Git tags are milestones in a project development history, such as patches, bug fixes, or new program versions. When debugging or developing a new feature, it is sometimes easier to clone those specific points than to clone an entire repository or development branch.
In this tutorial, you will learn to clone a Git tag.

Prerequisites
- Git installed (install Git on Windows, macOS, Ubuntu, CentOS 7, or CentOS 8).
- A remote and local Git repository.
- A GitHub account.
How to Clone a Specific Git Tag
Cloning a git tag requires a repository URL and running a specific command. Follow the steps below to clone a Git tag.
1. Obtain Git Repository URL
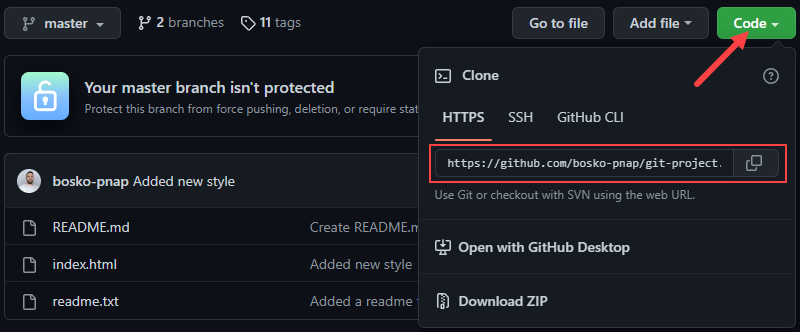
Log in to your GitHub account and select your repository. Click the Code button and copy the repository URL.
Note: Learn also how to clone Git submodules.
2. Clone Git Tag
Use the following syntax to clone a particular tag:
git clone -b [tag_name] [repository_url]- Replace
[tag_name]with the name of the tag you want to clone. - Replace
[repository_url]with the repository link obtained in the previous step.
For example:
git clone -b v1.2 https://github.com/bosko-pnap/git-project.gitThe command clones tag v1.2 from the specified repository URL.
Note: To download only the latest commit in the branch and reduce the download size, add the --depth 1 flag to the command.
After cloning the tag, Git states that the repository is in a detached HEAD state. The state occurs because the tag is in the middle of long commit history. Therefore, adding new commits can disturb the Git blockchain.
A detached HEAD still allows you to make and commit changes, but they don't update the repository. Instead, the changes create a new detached commit, which doesn't easily merge back to the master branch.
The detached commits don't belong to any branch, and they are only reachable directly by the commit's SHA hash. Resolve the detached HEAD state by creating and switching to a new branch before committing any changes.
Note: Git tags are objects, which means checkout works with Git tags as well. Follow our tutorial and see how to checkout a Git tag and resolve the detached HEAD state.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to clone a specific Git tag and resolve the detached HEAD state resulting from the tag cloning process.
For more Git tutorials, see how Git works or learn to work with Git Bash effectively.



