Linux users have access to a variety of command-line utilities for network performance measurement, bypassing the need for web-based testing tools. These utilities enable analysis of both local network throughput and external internet connection speeds, and work reliably in both standard terminal sessions and headless server environments.
This guide shows how to test network speed on Linux using CLI.
Prerequisites
- A machine running Linux.
- Administrative permissions.
- Command-line access.
Test Network Speed on Linux Via Command Line
The tools in this guide help test the Internet and LAN speed on a Linux machine. Choose a tool and refer to the corresponding section below for the explanation on how to use it.
Note: Ensure you use the appropriate package manager for your distribution, e.g., APT for Ubuntu/Debian and DNF for Fedora/RHEL.
Using speedtest-cli to Test Internet Speed
One of the most famous online internet connection test apps is speedtest.net. To install Speedtest on Linux via the terminal, use your distro's package manager.
On Ubuntu, enter:
sudo apt install speedtest-cli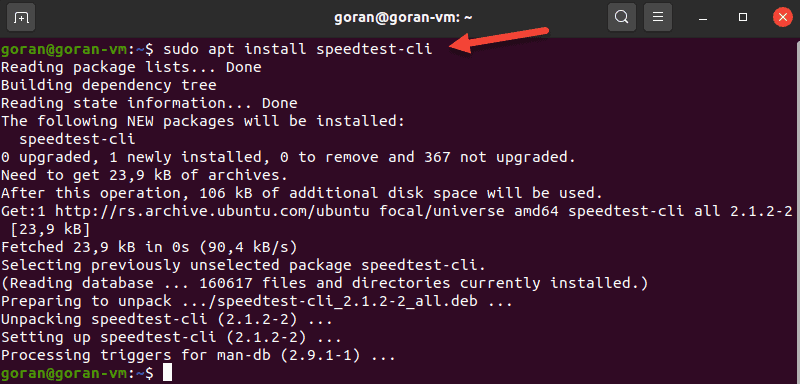
Optionally, use pip to install speedtest-cli in Python:
sudo pip install speedtest-cliTo run the test, type:
speedtest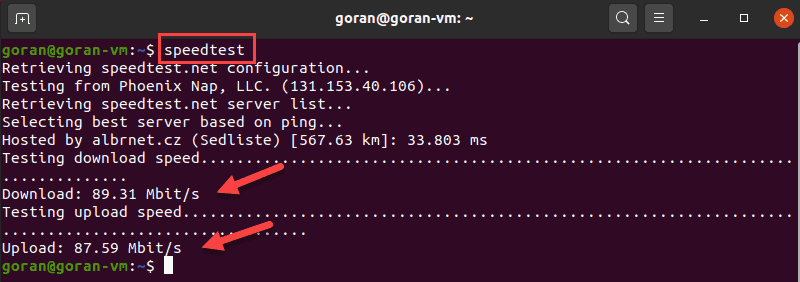
The standard speedtest-cli output shows all steps, including selecting a server. To display a shorter output, enter:
speedtest -simpleThe test is simple to use and provides multiple options. To view all of them, pass the -h flag to display the speedtest-cli help file.
Using fast-cli to Test Internet Speed
Fast is a lightweight CLI utility based on the fast.com web speed test. The test uses Netflix servers to provide results.
Fast-cli is simple to use, but you need the Node Package Manager (NPM) on your machine. The package comes with Nodejs.
For example, follow the steps below to install Node.js version 15:
1. Enter the command below:
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_15.x | sudo -E bash -Wait for the download to finish.
