MySQL is a highly customizable relational database management system (RDBMS) that allows users to store and manage data in a structured manner tailored to their specific needs. As with any other RDBMS, it is essential to know how to manage the database service.
This article will provide in-depth instructions on how to start, stop, or restart the MySQL server in Linux, macOS, or Windows.

Prerequisites
- A system with MySQL installed and configured.
- Access to the terminal or Command Prompt. (depending on the OS).
- A user account with sudo or root privileges.
Start MySQL Server
MySQL is available on a range of operating systems (OSs), including Linux, Windows, and macOS. To manage a MySQL-based application or website, it's crucial to understand how to start a MySQL server.
The following sections show how to accomplish that on different OSs.
Start MySQL Server on Linux
Depending on the Linux distribution and init system, there are several ways to start MySQL on Linux:
1. The systemctl start command.
The latest Linux distributions use systemd and its sytemctl command to start, stop, and restart services. For example, to start MySQL in Ubuntu or other Debian-based systems, run:
sudo systemctl start mysql
To start MySQL on RHEL-based systems is the same, except for the process name:
sudo systemctl start mysqldThe command doesn't provide any output. However, systemctl offers a way to verify whether a service is running. To confirm that MySQL has started, run:
sudo systemctl status mysql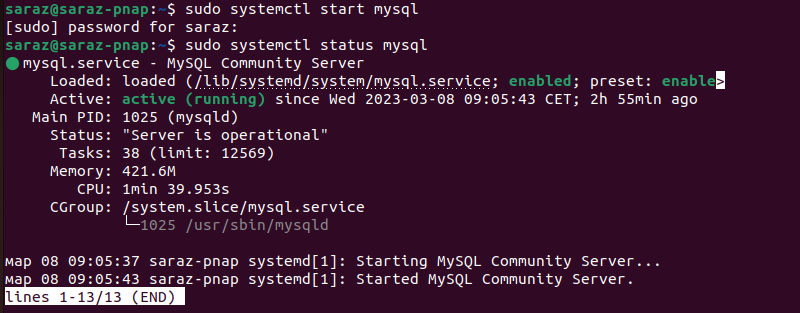
2. The service command.
Older versions of Linux systems don't use systemd. If the systemctl command did not work for you, use the service command. To start Linux using the service command, run:
sudo service mysql startNote: For the service name, use mysql for Debian-based systems and mysqld for RHEL-based systems.
The command doesn’t produce any output. Use the argument status with the service command to verify the result:
sudo service mysql start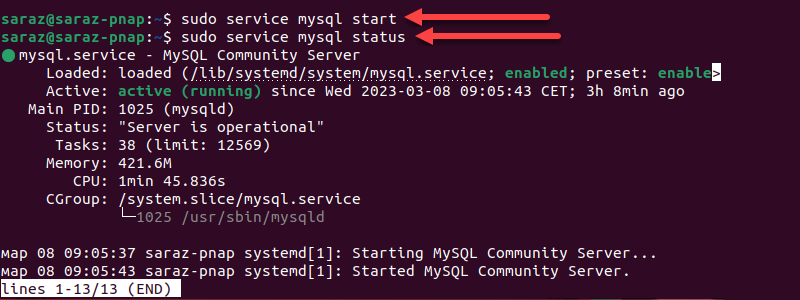
Note: While older Linux distributions usually use the service command, it works on newer distributions as well.
3. The mysql script.
In earlier versions of Ubuntu and CentOS, the /mysql script was commonly used to change the MySQL service state. The script is located in the /etc/init.d directory.
To start MySQL by executing the script, run:
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql startThe command works on older versions of Linux distributions and provides no output. However, in newer versions, the command was deprecated and replaced with other commands. For instance, when the script is run in Ubuntu 22.04, it invokes the systemctl command to start the MySQL service instead:

Note: The path in the example above is the default location for the mysql script. If the script is not in the /etc/init.d directory, the command returns an error message. Use the find command to locate any file on the system.
4. The mysqld_safe command.
The mysqld_safe command is a script that provides a wrapper around the mysqld binary. The script sets environment variables and checks for errors before launching the MySQL server.
Running the command starts the MySQL server process in the foreground and displays the process and any errors. Execute:
sudo mysqld_safe
Both output messages confirm that the MySQL server has started successfully. Note that the command is slower since it performs error checking before launching the server.
