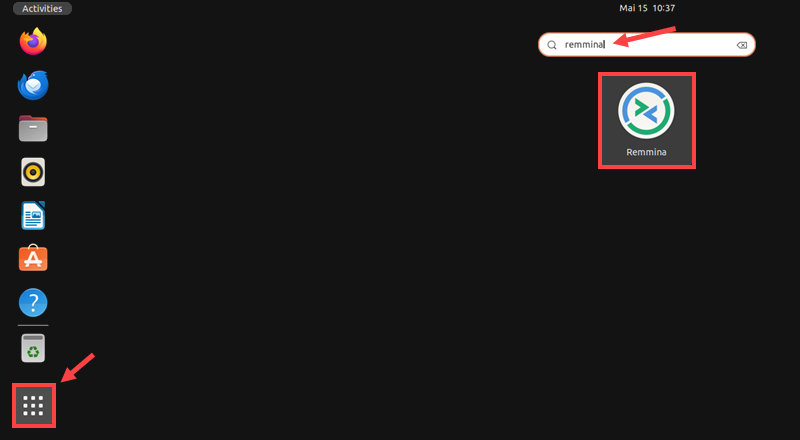
Step 1: Launch Remmina
Open the Show Applications menu at the bottom of your desktop environment screen. Use the search bar at the top of the menu to find and launch the Remmina app.
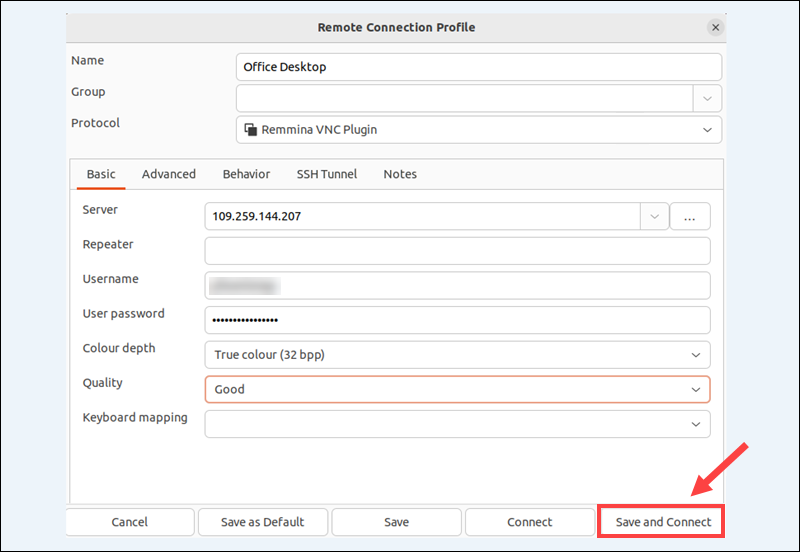
Step 2: Create and Configure New Connection Profile
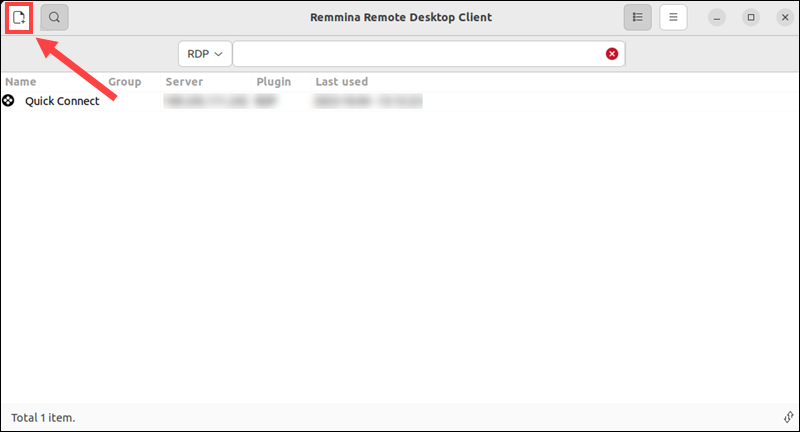
In Remmina, click Add a new connection profile to initiate a new connection.