2. Run the install command:
sudo apt install -y nodejs3. If needed, run the npm init command and then install Fast:
npm install --global fast-cli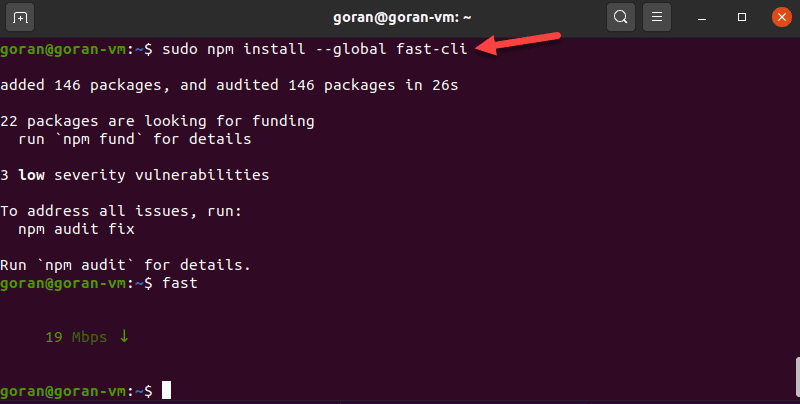
4. Test the download speed by entering:
fastTo show both the download and upload speed, add the -u option:
fast -u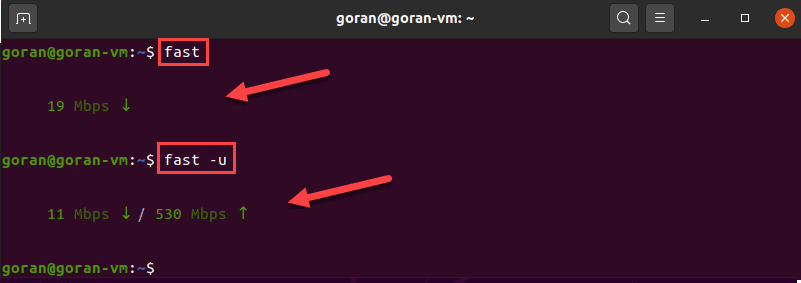
This internet speed test aims to provide only the information about your connection speed, without any bells and whistles.
Note: Since NPM is a requirement, installing fast-cli can be difficult for some. If you need more help with NPM installation, see our guides How To Install Node.Js And NPM On CentOS or How To Install Node.Js & NPM On Ubuntu.
Using CMB to Show Network Speed
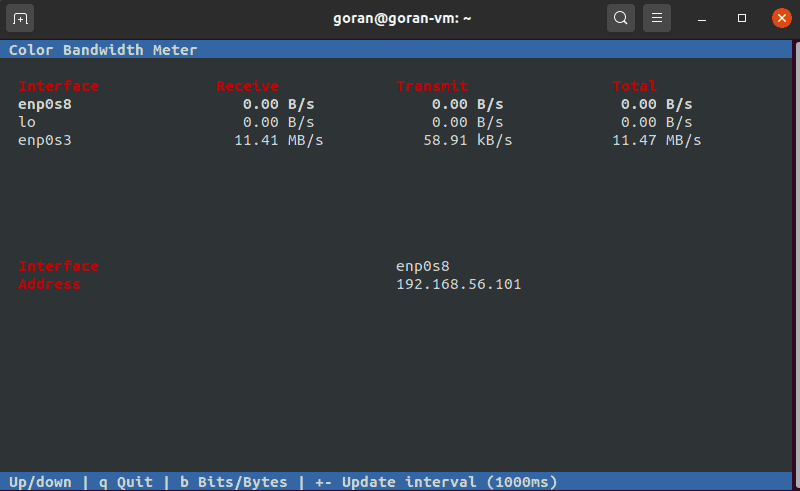
The Color Bandwidth Meter (CMB) is a Linux tool that displays activity on all network interfaces. After the installation, run the tool to see network speeds in color-coded columns.
To install CBM, run this command:
sudo apt install cbm
When the process finishes, run the tool:
cbmThe output displays the transmit, receive, and total speed. Use the arrows to switch between the interfaces.
Using iperf to Measure Network Speed Between Two Devices
The iPerf tool provides many options for testing the connection speed between a server and a client. Hence, to perform a test, you need to install the utility on both machines:
sudo apt install iperf
Make sure the client can reach the server. For quick confirmation, run a ping test.
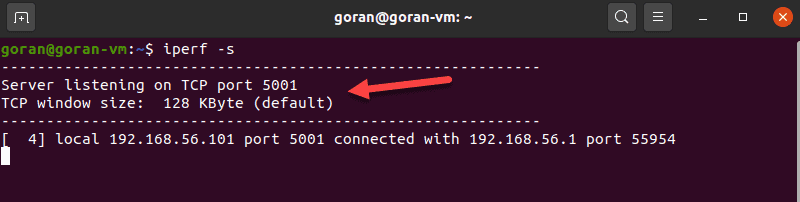
If port 5001 is open, the connection works. So, on the server machine, enter:
iperf -sThe device starts listening for a connection request.
