The XAMPP stack is an open-source Apache distribution of a PHP development environment consisting of cross-platform software (X): Apache (A), MariaDB (M), PHP (P), and Perl (P). Developers use the platform as a local host for testing software and web pages before transferring the data to a remote online server.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install XAMPP on Ubuntu, verify the installation, and uninstall the XAMPP package.

Prerequisites
- A machine running Ubuntu.
- A user account with root privileges.
- Access to the terminal.
What Is XAMPP?
XAMPP is a free, open-source, cross-platform web server stack package developed by Apache Friends. It is an easy-to-install package that provides a local server environment for web development and testing purposes.
Developers commonly use XAMPP to create and test dynamic web applications on a local machine before deploying them to a live server. It is available for Windows, Linux, and macOS, making it versatile for developers using different operating systems.
How to Install XAMPP on Ubuntu
In this tutorial, we will focus on how to install XAMPP on Ubuntu.
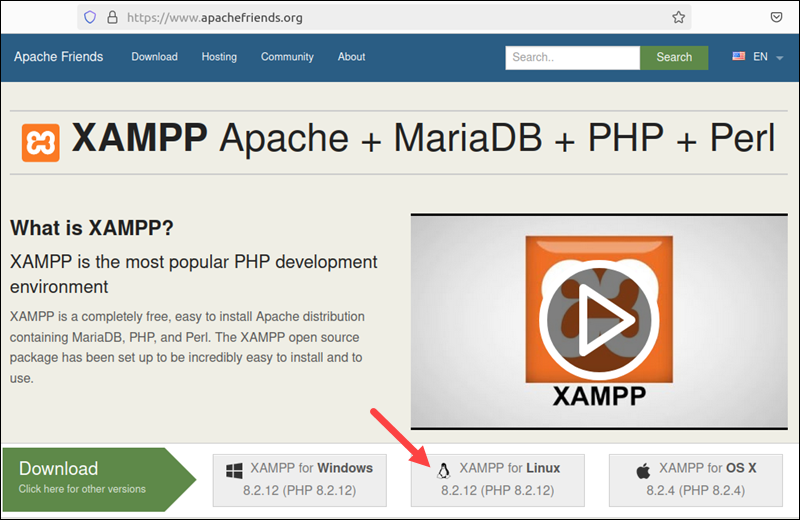
Step 1: Download Installation Package
Open an internet browser and navigate to the official Apache Friends webpage. Scroll down and click the XAMPP for Linux link to download the binary installation package.
Step 2: Make Installation Package Executable
To start the installation, change the file permissions to make the installer executable. Follow the steps below:
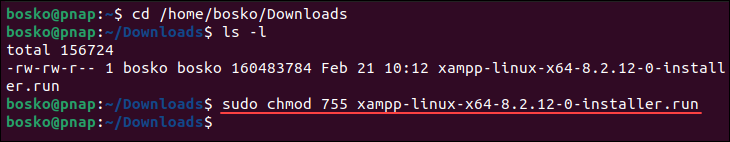
1. Open the terminal and change the directory to where your installation package is located. By default, the system stores it in the Downloads directory. Use the cd command with the following syntax:
cd /home/[username]/Downloads2. Make the file executable using the following syntax with chmod 755:
sudo chmod 755 [package_name]Replace [package_name] with the complete name of the downloaded package. You can use the ls command to list the contents of the directory and copy the full file name:
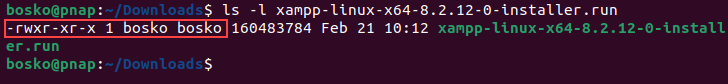
3. Since there is no confirmation or output after changing the file permissions, you can verify the change by listing the directory contents again:
ls –l [package_name]The output should include rwxr –xr –x 1 followed by the name of the user who can now execute the file, as in the image below:
Step 3: Install XAMPP
After setting the right permissions, you can use the installer to install and configure XAMPP. Follow the steps below:
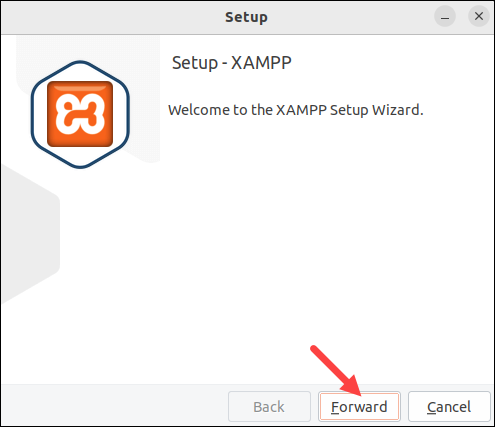
1. Run the installer using the syntax below:
sudo ./[package_name]For example:
sudo ./xampp-linux-x64-8.2.12.0-installer.runThe welcome screen opens in a new window:
2. Click Forward, and in the Select Components dialogue. Choose the components you want to install. We recommend keeping the default settings. Continue the installation by clicking Forward.
3. In the next step, the setup wizard shows the location for installing the software. To proceed, click Forward.
4. The wizard is now ready to install XAMPP on your system. Click Forward to start the installation.
The installation process starts, and a dialogue box showing the progress appears on:
5. When the setup finishes, complete the process and launch XAMPP by clicking Finish. If you don't want to launch XAMPP now, uncheck the Launch XAMPP box.

