MongoDB is a document database solution, a subset of NoSQL, known for availability and scalability. Its data is structured and stored in JSON documents known as collections (schema-less equivalents to tables in relational databases).
Depending on the local setup, there are different ways to create a database in MongoDB.
This guide shows how to create a new MongoDB database using different methods.
Prerequisites
- Access to terminal window/command line.
- Elevated user privileges (sudo, root, or administrator).
- A working MongoDB installation (see our guide on how to install MongoDB on Ubuntu).
Note: See also our MongoDB deployment guides:
How Do I Create a Database in MongoDB?
There are several ways to create a database in MongoDB. To create a MongoDB database, use one of the following methods:
- MongoDB Compass GUI.
- MongoDB Shell.
- A programming language with a MongoDB driver (we will use Python).
The sections below cover each method in greater detail. Use a method that best suits your preferences and requirements.
Method 1: Create a Database in MongoDB Using Compass
MongoDB Compass is a GUI for simplifying database management. To create a database using Compass, do the following:
1. Launch the MongoDB Compass program. If using Linux, run the following command in the terminal:
mongodb-compass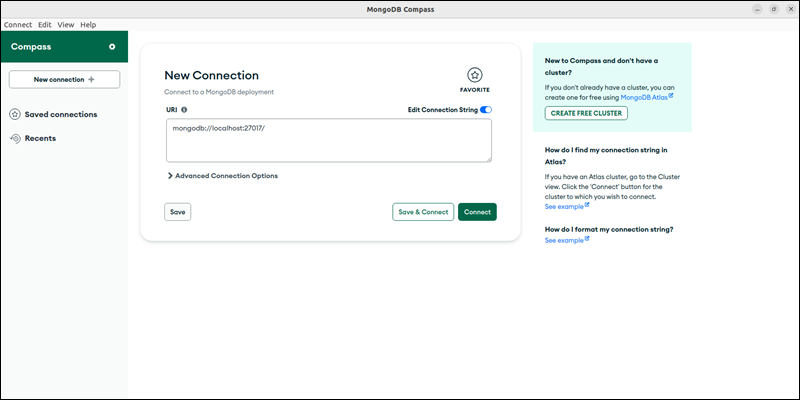
The command opens the MongoDB Compass UI.
2. Connect to the MongoDB instance. Adjust the URI if required and click Connect.
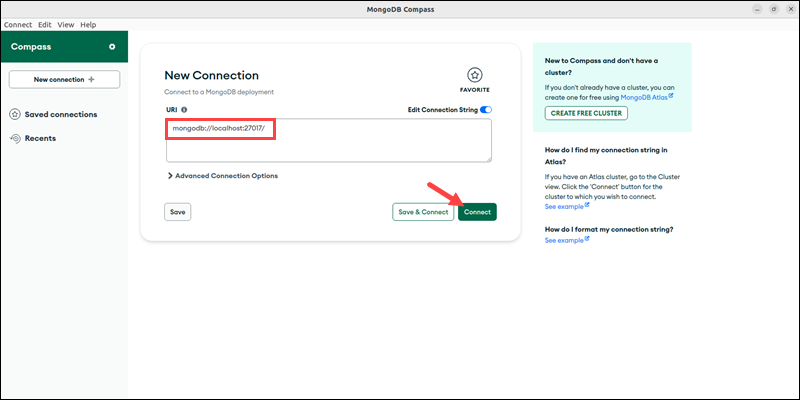
If using MongoDB Atlass, provide the connection string in the URI field.
3. Click the plus icon (+) next to Databases.
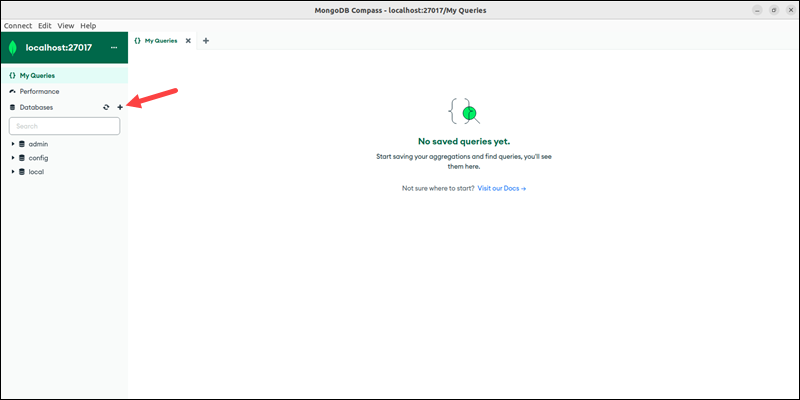
The action opens the Create Database dialog.