Start MySQL Server on Windows
MySQL is commonly used on Linux platforms. However, many Windows-based applications use a MySQL database as the backend. Developers or database administrators who work with MySQL databases on Windows machines need to start the MySQL server to access the database. The following text explains how to start the MySQL server on Windows.
1. Running the mysqld command.
Start the MySQL server on a Windows-based system from the Command Prompt. with the mysqld start command. To accomplish this, open the Windows Run dialog box (Windows Key + R) and type in cmd.
Once the Command Prompt starts, execute:
mysqld start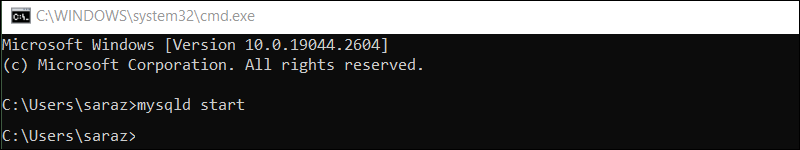
The command gives no output. However, if Windows doesn't find the command, the MySQL bin directory isn't in the system PATH environment variable. Add the directory to the PATH environment variable or use an alternative command.
Note: Refer to our article and find out how to fix MySQL ''command not found'' error.
2. Executing the net start command.
An alternative to mysqld start is the net start command. The command syntax is:
net start MySQL[version_number]Therefore, the MySQL version number is necessary to start the server. To find the version number, run the following in the Command Prompt:
net start
The command lists all active services. Locate the MySQL version running on the system.
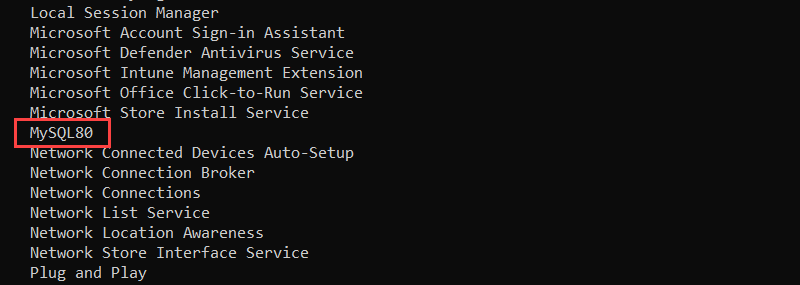
Run the command with the version number. In this case, the system runs MySSQL80:
net start MySQL80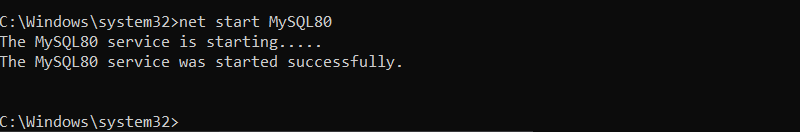
The terminal shows the process and informs the user once the service is installed.
3. Using the services window.
The MySQL service starts and stops the MySQL server process in the background and manages it. It comes installed together with the server.
To start the MySQL service and server, open the Run dialog (Windows key + R) and type in services.msc.
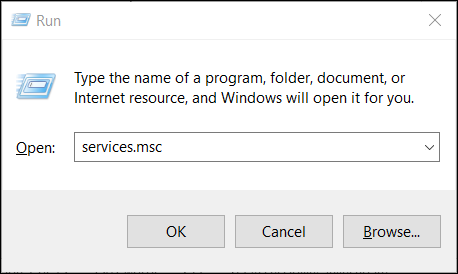
Once the Services Window opens, find the SQL Server service. The service name starts with SQL Server followed by the version.
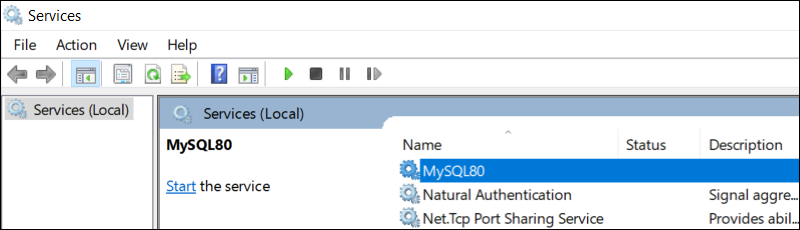
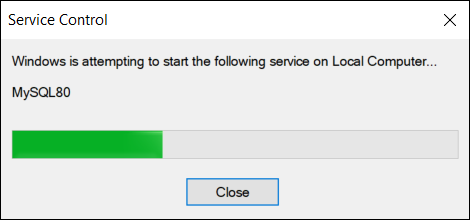
To enable the service and the server, click Start the service on the right-side menu.