Step 4: Launch XAMPP
If you chose to launch XAMPP in the setup wizard, the XAMPP control panel launches, and you can start managing your servers.
Alternatively, run the command below to open XAMPP:
sudo /opt/lampp/./manager-linux-x64.run

Click the Manage Servers tab to see all the available services and their status. You can change the status by selecting Start or Stop. You can also start all services simultaneously by clicking the Start All button.
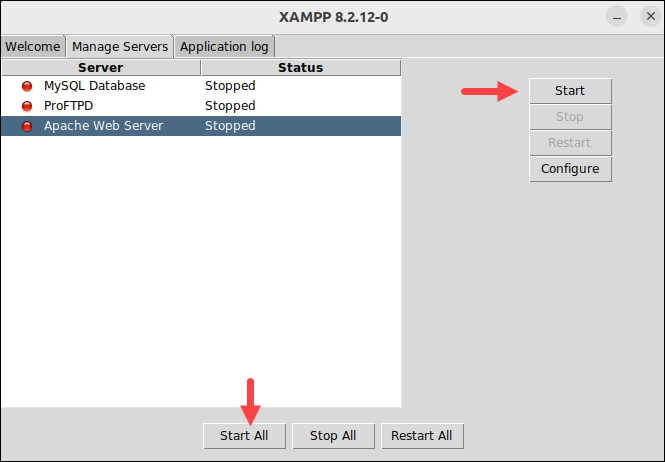
Important: If the services fail to start, make sure that the net-tools utility is installed on your system. To install net-tools, run the command below:
sudo apt install net-toolsStep 5: Verify XAMPP is Running
Make sure you have successfully installed the XAMPP stack by checking a few services. Follow the steps below:
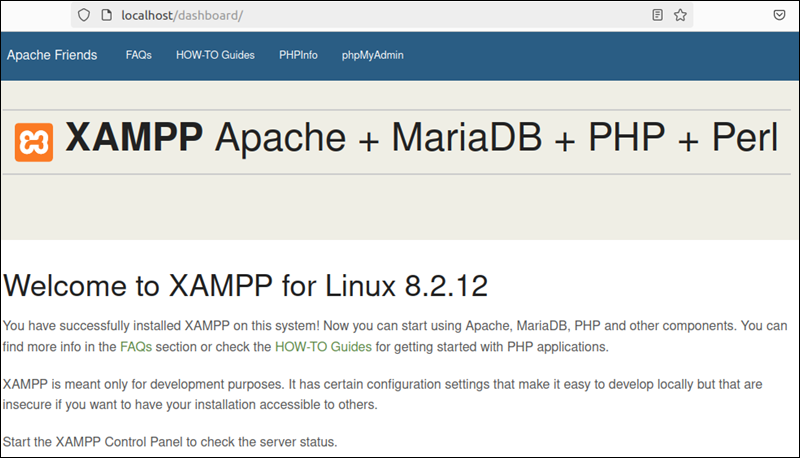
1. Verify localhost is working by entering the following URL in a browser:
http://localhost/dashboardIf the XAMPP dashboard page displays as in the image below, you have successfully installed the stack.
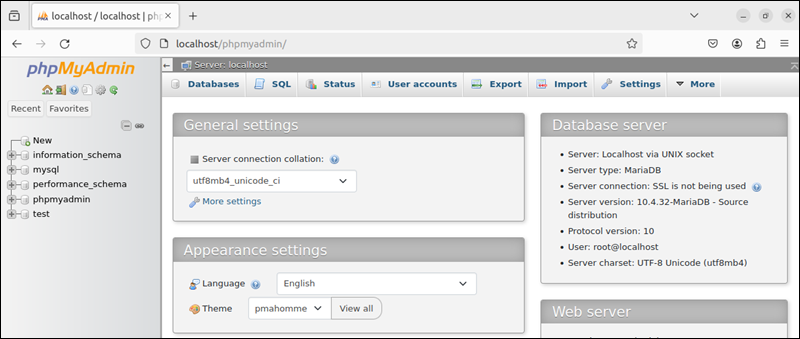
2. Next, verify that the MariaDB service is working. Paste the following URL in a browser:
http://localhost/phpmyadminThe output screen for a properly working database service should appear as below:
How to Uninstall XAMPP from Ubuntu
Uninstalling XAMPP from your system is done via an uninstallation script provided by the program. Follow the steps below:
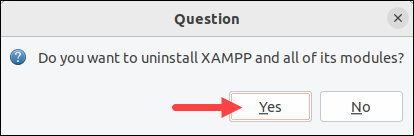
1. Invoke the script by running the following command:
sudo /opt/lampp/./uninstallA dialogue box opens and asks whether you want to uninstall XAMPP and all of its modules. Confirm by clicking the Yes button.
After the process is complete, the output confirms that XAMPP has been uninstalled.
2. After the program is uninstalled, remove the XAMPP directory using the rm command below:
sudo rm -r /opt/lampConclusion
After reading this article, you know how to install XAMPP in Ubuntu. Use XAMPP to test your web pages and apps before deploying them to a live server.
You can also explore alternative stacks, such as the LAMP stack or the MEAN stack, or learn the difference between Apache and Nginx.

