The MEAN stack is an open-source JavaScript (JS) stack for developing web applications. It includes several software tools for building dynamic websites and web applications.
As it uses JS in each layer of the stack, it significantly simplifies web development.
This article provides step-by-step instructions for installing the MEAN stack on Ubuntu 20.04 and 22.04.
Prerequisites
- A user with sudo privileges.
- Access to a terminal/command-line tool.
How to Install the MEAN Stack on Ubuntu
MEAN is an acronym, and it consists of the following programs:
- MongoDB. A document database.
- Express.js. A backend framework.
- Angular. A frontend framework.
- Node.js. A JS runtime environment.
MEAN is an alternative to the widely known LAMP stack, which uses JS or a JS framework on the client side and PHP on the server side.
Note: See our in-depth comparison between MEAN vs. LAMP.
Installing the MEAN stack requires installing each component separately. To do so, follow the steps in the sections below.
Step 1: Update Package Repository Cache
Before installing the MEAN stack, update Ubuntu's package repository:
sudo apt updateIf prompted, press y to accept installing suggested updates. Wait for the updates to be completed before proceeding to the next step.
Step 2: Install MongoDB
MongoDB does not maintain the MongoDB package in the APT package manager. The official community edition requires manual installation and supports 64-bit Ubuntu LTS releases.
To install the latest stable version of MongoDB, do the following:
1. Install cURL and GnuPG with the apt-get command:
sudo apt-get install gnupg curl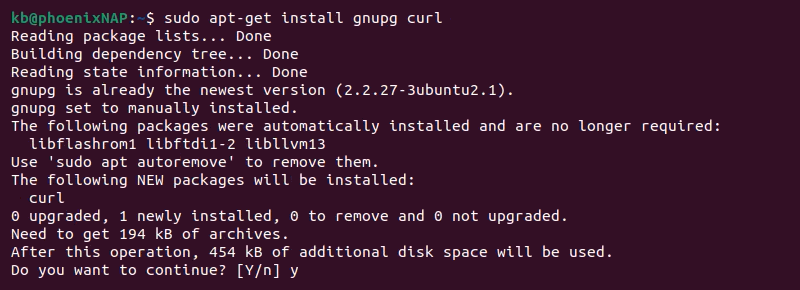
The two tools help import the MongoDB public GPG key. Press y to confirm the package installation.
2. Import the GPG key with the following command:
curl -fsSL https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-7.0.asc | sudo gpg -o /usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-7.0.gpg --dearmorThe command does not produce an output.
2. Next, create a list file for MongoDB so the command knows where to look for the packages:
echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-7.0.gpg ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs)/mongodb-org/7.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-7.0.listThe command determines the operating system codename. It then creates the MongoDB repo list file in the APT sources list using the appropriate name and the imported key from the previous step.
3. Update the local package database:
sudo apt-get update4. Install the latest MongoDB version with:
sudo apt-get install mongodb-org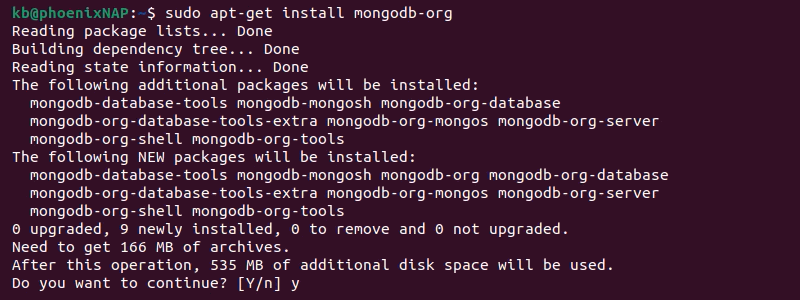
Wait for the installation to complete.
5. To start MongoDB, run the following systemctl command to start the service:
sudo systemctl start mongodThis command starts the database service.
6. Check the mongod service status with:
sudo systemctl status mongod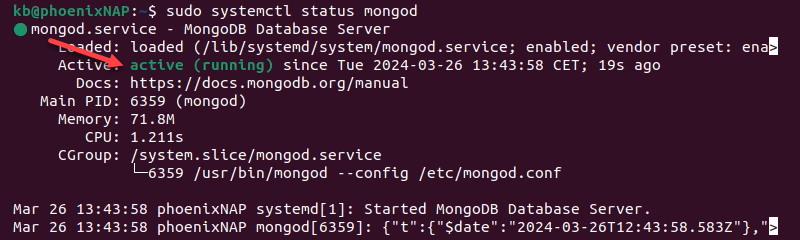
The output shows the service as active (running), which indicates the installation was successful.
6. The final step is to enable MongoDB:
sudo systemctl enable mongod
The command makes MongoDB start automatically when the system launches.
Step 3: Install Node.js and npm
Node.js is the runtime environment in the MEAN stack, enabling server-side JS execution. npm (the Node Package Manager) handles Node.js packages and dependencies and is used to install Express and Angular. Although Node.js is available in the APT repositories, it's not the latest stable version.