It takes a few moments for the service to start. Wait for the service to start.
4. Via the task manager.
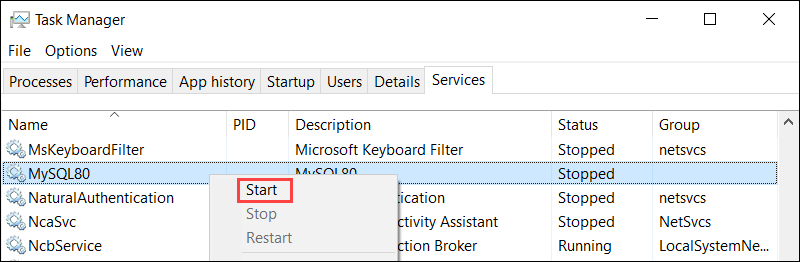
Another way to start MySQL is with the Windows Task Manager. Access the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) and go to the Services tab.
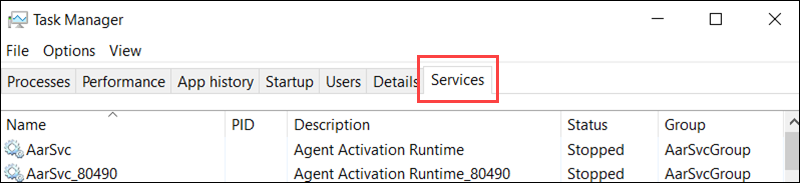
Locate the MySQL service, right-click on it, and select Start.
Start MySQL Server on Mac
Mac users who work with web applications and services that rely on MySQL databases, need to know how to start a MySQL server on this OS. Mac offers several ways to turn on MySQL.
1. Via the Terminal.
There are several commands to start the MySQL server via the terminal. Open the terminal and run:
mysql.server startThe output depends on the specific version of MySQL on Mac and the system configuration.
The second command executes the mysql.server script located in the /usr/local/mysql/support-files/ directory and starts the MySQL server. Run the following:
/usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start2. Via the System Preferences Panel.
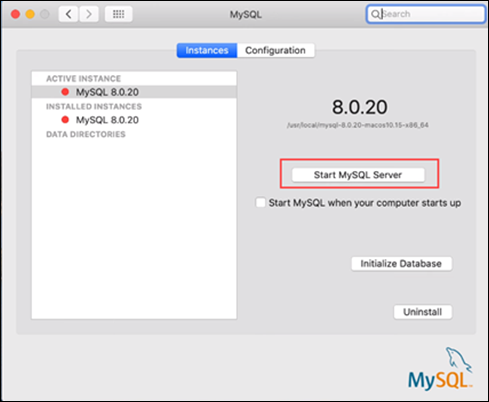
If the Terminal commands don't work, start MySQL by opening the System Preferences panel.

In the System Preferences section, choose the MySQL icon. Once the new window opens, click the Start MySQL Server button to start the server.
4. Using Homebrew.
Homebrew provides an easy and convenient way to install and manage MySQL on Mac. If MySQL is installed via Homebrew, run the following to start the server:
brew services start mysqlSince the command has no output, verify that the server is running with:
BB$ brew services list4. Using MySQL Workbench.
MySQL Workbench is a GUI tool that manages MySQL servers. MySQL Workbench interface offers plenty of ways to adjust and manipulate the server, as well as to set basic settings.
Note: Learn how to create MySQL database in Workbench.
