2024 saw a relentless rise in data breaches, with both the frequency and severity of these attacks reaching alarming levels. As technology continues to evolve, so do cybercriminals' tactics. Namely, the integration of artificial intelligence has further complicated cybersecurity, with AI being used to both enhance security measures and develop more sophisticated attacks.
This article will draw on the latest data and statistics on data breaches, exploring the most common types of attacks, their causes, impacts across industries, and practical strategies for prevention.
Data Breach Statistics 2024: Key Insights and Alarming Trends
To understand the current trends and risks, we analyzed the 2024 data breach reports from Verizon and IBM, two leading authorities in the field.
Based on these reports, here are some of the most alarming insights and key takeaways for 2024.
System Intrusion: Leading Cause with 36% of Breaches
System intrusion remains the foremost type of data breach, accounting for a staggering 36% of all incidents. These attacks involve unauthorized access to systems through sophisticated methods, often exploiting vulnerabilities and security gaps.
To understand the risks of system intrusion, it's essential to recognize its defining features:
- Use of stolen credentials. Attackers leverage valid but compromised login details to infiltrate systems. This method allows them to bypass security measures that rely solely on authentication, making detection more challenging. Notably, breaches involving stolen or compromised credentials took the longest to identify and contain, averaging 292 days.
- Exploitation of vulnerabilities. Attackers target unpatched software flaws and system vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access. Regular patching and vulnerability management are essential to mitigate this risk.
- Ransomware deployment. A significant portion of system intrusion incidents, approximately 70%, involve ransomware. Attackers encrypt critical data and demand ransom payments to restore access. The prevalence of ransomware has surged, accounting for 23% of all breaches.
System intrusion attacks are particularly concerning due to their complexity and the potential for significant disruption. The use of stolen credentials means attackers can operate under the guise of legitimate users, making detection difficult. Ransomware adds another layer of urgency, as organizations may face operational paralysis until they recover their data.
Key Stats
- Average cost per breach: $4.81 million.
- Average ransom demands: 1.34% of the victim organization's total revenue.
- Median financial losses from ransomware: $46,000 after recovery efforts.
Social Engineering Attacks Surge by 29%
Social engineering attacks have seen a significant increase, representing 29% of breaches. These attacks exploit human psychology to manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security.
To better defend against social engineering, it's essential to understand how attackers operate:
- Phishing. Attackers send deceptive emails or messages that appear legitimate to trick users into revealing sensitive data or clicking on malicious links. Phishing accounted for 15% of attack vectors.
- Pretexting. Attackers create fabricated scenarios to persuade victims to disclose information or perform actions. This tactic often involves impersonating trusted individuals or organizations.
Social engineering attacks capitalize on the trust and routines of individuals within an organization. With the advent of AI-powered tools, attackers can generate highly personalized and grammatically correct messages, making it harder for recipients to discern fraudulent communications.
Key Stats
- Average time to identify and contain phishing attacks: 261 days.
- Average cost per phishing breach: $4.88 million.
Human Error Causes 22% of Breaches
Human errors continue to be a significant factor in data breaches, accounting for 22% of incidents. These mistakes, often unintentional, lead to substantial data exposure and security incidents.
Understanding the types of human errors helps in developing targeted prevention strategies:
- Misdelivery. Sending sensitive information to the wrong recipient can result in unauthorized access to confidential data.
- Loss of Assets. Misplacement or loss of devices containing sensitive data, such as laptops or USB drives, can lead to significant security risks.
- Misconfiguration. Incorrect system settings or configurations leave systems vulnerable to attack or data exposure. Approximately 10% of breaches are due to misconfiguration.
Human error highlights the critical importance of robust security awareness training programs and a strong security culture within organizations. Regular training enables employees to recognize potential risks and understand the importance of diligently following security protocols.
Key Stats
- Breaches involving human error can increase the average cost by 16% compared to those without human error.
Malicious Insider Threats: Highest Cost at $4.99 Million
Attacks involving malicious insiders—employees or trusted individuals who intentionally misuse their access—result in the highest average cost per breach, at $4.99 million.
Recognizing the signs of malicious insider activity is vital for early detection:
- Insider threats. Malicious insiders exploit their authorized access to steal sensitive data or disrupt operations.