Follow the steps below to install Node.js and npm:
1. Add the NodeSource PPA (Personal Package Archive) and configure the repository with:
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_lts.x | sudo -E bash -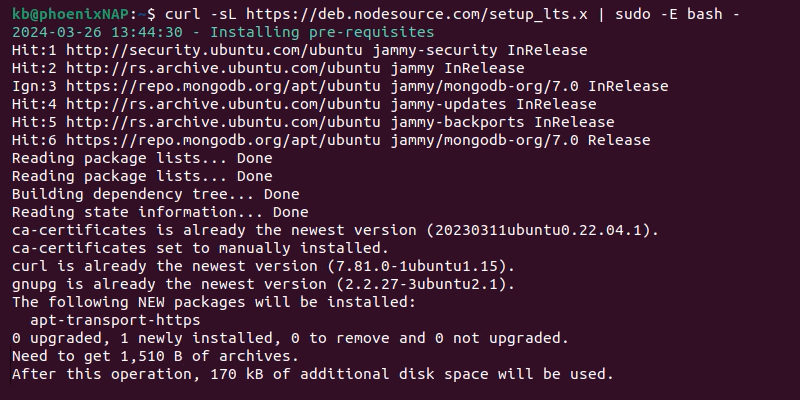
We recommend using the LTS version. Replace lts.x with the preferred version number for a specific version.
2. Install Node.js and npm by typing the command:
sudo apt install nodejs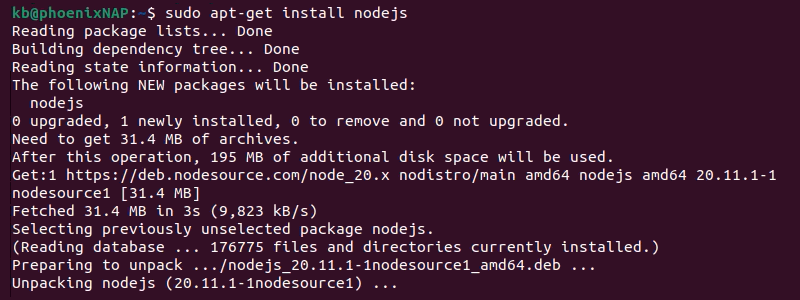
3. Verify the installation with the following two commands:
nodejs --versionnpm --version
The first command outputs the Node.js version, while the second shows the npm version.
Step 4: Install Angular CLI
Angular CLI is a command-line tool for making and managing Angular applications. Install it with the following command:
sudo npm install -g @angular/cli
The command installs Angular CLI globally and enables installing Angular for local projects. When creating a new project, the following Angular CLI command installs Angular locally:
ng new [application_name]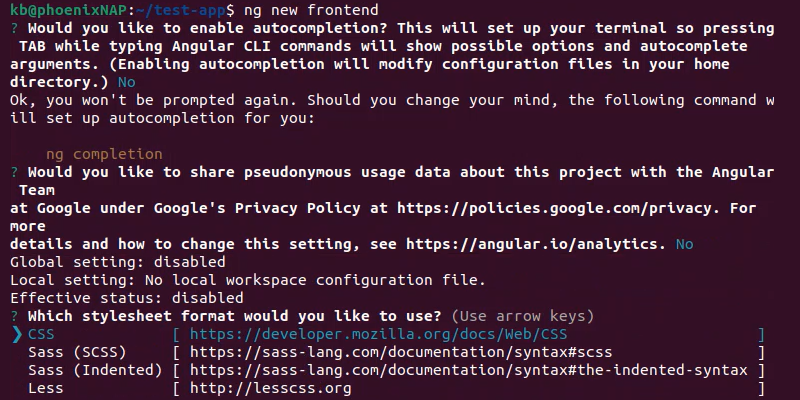
The installation asks several questions, and answers depend on the project's requirements.
Step 5: Install Express.js
Express.js is a backend framework for Node.js. It facilitates the backend part of the MEAN stack. When creating the project's backend, first initialize the local project directory:
npm init -y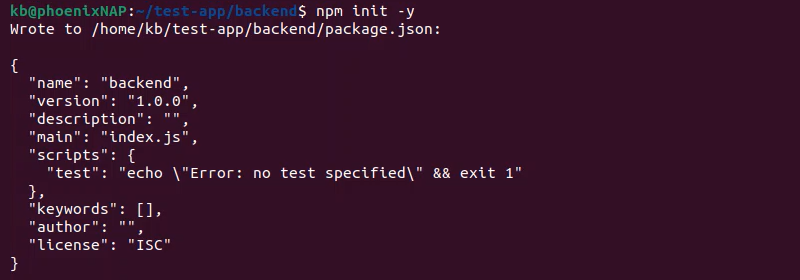
Then, install Express.js locally in a project folder with the following command:
npm install express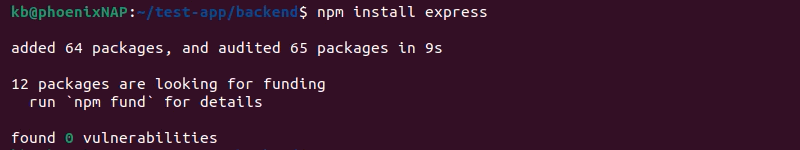
The npm command automatically adds it as a project dependency. A global installation is not recommended due to dependency issues.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you know how to install all the necessary dependencies and software packages for the MEAN stack on Ubuntu. The stack enables the development of fast and robust web applications.
Next, read more about software dependencies.