Go, or Golang, is an open-source language created by Google. Its purpose is to streamline software development and enable users to create simple and reliable apps.
As a modern language, Go offers memory allocation, concurrency support, garbage collection, and coordination avoidance.
This article explains how to install Go on Debian 12 in a few simple steps.

Prerequisites
- Debian system (this tutorial uses Debian 12).
- A sudo user.
- Access to the command line.
How to Install Go on Debian 12
Before starting the installation, ensure the Debian server is up to date. Update the repository with the following:
sudo apt update -y
Step 1: Download Go
To start the installation process:
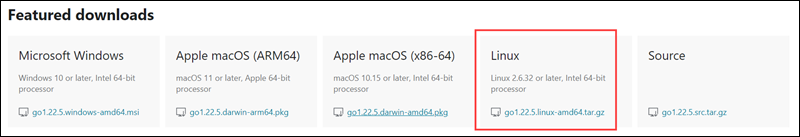
1. Visit the Go downloads page.
2. Click the Linux box under Featured downloads to start the download.
Step 2: Extract Files
Extract files to the /usr/local directory. To do that, take the following steps:
1. Navigate to Downloads using the cd command:
cd ~/Downloads
2. Run the following command to extract files:
sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.22.5.linux-amd64.tar.gz
The command doesn't print any output. However, tar extracts the specified file (go1.19.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz) to the desired directory.
Step 3: Set the Environment
To set the environment variable, add /usr/local/go/bin to PATH.
Take the following steps:
1. Access .profile in Vim or another text editor.
vim .profile2. At the end of the file, paste the following lines:
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
export GOPATH=$HOME/go
export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin
4. Reload your shell configuration to apply the changes with:
source ~/.profileThe command has no output.
Note: To install Go system-wide, edit /etc/profile. To install it for the current user, access $HOME/.profile.
Step 4: Test the Installation
After installing Go and setting the paths, verify that Go is functioning properly. To do that, set up a basic Go development environment and create a simple "Hello, World!" program.
Take the following steps:
1. Create a new directory for your Go workspace where Go will compile its files. Use the mkdir command:
mkdir $HOME/go_workspaceThe command has no output.
2. Set up a directory structure within this workspace. In this example, we use a directory called my_project:
mkdir -p $HOME/go_workspace/src/my_project/helloThe command consists of:
mkdir. The command that creates the necessary directory.-p. The option that ensures any necessary parent directories are created along with the target directory.go_workspace. The main workspace directory for Go projects.src. A common subdirectory in Go workspaces where source code files are stored.my_project. A project-specific directory within thesrcdirectory.hello. A subdirectory withinmy_projectwhere the "Hello, World!" Go program will be placed.
3. Open a new file to place the new Go program:
vim $HOME/go_workspace/src/my_project/hello/hello.go4. Paste the following into the file:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello, World!")
}
The code includes the main Go package, imports the formatted I/O package, and defines a function to print "Hello, World!" when executed.
5. Save and exit the file.
6. Go to the project directory:
cd $HOME/go_workspace/src/my_project/hello
7. Compile the program with the following:
go install
8. Run the compiled program with:
hello
The output shows that Go is installed, and you can run Go programs.
Conclusion
This tutorial explained how to install Go on Debian, set environment variables, and test the installation using a simple example.
Next, learn about Go maps, one of the most efficient data structures for key-value pair management, or read about the differences between a Debian and a Ubuntu server.