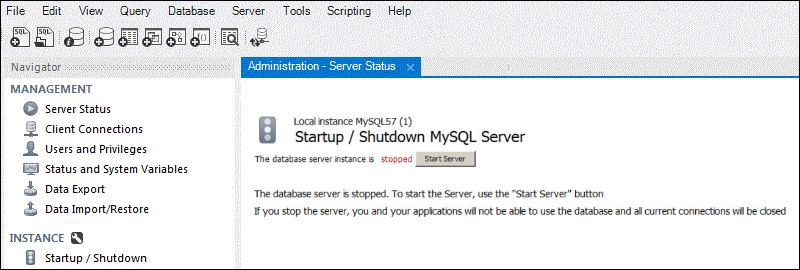
To start the server with MySQL Workbench, select Server from the top menu or Startup/Shutdown from the Navigator sidebar.
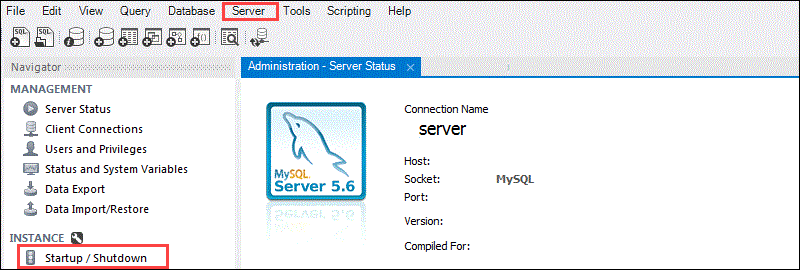
Once the MySQL server is visible, click the Start Server button,
Stop MySQL Server
The ability to suspend a MySQL server is fundamental for server management and database administration. Whether for maintenance, troubleshooting, or resource optimization, it is essential to know how to stop the server when needed.
The following sections show how to do it on different operating systems.
Stop MySQL Server on Linux
Shutting down a MySQL server on Linux depends on the distribution and init type, just like starting the server. The methods used to achieve a proper shutdown are presented in detail below.
systemctl Command
The systemctl stop command is the go-to method for stopping the server on modern Linux distributions that use systemd. The main syntax is:
sudo systemctl stop [process_name]The different names for the MySQL server process in Ubuntu and CentOS also apply here. Therefore, stop MySQL in Ubuntu with:
sudo systemctl stop mysqlThe command takes a few seconds to execute but produces no output. Verify the result with:
sudo systemctl status mysql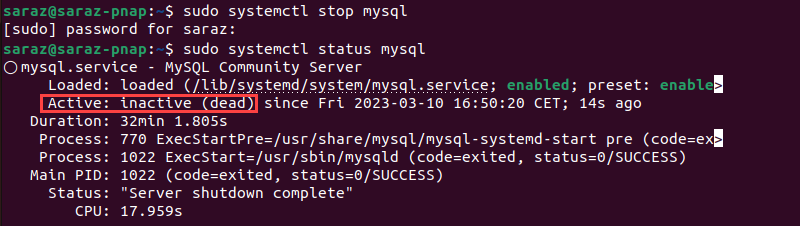
The same command applies to CentOS, Fedora, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux, with the change in the process name:
sudo systemctl stop mysqldservice Command
In older Linux distributions that use systemd, the service command is the preferred way of stopping MySQL. However, the command does work in new systems as well.
To stop MySQL on Debian, Ubuntu, or Linux Mint, run:
sudo service mysql stopCheck the server status with:
sudo service mysql status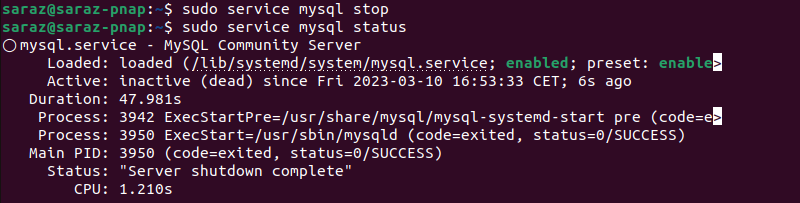
For CentOS, Fedora, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux, execute:
sudo service mysqld stopSince the command prints no output, verify the result with:
sudo service mysqld status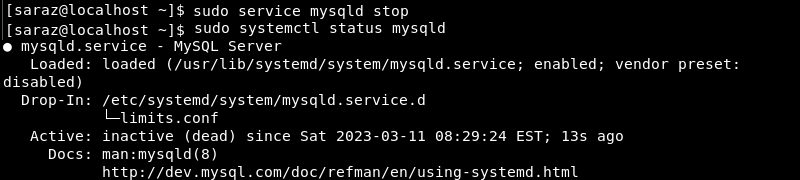
Note: The service and systemctl commands stop or restart a service in a controlled manner. Therefore, they are generally considered safe methods for stopping (or restarting) the MySQL server in Linux. Using other commands carries a higher risk of data loss or corruption.