- Privilege escalation. Insiders may seek to gain higher access levels to obtain more valuable information.
- Data exfiltration. This involves the unauthorized transfer or theft of data, often to benefit a competitor or for personal gain.
Malicious insiders pose a unique challenge as they operate within the trusted boundaries of an organization. Detecting such threats requires sophisticated monitoring and behavioral analytics to identify anomalous activities. Implementing strict access controls and the principle of least privilege helps mitigate these risks.
Key Stats
- Average time to identify and contain insider threats: 287 days.
- Although malicious insider attacks accounted for 7% of breaches, their financial impact is disproportionately high.
What Is the Leading Cause of Data Breaches?
Data breaches in 2024 are primarily driven by a combination of external attacks and internal vulnerabilities. Here are the top causes:
- Human error and system glitches (45% of breaches). This category encompasses both inadvertent employee mistakes and technical failures, underscoring the importance of both human and technical safeguards.
- Ransomware attacks (23% of breaches). Ransomware attackers encrypt critical data and demand ransom payments for its release, causing significant operational disruptions and financial losses. The prevalence of ransomware reflects attackers' shift toward methods that maximize impact and profitability.
- Stolen or compromised credentials (16% of breaches). Attackers obtain valid login details through methods like phishing, social engineering, or purchasing credentials from the dark web. Once inside, they can navigate systems undetected.
- Phishing attacks (15% of breaches). Phishing remains a prevalent method due to its effectiveness in tricking users into revealing sensitive information or installing malware.
- Malicious insider threats (7% of breaches). Attacks involving malicious actors within an organization pose substantial risks. Insiders can exfiltrate data or sabotage systems, resulting in higher costs and longer detection and containment times.
The percentages presented above add up to more than 100% because data breaches often involve multiple causes or attack vectors. In reporting, each breach may be counted under all applicable categories, meaning the percentages represent the frequency of each cause among all breaches but are not mutually exclusive, leading to a total exceeding 100%.
How Common are Data Breaches?
Data breaches have become more common, affecting organizations across all sectors and regions. They are not isolated incidents but a widespread challenge. Here are some statistics that illustrate the scope of the problem and the areas that require immediate attention.
Global Statistics
The global landscape of data breaches in 2024 reveals the following trends:
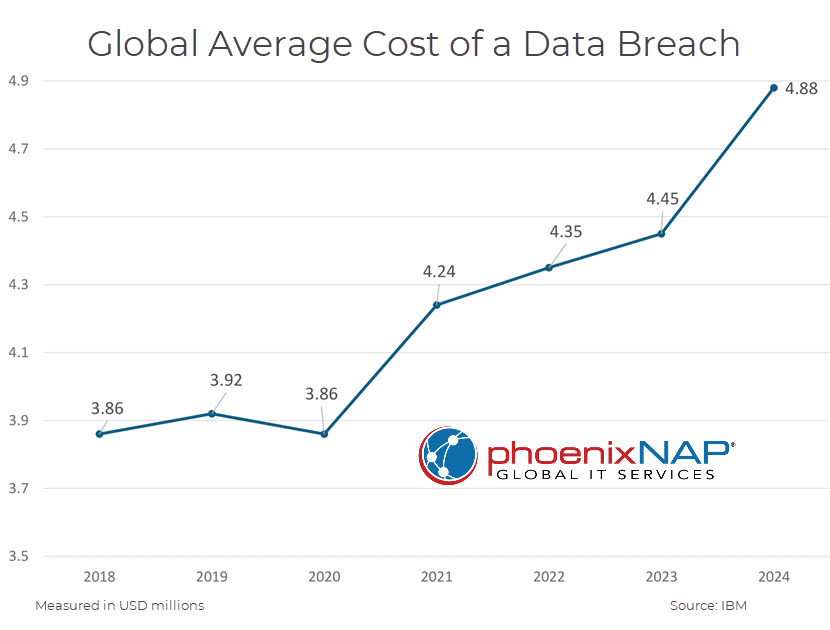
- Average cost increase. The average cost of a data breach rose by 10% to $4.88 million, marking the highest increase since the pandemic began. This rise is driven by business disruption, lost revenue, and the increasing complexity of cyberattacks.