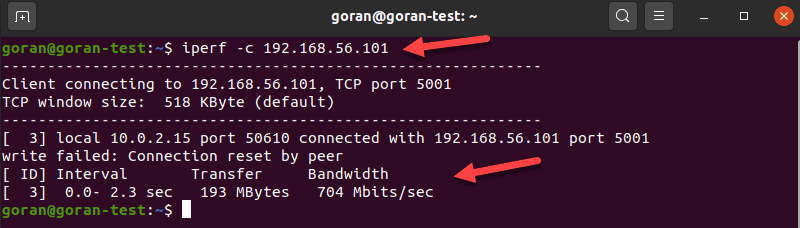
On the other machine, enter:
iperf -c [server_IP]For example:
iperf -c 192.168.56.101The output shows the transfer and bandwidth information:
Using nload to View Incoming and Outgoing Network Traffic
Nload is a tool that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic on the network interface you specify. The application splits the traffic into two sections for easier data analysis.
To install the tool, enter:
sudo apt install nload
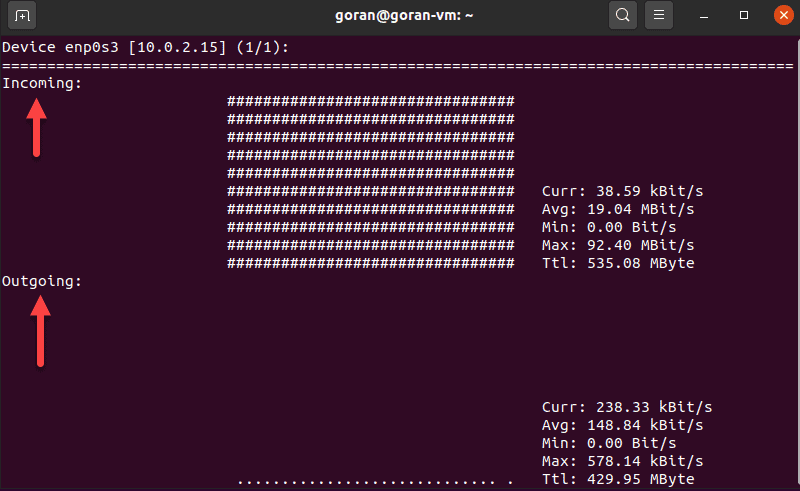
To run the application, specify the network interface:
nload enp0s3If there is activity on the selected interface, nload displays network speed details.
Using tcptrack to Test Network Activity
TCPtrack shows the connection status for a network interface. When the machine’s network is active, run this tool to view and monitor bandwidth speed and usage.
To install TCPtrack on Linux Ubuntu, enter:
sudo apt install tcptrack
View network activity with TCPtrack by specifying the network interface. To find the device name, use the ifconfig tool.
In the following example, the device name is enp0s3.
sudo tcptrack -i enp0s3The terminal displays the network activity on the selected interface. The total network speed is at the bottom of the terminal:
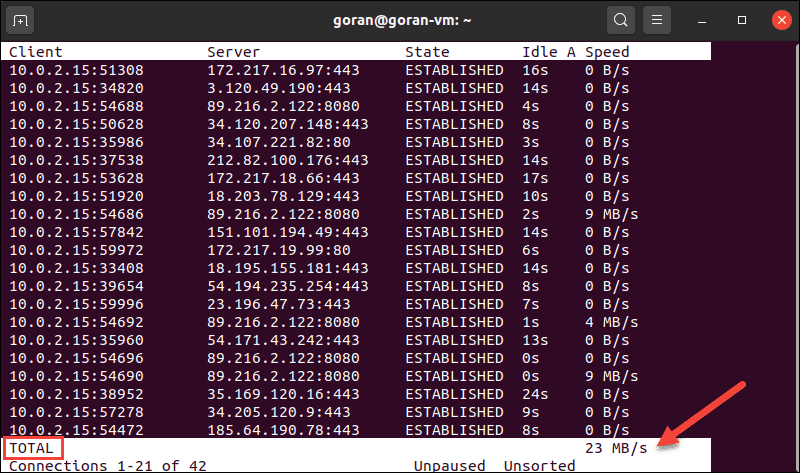
Note: Make sure you run tcptrack with sudo. Otherwise, this error pops up: pcap_open_live: enp0s3: You don’t have permission to capture on that device (socket: Operation not permitted)
TCPtrack is customizable and offers options to narrow down the test to specific ports, for example.
To do so, pass the port argument followed by the port number:
sudo tcptrack -i enp0s3 port 443If there is no activity on the port, the output is blank.
Using iftop to Test Speed on a Network Interface
Iftop lets you view network speed for a defined interface. The tool produces output similar to that of TCPtrack.
To install iftop, run this command:
sudo apt install iftop
To launch the utility, use the -i flag and specify your network interface. For example:
sudo iftop -i enp0s3The output shows the device's activity. The bottom of the screen provides a traffic summary.