mysql Script
The mysql script is used to stop the server in older Linux distros. To do this, use the following syntax:
sudo [script_path] stopFor example, if the script is located in /etc/init.d, run
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stopNote: The script has been deprecated in newer Linux distributions and triggers the system to run the systemctl command instead.
mysqld_safe Command
To shut down the MySQL server that is running using the mysqld_safe script with elevated privileges, execute the command with the --shutdown argument. The command stops the MySQL server by manually shutting down the MySQL process.
Execute the following:
sudo mysqld_safe --shutdown
The command logs any output to the error.log file and shuts down the server. However, this command is often unreliable. If an existing mysqld process is running, the --shutdown command may not stop the server or may lose data before shutting down the server.
mysqladmin shutdown Command
The mysqladmin command is a command-line utility that comes installed with the MySQL server and performs administrative tasks. Run mysqladmin with the shutdown argument to turn off the server:
sudo mysqladmin shutdown
The command stops the MySQL server, even if there are active client connections or running transactions, potentially resulting in data loss or corruption.
kill Command
Another way to terminate MySQL is with the kill command. The command first looks for the mysqld process ID (PID) with:
ps aux | grep mysqld
The command prints the mysqld PID. Use the PID with kill to stop MySQL:
sudo kill 3662
MySQL Client
MySQL client is a command-line tool that provides a simple interface to execute SQL commands and a simple way to stop the server. Execute the following to log in to the MySQL Client:
sudo mysql -u root -pProvide the MySQL root password when prompted.

Once the client starts, type SHUTDOWN; to stop the server and hit Enter. Typing exit gets you back to the CLI.

Stop MySQL Server on Windows
Windows also offers several ways to stop the MySQL server. The following text presents several methods to shut down this server on Windows.
mysqld command
The mysqld stop is the basic Windows command for shutting done MySQL. Access the terminal and type:
mysqld stopIf the command works, the terminal shows no output.
net stop command
If the mysqld stop is not an option, run net stop to shut down the server. First, run net start without arguments to find the MySQL version number. Next, scroll down to find MySQL and verify the version running on the system.
Execute the following command with the version number to shut down the server:
net stop MySQL80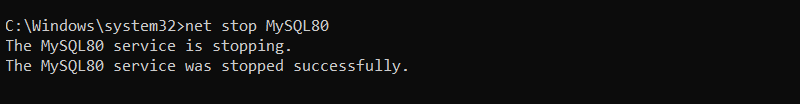
Services Window
Another way to shut down the MySQL server is to turn off its service. Access the Service Window through the Run dialog box (Windows key + R), by typing services.msc.
Scroll down to the SQL Server service, select it, and click Stop the service from the right-side menu.
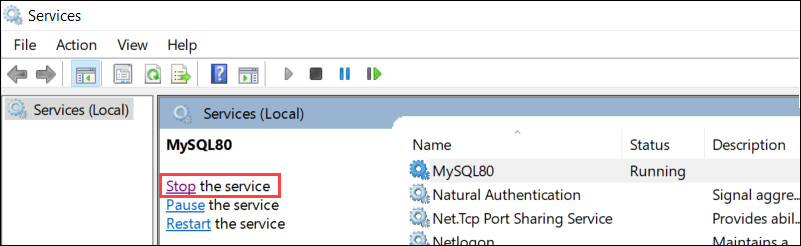
MySQL Command Line Client
MySQL Command Line Client is a tool that comes preinstalled with MySQL and enables users to perform different administrative tasks, such as shutting down the server.
Search for the MySQL Client in the Search bar and open the app.