- Average time to identify and contain a breach. The average time decreased to 258 days, suggesting improvements in detection and response capabilities. Specifically, it took an average of 169 days to identify a breach and 58 days to contain it. While this reduction is a positive development, the duration still provides attackers ample time to cause significant damage, steal sensitive data, or disrupt operations.
- Frequency of breaches. A total of 10,626 confirmed data breaches were recorded, nearly double the previous year (5,199). This high number reflects both attackers' growing capabilities and organizations' expanding digital footprints.
Regional Highlights
Data breach impact varies across different regions due to factors like regulation, economic conditions, and the type of cyber threat prevalent in the area. Understanding these nuances is crucial for developing a targeted IT security policy.
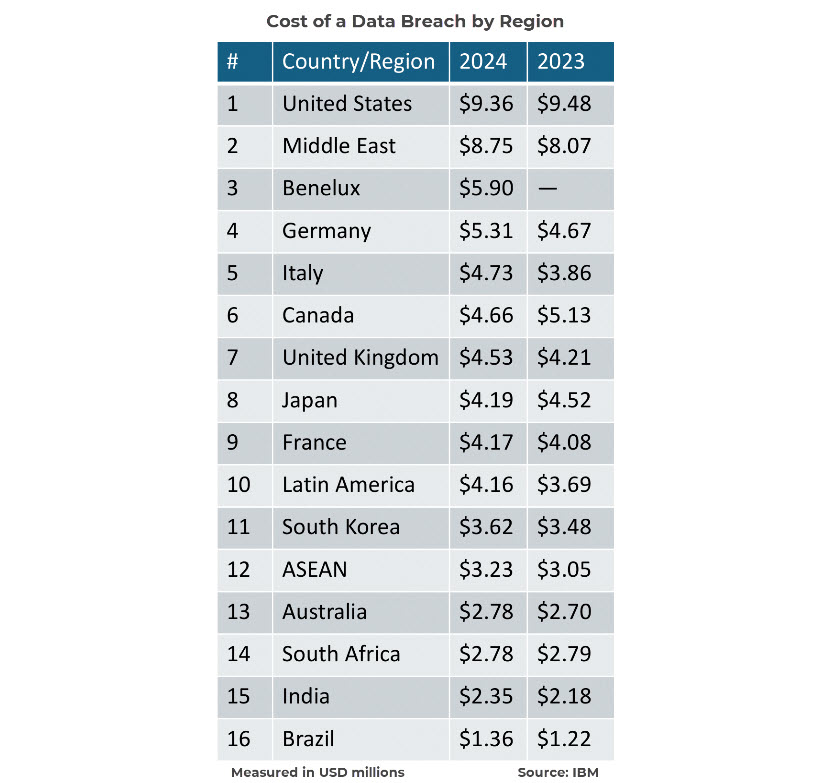
- United States. The U.S. experienced the highest average breach cost at $9.36 million. This high cost reflects the substantial financial implications of breaches in a market with a high cost of business operations, strict regulatory requirements, and significant reputational stakes. Additionally, the large market size and the value of data held by U.S. organizations make them prime targets for sophisticated attacks.
- Southeast Asia (ASEAN). Breaches in the ASEAN region often involved complex attacks, with system intrusion and social engineering being prevalent. The diversity of economies and varying levels of cybersecurity maturity in ASEAN countries contribute to this trend. The region's rapid technological growth and large user base present both opportunities and challenges in securing digital assets.
- Middle East. The average breach cost rose significantly to $8.75 million, highlighting growing cyber threats in the region. Factors contributing to this rise include increased digitization, rapid adoption of new technologies, and potentially less mature cybersecurity infrastructures. The region's strategic importance and critical industries, such as oil and gas, also contribute to making it an attractive target for cybercriminals.
Data Breach by Industry
Different industries face unique cybersecurity challenges based on the nature of their operations, the value of the data they handle, and the regulatory environments in which they operate.
