Nmap (Network mapper) is a powerful network discovery and network security auditing tool. It is free, open-source, and easy to install. Nmap scans for vulnerabilities on a network, performs inventory checks, and monitors host or service uptime, alongside many other useful features.
System and network administrators use Nmap to scan networks, identify connected devices, check open ports, and gather data about running services. The tool supports various scanning techniques, including UDP, TCP, and stealth scanning. Nmap is an essential tool for cybersecurity and IT professionals.
This tutorial shows how to install Nmap on Ubuntu in three simple steps.
Prerequisites
- Access to a terminal.
- The APT package manager.
- A user with sudo privileges.
Note: The steps in this guide are tested and working on Ubuntu 18.04, 20.04, 22.04, and 24.04.
Step 1: Update Ubuntu Package List
Before installing software on Ubuntu, update the system's package list to ensure the latest version and avoid dependency issues.
Run the following command to update the package list:
sudo apt update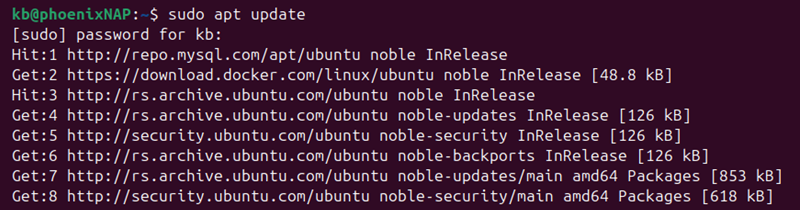
The system updates the package lists and confirms that the action is complete. Once the update is completed, proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Install Nmap
To install Nmap on Ubuntu, run the command:
sudo apt install nmap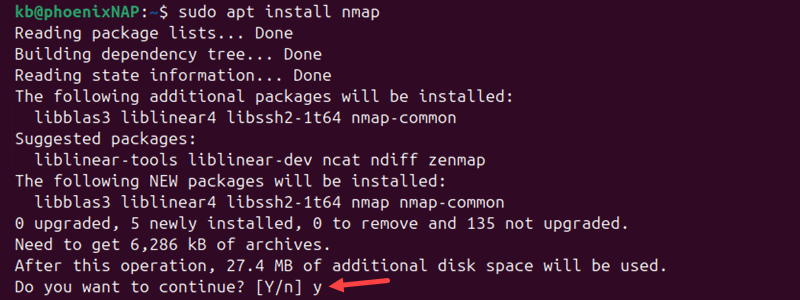
The system prompts you to confirm and continue the installation. Press y and then Enter to continue. After confirming, the package manager downloads and installs Nmap and any dependencies.
Note: For different installation methods, see our in-depth guide on installing and useing Nmap on Linux.
Step 3: Verify Nmap Version Installed
Verify the installation was successful by checking the Nmap version:
nmap --version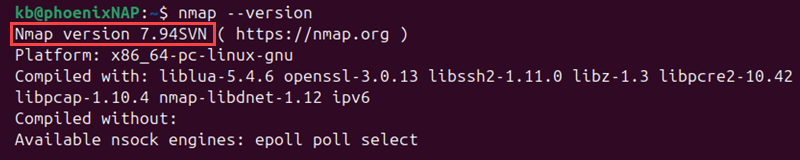
The output shows detailed information about Nmap and build details.
Additional Nmap Usage Examples
Nmap has a variety of scanning options to address different use cases. Common examples include:
- Scan a single specific host or IP address:
nmap 192.168.1.1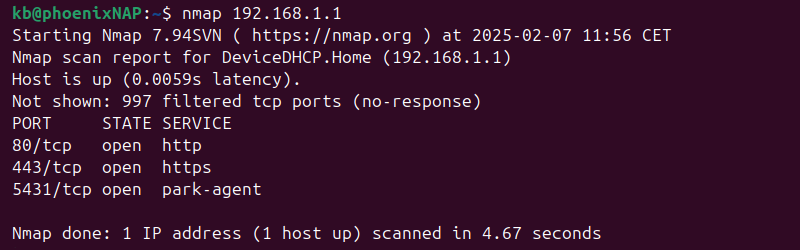
- Scan devices in a subnet:
nmap -sP 192.168.1.0/24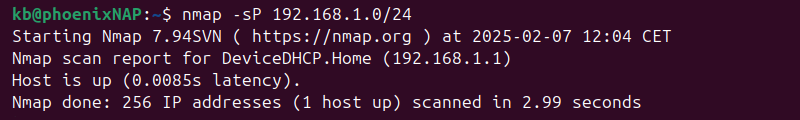
nmap -p 1-65535 192.168.1.1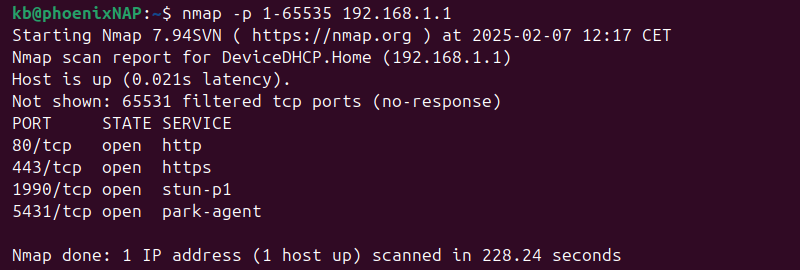
- Identify running services and their versions:
nmap -sV 192.168.1.1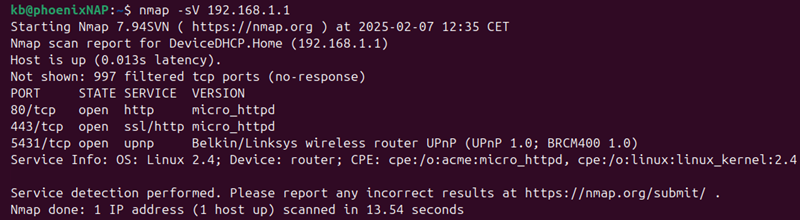
Note: Nmap has many options available for scanning scan remote systems. Explore the most common Nmap commands.
Conclusion
This guide showed how to install and use Nmap on Ubuntu. This versatile and powerful network scanning tool is easy to install.
Next, see our comprehensive list of Linux network commands, which includes a free cheat sheet.