4. Enter the database and collection name in the appropriate fields.
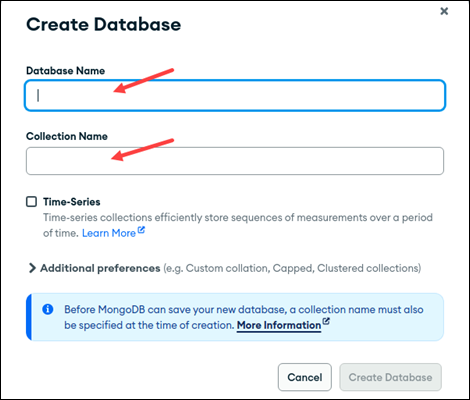
5. (Optional) Check the Time-Series box if the database contains time-series data.
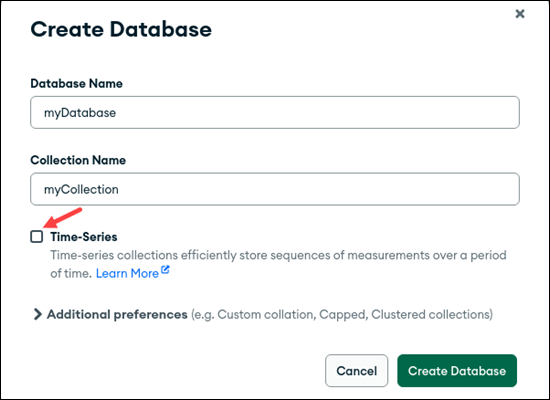
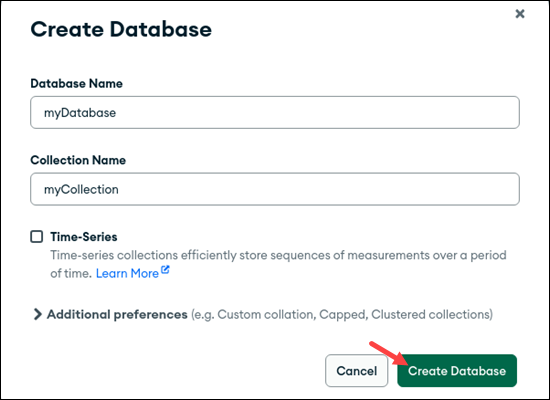
6. Review the names and options. Once ready, click Create Database.
The database and collection appear in the database listing on the left.
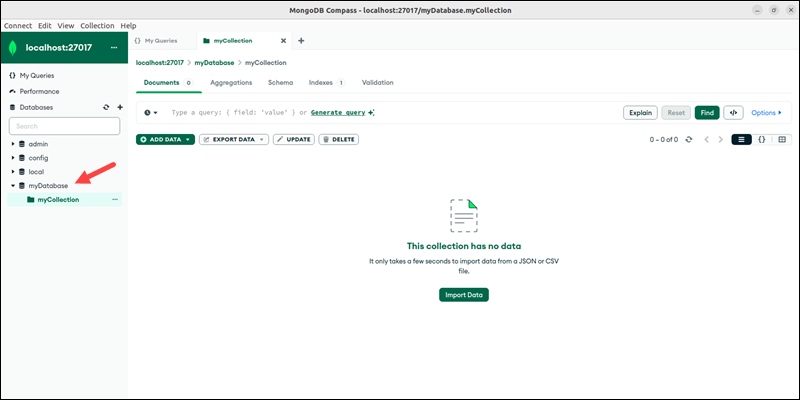
The database and collection are ready for use. Continue by adding documents to the new database and collection.
