Debian 12 (Bookworm) is a stable version of the Debian Linux distribution released in 2023. It replaced version 11 (Bullseye) and introduced new features and improvements, including Linux kernel 6.1, APT Package Manager 2.6, and new versions of popular desktop environments.
This article will show you how to upgrade an existing Debian 11 installation to Debian 12.
Prerequisites
- Debian 11 installed.
- Command-line access.
- Root access or sudo privileges.
Why Upgrade to Debian 12?
Debian maintainers strongly recommend upgrading to the newest release as soon as possible. Older versions receive security updates for 12 months after the release of the succeeding stable version. Upgrading keeps the system secure after the grace period. Debian 12 was released in June 2023, so the official support for Debian 11 ended in July 2024.
Other reasons to upgrade to Debian 12 include:
- Long-term support (LTS). Debian 12 is an LTS release, meaning it will remain supported for 5 years until 2028.
- Better performance and compatibility with new hardware.
- Updated apps, such as Firefox, LibreOffice, and GIMP.
How to Upgrade from Debian 11 to 12
Upgrading from Debian 11 to 12 involves updating packages from the old release, updating the APT sources list, and migrating the operating system to the new version. Follow the steps below to learn how to upgrade a Debian 11 system.
Step 1: Backup System
A Linux system upgrade is a complex process that can result in data loss. Before upgrading to Debian 12, a full system backup is recommended.
Use tools such as Timeshift or rsync to create and store a system backup securely, then proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Update Debian 11
Start the upgrade by updating the current Debian 11 installation and obtaining the latest packages. Follow these steps:
1. Use APT to refresh the package list and perform the necessary package upgrades:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y2. Execute the full-upgrade subcommand to install packages necessary for the release upgrade.
sudo apt full-upgrade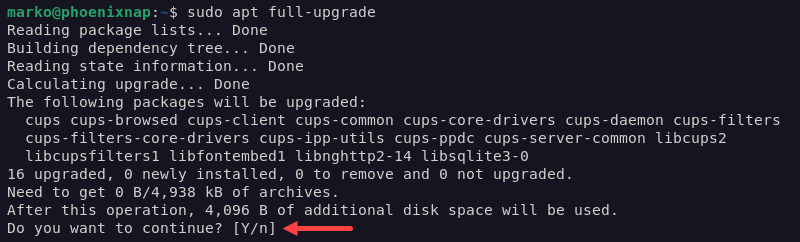
3. Remove the unnecessary packages:
sudo apt autoremoveStep 3: Update APT Sources List
The sources.list file contains a list of repositories Debian uses to look for packages. Follow the steps below to edit the file and prepare Debian 11 for an upgrade:
1. Open the sources.list file in a text editor. The following example uses Nano:
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list2. Change all the Debian 11 (bullseye) references to Debian 12 (bookworm).
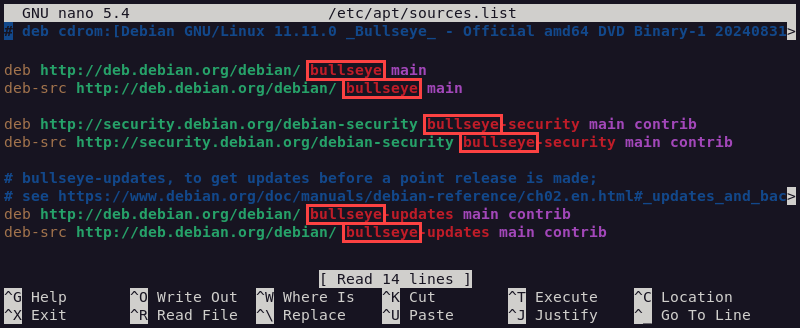
The following is what the updated file should look like:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian/ bookworm main
deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian/ bookworm main
deb http://security.debian.org/debian-security bookworm-security main contrib http://security.debian.org/debian-security bookworm-security main contrib
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian/ bookworm-updates main contrib
deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian/ bookworm-updates main contrib3. Save the file and exit.