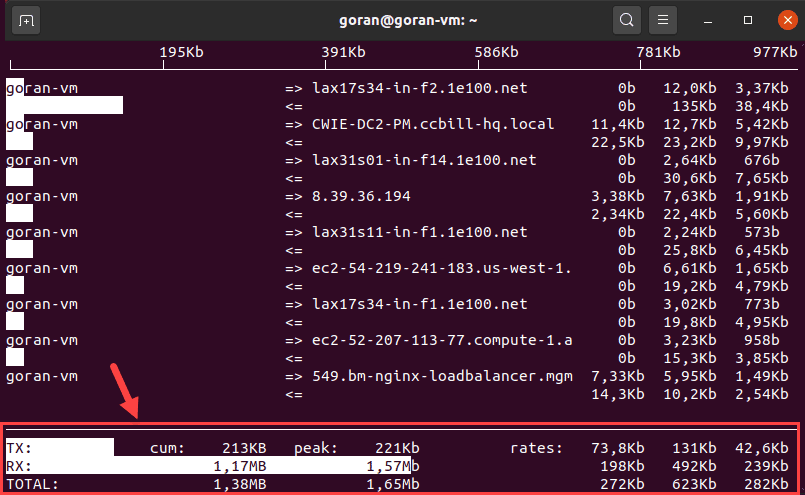
If no network interface is specified, iftop selects the first available. Run the command with sudo to avoid errors.
Using wget to Test Download Speed
Wget is a CLI tool for downloading content from web servers. Since the tool does not upload files, use it to test the download speed.
If you do not have wget on your Ubuntu machine, enter the command below to install it:
sudo apt install wgetChoose a reliable server to download a file and test your internet speed. For example, use phoenixNAP’s 1GB test file from the list.
This example uses a server located in Phoenix:
wget -O /dev/null -q --show-progress http://174.138.175.114/PHX-1GB.test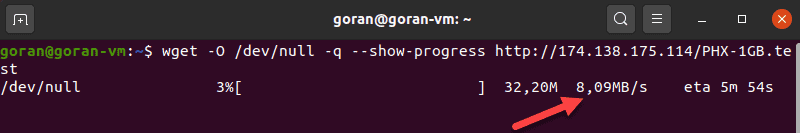
Using youtube-dl to Test Internet Speed
An unconventional way to test download speed is to use the youtube-dl CLI utility. The tool allows users to download YouTube videos and view download speeds. Follow the steps below to test internet speed with youtube-dl:
1. Install youtube-dl:
sudo apt install youtube-dl2. Choose the video to download and save its URL.
3. Enter the following command, replacing [url] with the chosen URL:
youtube-dl -f best --no-part --no-cache-dir -o /dev/null --newline [url]The terminal shows the download progress, file size, download speed, and ETA.
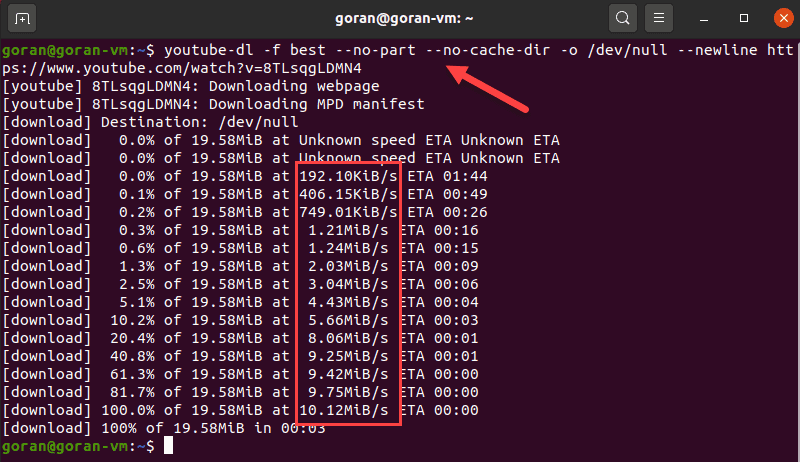
The command above does not save the file to any filesystem, hence the /dev/null part.
This example used a short phoenixNAP BMC demo video of around 19MB. Choose a longer video for more precise results.
Conclusion
The article showed nine ways to test network speed in Linux via CLI. Choose the tool depending on whether you want to test local network speed, internet speed, etc.
The tools work for all Linux distributions, so make sure you use the right package manager.