As the basic units of Kubernetes deployments, pods provide storage and network access for the containerized apps. Due to their ephemeral nature, pods can fail for multiple reasons. However, Kubernetes offers automatic and manual ways to restart them.
This tutorial will explain how to restart pods in Kubernetes manually.

Prerequisites
- Command-line access.
- A Kubernetes cluster.
- kubectl command-line tool.
How to Restart Pod in Kubernetes
The kubectl command-line tool does not have a direct command to restart pods. However, the following workaround methods can save you time, especially if your app is running and you do not want to shut the service down.
Depending on the restart policy, Kubernetes may try to restart the pod automatically. If Kubernetes cannot fix the issue or the administrator needs to restart a healthy pod, a manual restart may be necessary.
Note: Modern DevOps teams have a shortcut to redeploy the pods as a part of their CI/CD pipeline. While this method is effective, it can take quite a bit of time. Your pods will have to run through the whole CI/CD process.
The following sections cover five simple methods to restart Kubernetes pods in an active deployment.
Via kubectl scale Command
The scale command changes how many replicas of the malfunctioning pod are running. Setting this amount to zero turns the pod off.
Follow the procedure below to use the scale command to restart pods:
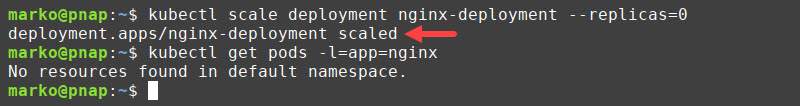
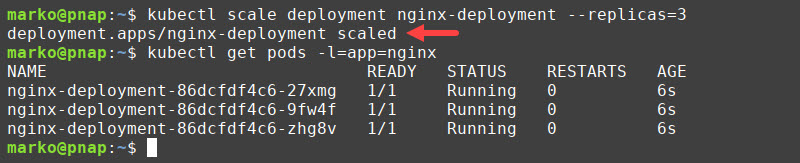
1. Scale the number of replicas to zero by typing:
kubectl scale deployment [deployment-name] --replicas=02. Test the results by listing the pods that belong to the deployment:
kubectl get pods -l=app=[deployment-app-label]The output confirms that no pods are running after the scaling.
3. Restart the pods with the scale command by providing a non-zero number to the --replicas flag:
kubectl scale deployment [deployment-name] --replicas=[number-of-replicas]Kubernetes creates new pods to achieve the desired state of the system.
Via kubectl delete pod Command
Kubernetes always attempts to maintain the desired deployment state defined in the YAML file. Therefore, when the user manually deletes a pod, Kubernetes creates a new one as a replacement, effectively restarting the pod.
To delete a pod and force Kubernetes to generate another one, type:
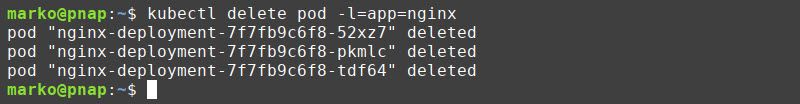
kubectl delete pod [pod-name]While this method can be used with a small number of pods, it is impractical in larger deployments. A workaround is to use labels, i.e., simple key-value pairs assigned to pods. Enter the following command to delete multiple pods with the same label:
kubectl delete pod -l=[label-key]=[label-value]For example, to delete all pods labeled app:nginx, type:
kubectl delete pod -l=app=nginxKubernetes finds all pods with the nginx label and deletes them at once. The pods are then automatically regenerated.
Via kubectl rollout restart Command
As of update 1.15, Kubernetes allows a rolling restart of a deployment. Perform a rolling restart with the following command:
kubectl rollout restart deployment [deployment-name]The above command performs a step-by-step shutdown and restarts each pod in the deployment. The app remains available as most pods are running at any given time.

Note: Learn how to monitor Kubernetes with Prometheus. Monitoring Kubernetes gives you better insight into the state of your cluster. To better manage the workload complexity, we suggest you read our article Kubernetes Monitoring Best Practices.
Via kubectl set env Command
Another method is to set or change an environment variable to force pods to restart and sync up with the changes you made.
For instance, you can change the container deployment date with:
kubectl set env deployment [deployment-name] DEPLOY_DATE="$(date)"The kubectl set env command changes the DEPLOY_DATE environment variable and forces the pod to restart.

Note: Learn more about using environment variables by referring to our tutorials on Setting Environment Variables in Linux, Setting Environment Variables in Mac, and Setting Environment Variables in Windows.
Via kubectl replace Command
Passing a pod declaration to the kubectl replace command tells Kubernetes to replace the given pod with a new one. Follow the steps below to restart a pod this way:
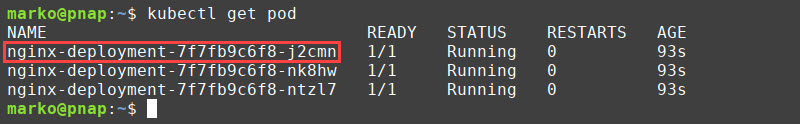
1. List the running pods:
kubectl get pod2. Note the name of the pod you want to restart.
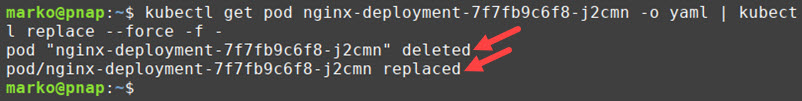
3. Execute the following command:
kubectl get pod [pod-name] -o yaml | kubectl replace --force -f -The command obtains the pod's YAML and pipes it to kubectl replace. The output confirms the pod was deleted and replaced.
Why Restart Kubernetes Pods?
Restarting a pod is an action Kubernetes administrators perform frequently and for many reasons. Some of the most important reasons include:
- A pod is stuck in an error or a terminating state.
- A pod configuration update (e.g., an update to environment variables, secrets, ConfigMaps) requires a manual pod restart to apply the changes.
- Restarting pods may eliminate Kubernetes as a culprit when troubleshooting misbehaving apps.
- A pod consumes too many resources, or Kubernetes terminates a pod due to an OOM (Out of Memory) error.
Conclusion
Use the five methods listed in our tutorial to restart Kubernetes pods quickly and safely. Knowing how to restart pods correctly lets you update, maintain, or troubleshoot your system without shutting down the service for your customers.
Next, learn more about Kubernetes objects by reading our Kubernetes Objects Guide.