Method 2: Create a Database in MongoDB Using MongoDB Shell
The MongoDB Shell uses commands to create and manage a database. To create a database using mongosh (MongoDB Shell):
1. Start the MongoDB Shell in the terminal:
mongosh
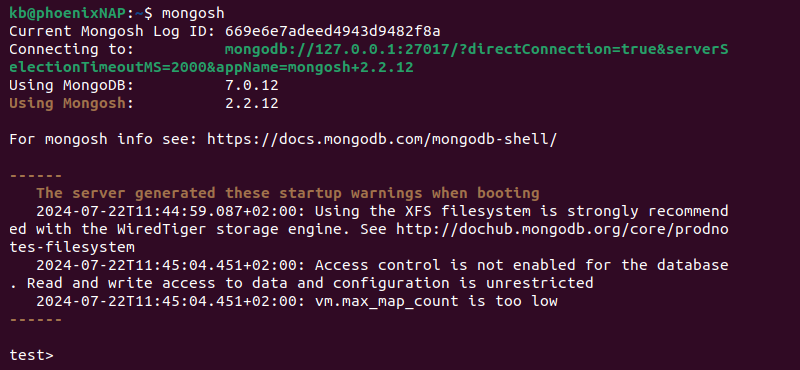
The prompt changes to the MongoDB shell in test mode (test>).
Note: If you can't access the MongoDB Shell, check whether the MongoDB service is active with sudo systemctl status mongodb. The output should confirm that the service is active (running).
2. Run the use command:
use [database_name]
The command creates a new database if it does not exist. However, the database only appears on the database list once data is added.
3. Insert a single document into a new collection:
db.[collection_name].insertOne({ [field]: "[value]" })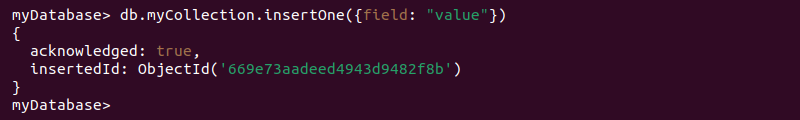
Replace the placeholders with the actual collection, field, and value names. The command creates the database and collection and inserts the new document.
4. Verify the database creation worked with:
show dbs
The new database appears on the listing, indicating the creation was successful.
Method 3: Create a Database in MongoDB Using Python
Creating a database using a programming language involves installing the specific MongoDB driver (library) for that language. As MongoDB is available for many programming languages, the process is different for each language.
The steps below show how to create a MongoDB database using Python:
1. Install the MongoDB library for Python. For example, if using pip, run:
pip3 install pymongo
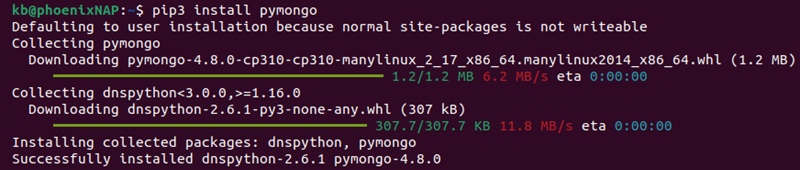
Wait for the installation to complete.
2. Create a Python script to import the pymongo library and connect to the database instance:
from pymongo import MongoClient
client = MongoClient("[connection_string]")
Replace the [connection_string] in the second line with the connection URI. If connecting via localhost, use mongodb://localhost:27017/. Alternatively, use the MongoDB Atlas connection string.
3. Create a database and collection. Add the following two lines to the script:
db = client["[database_name]"]
collection = db["[collection_name]"]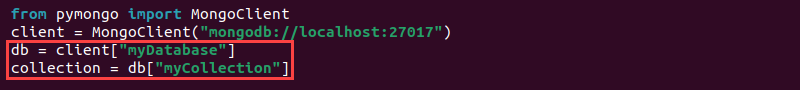
Provide the database and collection names in the appropriate places.
3. The database and collection are only created once there is data. To insert a document (a record), use the insert_one() method:
collection.insert_one({"[field]":"[value]"})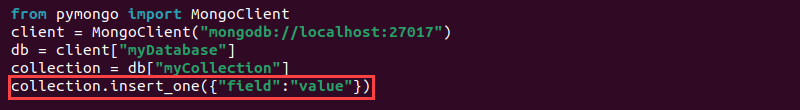
The code inserts a single document into the collection using the dictionary format. Replace the field and value with actual data.