Note: If you added other repositories to the sources.list file, ensure they are compatible with Debian 12, or remove them before proceeding.
4. Update the sources list:
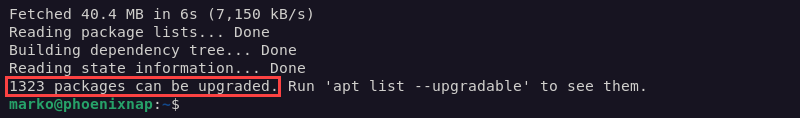
sudo apt updateThe output shows new upgrades are available.
Step 4: Perform Upgrade
With the sources-list file configured, apply the steps below to finish upgrading Debian 11 to 12:
1. Start the package upgrade:
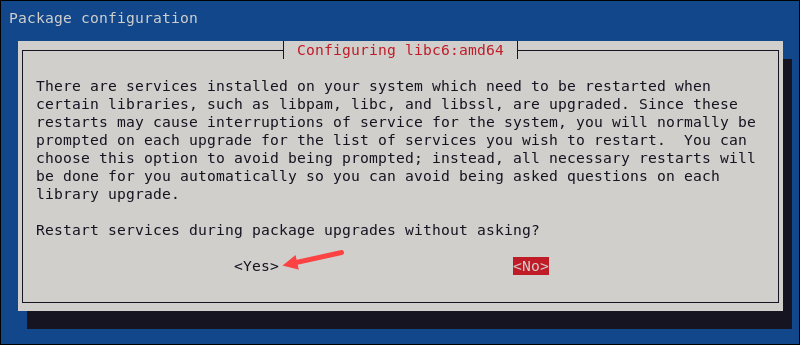
sudo apt upgrade -y2. Select Yes to restart services automatically during package upgrades.
3. Install packages necessary to achieve a fully upgraded state:
sudo apt full-upgradeThe full-upgrade subcommand installs new and removes unnecessary old packages.
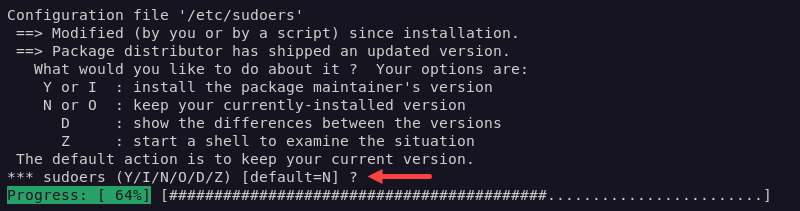
4. During the upgrade, the system may prompt the user to resolve package conflicts. Address each issue on a case-by-case basis.
To leave all the files unchanged, enter N for each prompt. The example below shows the system detecting changes to the /etc/sudoers file.
Step 5: Clean Up System and Reboot
Once the system finishes the upgrade, use the command below to remove any Debian 11 leftover files:
sudo apt autoremoveReboot the system for the changes to take effect:
sudo rebootStep 6: Verify Upgrade
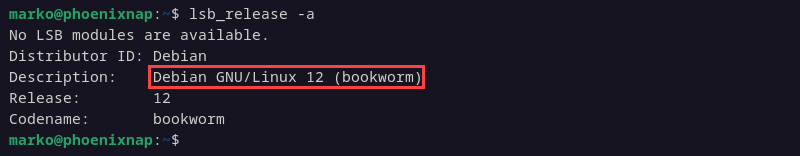
Check the current Debian version to confirm that the upgrade was successful. Enter the following command:
lsb_release -aThe output shows basic information about the system. The Description field references Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm).
The Debian installation is now upgraded to Debian 12.
Conclusion
This tutorial taught you how to upgrade Debian 11 to Debian 12 safely. The article also highlighted the importance of keeping your Debian system up to date.
If you are a Linux beginner, read our Linux Commands Cheat Sheet and download a handy PDF for future reference.