Once the Client opens, provide the password and run:
SHUTDOWN;
Via the Task Manager
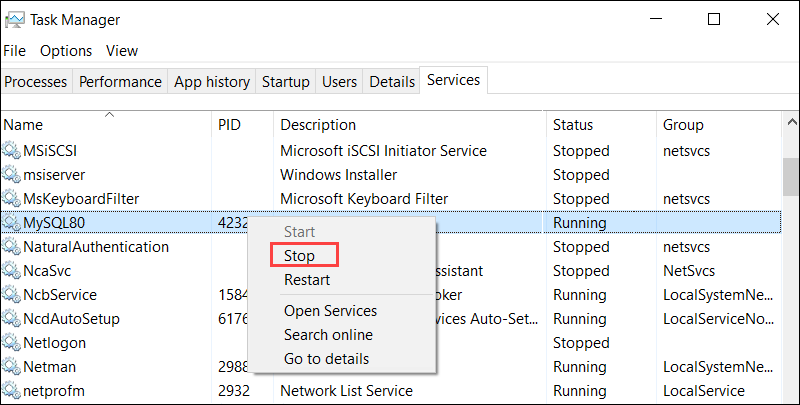
Windows Task Manager has the ability to stop any service, including MySQL. To accomplish this, access the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift +Esc) and choose the Services tab.
Find the MySQL service, right-click on it, and choose Stop:
Stop MySQL Server on Mac
There are several ways to shut down MySQL servers. The following text offers efficient methods for stopping MySQL both via the terminal and GUI.
Terminal
The basic command to stop MySQL on macOS is:
mysql.server stopThe output depends on the MySQL version, but it does inform the user that the server is shutting down.
An alternative command is:
/usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server stopSystem Preferences Panel
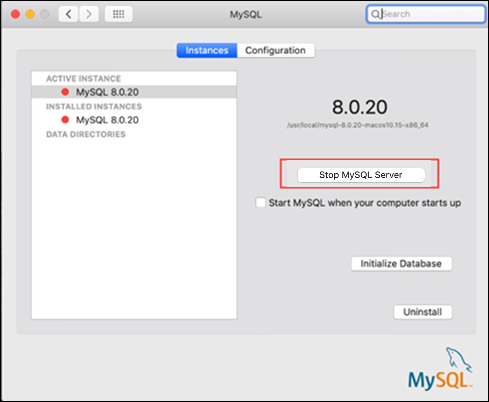
To shut down MySQL via the System Preferences Panel, access the panel and find and click the MySQL icon. Once the new window opens, click the Stop MySQL Server button to shut it down.
Using Homebrew
As an ultimate managing tool, Homebrew allows users to stop MySQL. Open the terminal and run:
brew services stop mysqlThe command has no output, but run the following command to verify the server is no longer running.
BB$ brew services listMySQL Workbench
One more way to stop the server is with the MySQL Workbench. Access the Startup/Shutdown Navigator section or the Server tab at the top menu. Shut down the server by clicking the Stop Server button.
kill Command
Turn off MySQL with the kill command. Execute the following:
sudo kill `cat /usr/local/mysql/data/*.pid`This command works by reading the PID of the MySQL server from the .pid file and terminating the associated process. If the process is successful, there is no output.
Restart MySQL Server
It's crucial to understand how to restart the MySQL server, as it allows users to resolve issues, implement configuration changes, upgrade the system, or perform maintenance tasks. While manually shutting down and restarting the server is an option, several methods simplify the process and enable a quick, efficient restart.
The following text shows how to accomplish this on different operating systems.
Restart MySQL Server on Linux
Linux offers three commands that allow for a one-step MySQL server restart. The following text elaborates on these methods:
systemctl restart Command
The systemctl restart command follows the same rules as the systemctl start and stop commands. The main syntax is:
sudo systemctl restart [process_name]For example, restart MySQL in Ubuntu with:
sudo systemctl restart mysql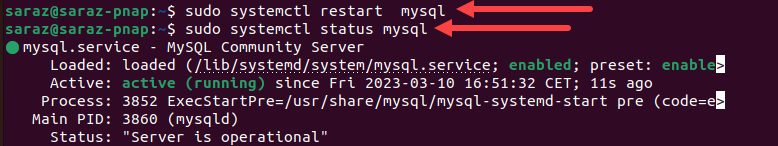
While the command shows no output, the systemctl status command verifies the result.