4. To check if the database exists, use:
print(client.list_database_names())
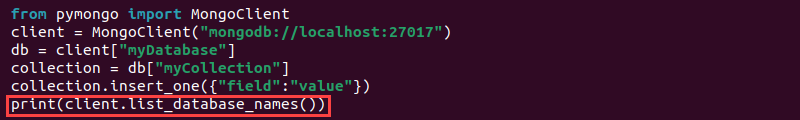
The method lists all databases.
5. The complete script looks like the following:
from pymongo import MongoClient
client = MongoClient("[connection_string]")
db = client["[database_name]"]
collection = db["[collection_name]"]
collection.insert_one({"[field]":"[value]"})
print(client.list_database_names())Save the script in a .py file and run it via an IDE or terminal:
python3 [script_name].py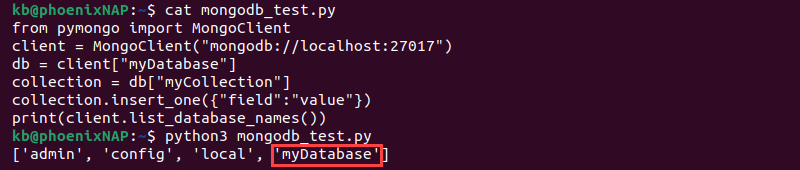
The script lists all databases, including the newly created one.
How to See the Available Databases in MongoDB?
There are different ways to see available databases in MongoDB. The process differs depending on the access method:
- MongoDB Shell. The shell has a command for viewing available databases:
show dbs

- MongoDB Compass. After connecting to the MongoDB instance, the UI lists all databases in the left menu.
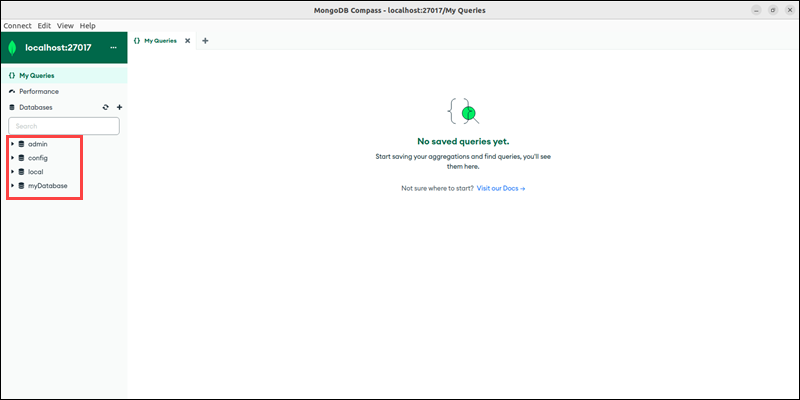
- Programming languages. The MongoDB driver features a function to display all databases. For Python, the command is:
client.list_database_names()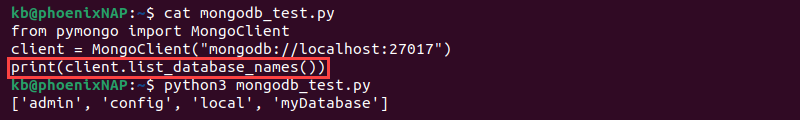
How Many Databases Can Be Created in MongoDB?
MongoDB does not have a database number limit. However, when increasing the number of databases, several factors create constraints:
- Namespaces. The default namespace file size is 16MB, which theoretically results in 240,000 entries (collections and indexes). The default namespace file size can be adjusted to a maximum of 2GB (around 3 million entries).
- Memory and disk space. Databases and collections consume memory and storage space. Memory and database numbers are directly proportional. Likewise, databases require an adequate data storage solution to ensure sufficient space.
- Performance and complexity. Internal operations, background tasks, I/O operations, and concurrently active databases affect performance. Additionally, database maintenance, monitoring, and security become more complex.
There are several ways to approach the difficulties that arise when working with many databases. Reevaluate the database design, implement sharding across distributed servers, and utilize scalable storage solutions.
Conclusion
This guide showed how to create a database in MongoDB. Depending on your requirements and environment, there are different ways to run MongoDB and create a database.
Next, see how MongoDB compares to other database solutions, such as MongoDB vs. MySQL and Cassandra vs. MongoDB.