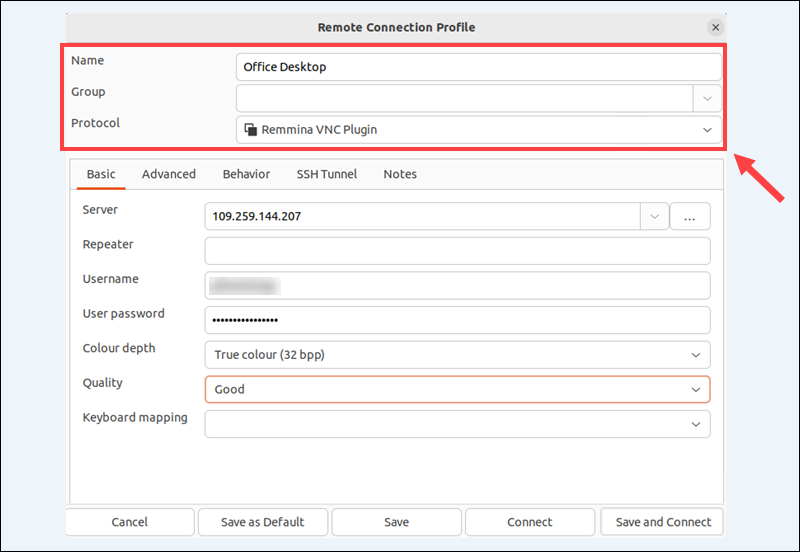
Provide the following connection details to set up the profile:
- Name. Enter a descriptive name for the connection, such as Email Server or Office Desktop.
- Group. An optional field for organizing multiple connections.
- Protocol. Select Remmina VNC Plugin from the drop-down menu. In some distributions, this protocol option may be listed as VNC - Virtual Network Computing.
Note: If you have installed xrdp on Ubuntu and configured an RDP server, you can select the RDP-Remote Desktop Protocol option in Remmina.
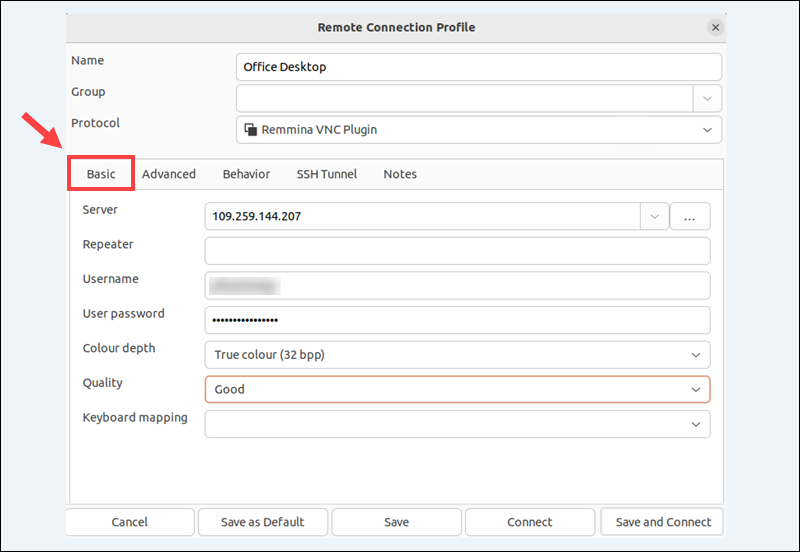
Open the Basic tab and enter the following information:
- Server. Enter the IP Address of the Ubuntu host system or the server name.
- Repeater. Leave this field blank.
- User Name. Enter the username set in Desktop Sharing on the host system.
- Password. Enter the password you set in Desktop Sharing on the host system.
- Colour depth. This is a trade-off between speed and quality. Choose the best fit for your network.
- Quality. Start with the Good and adjust later if necessary.
- Keyboard mapping. You can leave this field blank.
Step 3: Connect to Remote Ubuntu Host
Click Save and Connect to save the profile as a favorite and establish the connection to the remote Ubuntu host.
Note: If the connection is being blocked, check open ports on both the client and the host systems. Adjust firewall settings to enable port 5900 for VNC connections and port 3389 for the RDP protocol.
A notice appears on the host system, indicating that another user is controlling the desktop and listing the IP address of the connecting system. New connections must ask for permission, and the user on the host machine must manually grant access.
Note: To enhance server security, remember to disable Desktop Sharing on the host device when it is not being used.
Conclusion
You have set up your Ubuntu system for remote desktop connections and connected from a remote Linux system.
If you need to establish cross-platform connections, check out our guides on how to remotely connect from Mac to Ubuntu and RDP from Windows to Ubuntu.