service restart Command
The service command is the go-to tool for restarting MySQL in older systems, though it works in newer distros as well. The syntax is:
sudo service [service_name] restartTo restart MySQL in older Debian, Ubuntu, and Linux Mint systems, run:
sudo service mysql restartAs the command has no output, verify the result with:
sudo service mysql status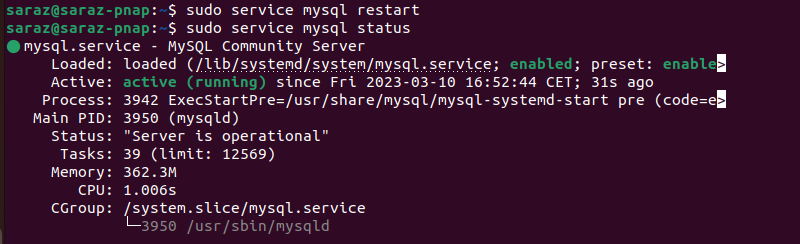
mysql Script
The mysql script offers another way to restart the server. The script is, by default, in the /etc/init.d directory.
Restart MySQL using the script with:
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restartThe command is used in older systems, where it provides no output. However, on newer distributions, the script is deprecated. When run in a newer distribution, the system replaces the script with the appropriate command. For example, in Ubuntu 22.04, the output is:

Restart MySQL Server on Windows
On Windows, there are a few ways to restart the MySQL server, such as using the mysqld or net start commands to stop and then start it again. However, there are also two other methods available to restart the server in a single step.
Services Window
Apart from starting and stopping MySQL, the Services Panel lets users restart the server. To accomplish this, access the Run dialog box (Windows key + R) and type in services.msc:
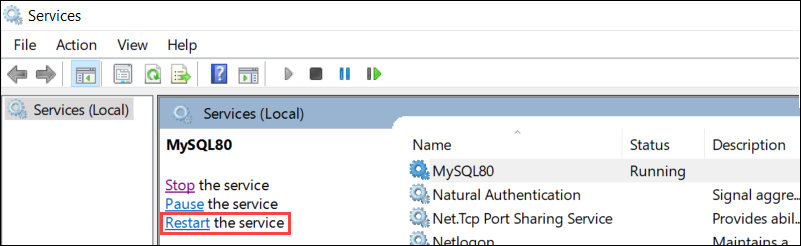
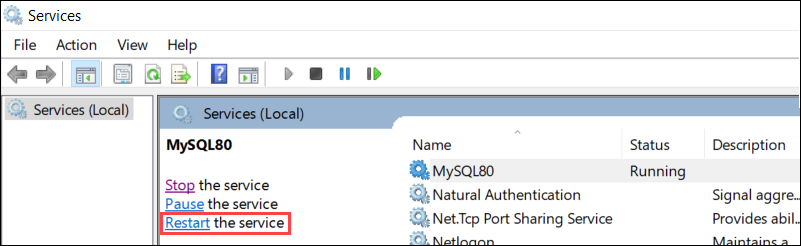
Once the Services Window opens, Find the MySQL Server service and select it. The right-side menu includes the name of the service and three options. Choose Restart the Service.
Task Manager
Windows Task Manager offers another way to restart MySQL in one go. After accessing the Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc), click the Services tab and look for the MySQL service.
Right-click on the MySQL service and choose Restart.
Restart MySQL Server on Mac
On macOS, users restart a MySQL server by either using the command line to shut it down and then start it up again or accessing the System Preferences panel or MySQL Workbench to turn it off and on. However, there are alternative methods available that are more efficient or easier to use.
Note: All of these methods require administrator privileges to execute.
Terminal
Using the Terminal is an efficient way to restart MySQL on macOS in one go. To restart the server via Terminal, use one of two commands:
mysql.server restartThe mysql.server restart command triggers the built-in MySQL server script, which restarts the server.
However, the command also stops any ongoing queries or active connections to the database. Therefore, users need to re-establish a connection to the server and restart their queries.
The alternative command is:
/usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server restartThe second command restarts the server using the MySQL server script located in the /usr/local/mysql/support-files/ directory, instead of the default, built-in script. Execute the command to specify which MySQL version to restart if multiple versions are present on the system.
Homebrew
For users who are familiar with Homebrew, the brew services restart command is a convenient option:
brew services restart mysqlConclusion
This tutorial explained how to start, stop, and restart a MySQL server on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
Next, learn how to create a table in MySQL.