Healthcare Remains the Costliest Industry
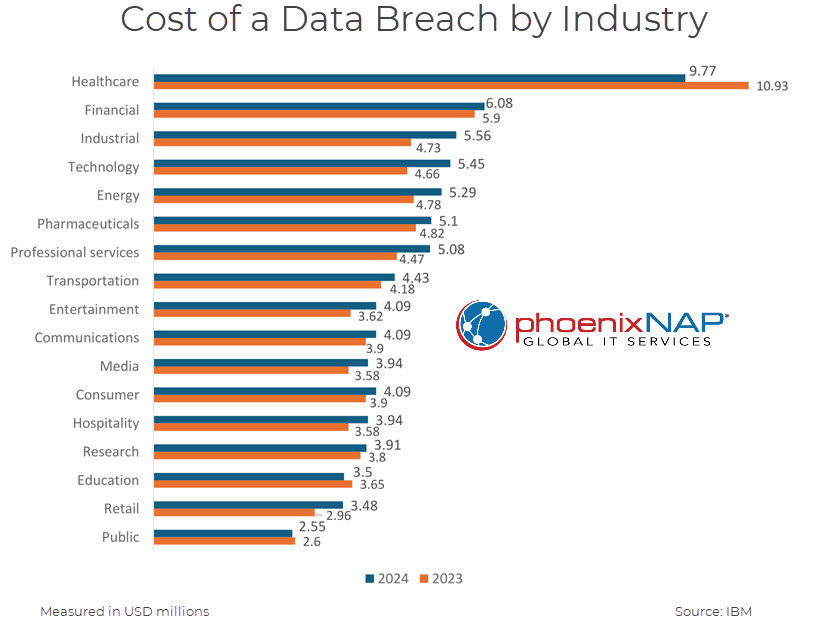
The healthcare sector continues to bear the highest cost of data breaches. The sensitive nature of patient data and strict regulatory requirements contribute to the significant financial impact when breaches occur. The average cost of a data breach in the healthcare sector in 2024 was $9.77 million, marking the 13th consecutive year that healthcare has had the highest breach costs among all industries.
To understand why healthcare is particularly vulnerable, we must recognize the specific challenges the industry faces:
- Sensitive patient data. Healthcare organizations store vast amounts of personal health information (PHI), including medical histories, diagnoses, and treatment plans. This data is highly valuable on the black market, making healthcare providers attractive targets for cybercriminals.
- Operational impact. Cyberattacks can disrupt critical healthcare services, potentially endangering patient lives. Ransomware attacks, for example, can render systems unusable, delaying treatments and compromising care.
- Regulatory compliance. Laws like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. impose strict requirements for protecting patient data. Non-compliance results in hefty fines and penalties, amplifying the cost of breaches.
Read our article on ransomware in healthcare to understand why criminals target hospitals and how healthcare organizations can protect themselves against these attacks.
Financial Services Under Siege
The financial services industry remains a prime target for cybercriminals due to the direct access to monetary assets and sensitive financial information. The sector faces constant threats that require vigilant and sophisticated security measures.
- Average breach cost. The average cost of a data breach in the financial sector was $6.08 million, higher than the global average across industries.
- Regulatory fines. Increased enforcement actions under regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and industry-specific standards add to the financial burden post-breach.
The financial services sector also has some industry-specific risks:
- Financial losses. Direct theft, fraud, and operational disruptions have immediate and significant financial impacts on institutions and their customers.
- Increased reputational damage. Trust is vital in the financial sector. Data breaches erode customer confidence, leading to client attrition and challenges in acquiring new customers.
Industrial Sector Faces Highest Cost Increase
The industrial sector, which encompasses manufacturing and critical infrastructure, has seen the largest rise in data breach costs. The integration of operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) systems has expanded the attack surface, making security more complex.
- Average breach cost increase. The industrial sector saw an average cost increase of $830,000 per breach over the previous year.
- Average time to identify and contain. Breaches in this sector took an average of 219 days to identify and 85 days to contain, exceeding the overall average and indicating challenges in detection and response.
The unique nature of the industrial sector also presents specific vulnerabilities:
- Downtime sensitivity. Disruptions halt production lines, leading to significant revenue loss and supply chain delays. The cost of downtime in manufacturing is substantial, affecting not only the company but also its partners and customers.
- Legacy systems. Older industrial control systems often lack modern security features, making them vulnerable to attacks. Upgrading or patching these systems is complicated due to operational constraints.
- Supply chain dependencies. Attacks have cascading effects across the supply chain. A breach in one organization can impact suppliers, distributors, and customers, amplifying the overall damage.
- Cyber-physical risks. Attacks can have physical consequences, such as equipment damage, safety hazards, or environmental incidents. This factor raises the stakes beyond financial loss to include human safety.

How Many Data Breaches Go Undetected?
Long detection times allow attackers to establish a foothold, exfiltrate data, and potentially cause more damage. The extended presence increases the risk of significant data loss and operational disruption. Breaches involving specific attack vectors tend to have longer detection and containment periods:
- Stolen credentials. These breaches took an average of 327 days to identify and contain, the longest among all breach types. Attackers using valid credentials can move laterally within networks without triggering immediate alarms.
- Shadow data breaches. Breaches involving shadow data—unmanaged and unmonitored data—took 291 days on average to identify and contain, 24.7% longer than breaches without shadow data.
- Malicious insider attacks. These breaches averaged 306 days before detection, highlighting the difficulty in identifying insider threats who have legitimate access and may not exhibit overt malicious behavior.
Factors Contributing to Undetected Breaches
Understanding these factors can help organizations improve their detection capabilities:
- Sophisticated attack methods. Advanced persistent threats (APTs) use stealthy techniques, such as encryption and obfuscation, to avoid detection. Attackers may use zero-day exploits and custom malware to infiltrate systems.
- Shadow data. Unmanaged and unmonitored data sources, such as outdated databases or forgotten cloud storage, can be exploited without detection. Attackers target these neglected areas to access sensitive information.
- Lack of monitoring tools. Insufficient monitoring and detection capabilities hinder timely identification. Organizations lacking robust security information and event management (SIEM) systems or endpoint security tools may miss critical indicators of compromise.
Shadow IT refers to any unauthorized device, IT service, or app employees use without the knowledge of the company's security department.
While relatively harmless at first sight, shadow IT causes major risks for companies. In 2022, nearly 7 out of 10 organizations experienced a security incident due to employees using unsanctioned hardware or software.
How Much Does a Data Breach Cost?
The global average cost of a data breach in 2024 increased to $4.88 million, a 9.2% rise from the previous year's average of $4.45 million. The cost per lost or stolen record rose to $165, with personally identifiable information (PII) being the most expensive data type. Employee PII breaches cost organizations $4.90 million on average.
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of a data breach:
- Business disruption. Lost business costs, including customer turnover, system downtime, and reputational damage, accounted for the most significant portion of breach costs, averaging $1.42 million.
- Implementing security automation. Automation and AI in security operations reduce breach costs by an average of $1.76 million.
- Post-breach response. Expenses related to customer support, identity protection services, legal fees, and regulatory fines increased in 2024. The average cost for post-breach response was $1.49 million.
- Encrypting data. Extensive use of encryption reduced the average cost by $220,000.
- Developing incident response plans. Organizations with an incident response team and regularly tested incident response plans saved an average of $2.66 million.
- Regulatory fines. The number of organizations paying fines over $1 million increased, reflecting stricter enforcement of data protection laws.
Cost Variation by Breach Type
The nature of the breach affects the financial impact:
- Malicious insider attacks. These breaches had the highest average cost at $4.9 million, due to the difficulty in detection and the potential for extensive damage from trusted individuals.
- Ransomware attacks. The average cost of a ransomware attack was $5.13 million, not including the ransom payment. Organizations that reported the attack to law enforcement saved an average of $470,000 compared to those that did not.
Should I Be Worried about Data Breaches?
Data breaches pose significant risks to both organizations and individuals, with far-reaching consequences. Acknowledging these risks is the first step toward implementing effective prevention strategies.
Here are the key concerns:
- Financial losses. Direct costs from breach response and indirect costs from business disruption can be substantial.
- Operational disruption. Significant downtime hampers productivity and affects service delivery.
- Reputational damage. Loss of customer trust leads to decreased revenue and long-term brand damage.
- Legal and regulatory consequences. Regulatory fines are on the rise, with higher penalties for non-compliance. Furthermore, ever stricter reporting requirements lead to additional scrutiny and costs.
- Supply chain risks. Third-party breaches can directly impact your organization, extending vulnerabilities beyond immediate control.

How to Prevent a Data Breach?
Preventing data breaches requires a combination of technology, policies, employee awareness, and continuous improvement. However, implementing effective strategies significantly reduces the risk and impact of potential breaches.
Leverage AI and Automation
Here are the benefits of implementing AI and automation in your security operations:
- Cost savings. Organizations extensively using AI saved an average of $1.88 million on breach costs.
- Improved prevention. AI aids in proactive threat detection, vulnerability management, and predictive analytics.
- Faster detection and response. Breaches were identified and contained nearly 100 days faster with AI and automation.
- Automate routine tasks. Automation frees up security personnel to focus on complex threats.
You must continuously update AI models to make sure they function properly. Ensure AI tools are trained on the latest threat intelligence.
Address Security Staffing Shortages
Security teams are often understaffed, leading to vulnerabilities and increased breach costs. Organizations with high levels of security staffing shortages experienced an average breach cost of $5.74 million. Here are some solutions:
- Invest in training and development. Upskill staff so they can manage advanced security challenges.
- Use managed IT services. Outsource certain security functions to specialized providers to supplement internal teams.
- Attract and retain talent. Offer competitive compensation, career growth opportunities, and a supportive work environment.
Enhance Employee Training and Awareness
Human error is a significant factor in data breaches. Subsequently, comprehensive training programs significantly reduce breach costs. Here are the key areas to focus on:
- Regular security awareness training. Educate employees on phishing, social engineering, and safe data handling practices.
- Promote a security culture. Encourage proactive reporting of suspicious activities and reinforce the importance of security in daily operations.
- Phishing simulations. Conduct drills to improve employees' ability to recognize and report phishing attempts.
Strengthen Security Policies and Controls
Implementing robust policies and technical controls mitigates risks and ensures compliance, reducing the likelihood of breaches due to procedural weaknesses. Here are the key measures to take:
- Identity and access management. Enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring users have only the access necessary for their roles.
- Data encryption. Protect sensitive data both at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Incident response planning. Develop, update, and regularly test incident response plans to ensure effective breach response.
- Regular audits and assessments. Conduct security assessments to identify and remediate vulnerabilities.
Monitor and Secure Shadow Data
Securing shadow data is essential to prevent unauthorized access and data loss. Breaches involving shadow data accounted for 35% of breaches and cost 16% more than those without shadow data. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Data discovery and classification. Use tools to identify and classify all data assets across the organization.
- Policy enforcement. Establish and enforce guidelines for data storage, access, and sharing.
- Continuous monitoring. Implement solutions to monitor data movement and access in real time.
Collaborate with Law Enforcement in Ransomware Attacks
Engaging law enforcement improves outcomes in a ransomware attack. It deters attackers and provides access to additional resources. Here are the advantages of collaborating with law enforcement:
- Avoiding ransom payments. 63% of organizations involving law enforcement did not pay the ransom.
- Improved recovery. Authorities provide resources and assist in response efforts.
- Cost reduction. Organizations involving law enforcement saved nearly $1 million on breach costs.
- Legal compliance. Collaborating with law enforcement ensures compliance and reduces liability.
Secure Generative AI Initiatives
The adoption of AI introduces new risks, including potential misuse and data leakage. A security-first approach ensures that AI initiatives do not compromise organizational security. Here are the best practices:
- Protect AI assets. Secure training data and models against unauthorized access and manipulation.
- Extend security training. Include AI developers and data scientists in security awareness programs.
- Implement AI governance. Establish policies for ethical and secure AI usage, including data privacy considerations.

Securing the Digital Frontier in 2024 and Beyond
The cybersecurity landscape of 2024 is marked by unprecedented challenges, with data breaches becoming increasingly frequent, costly, and sophisticated. The rise of social engineering, amplified by generative AI, has made phishing attacks more convincing and challenging to detect. Human error remains a significant vulnerability, compounded by insider threats and the proliferation of shadow data. To exacerbate these challenges, a notable shortage of cybersecurity professionals persists.
In the face of these threats, the adoption of artificial intelligence and automation offers a promising path forward. Organizations leveraging these technologies have significantly reduced breach costs and improved response times. However, technology alone is not sufficient. A holistic approach that integrates advanced tools with robust security policies and a culture of vigilance is essential.
Prioritizing Holistic Cybersecurity Strategies
Looking ahead, organizations must prioritize comprehensive cybersecurity strategies that address both technological and human elements. By proactively enhancing defenses, investing in employee education, and embracing innovation, businesses can navigate evolving threats, protect their critical assets, and maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders.



