Node.js is an open-source JavaScript (JS) runtime environment for developing web applications. It is lightweight and efficient, thanks to its event-driven, non-blocking I/O model and cross-platform support.
There are several ways to install Node.js on Debian. The best approach depends on the specific Node.js version.
This guide explains how to install Node.js on Debian using three different methods.
Prerequisites
Note: For other operating systems, check out the following guides:
Method 1: Install Node.js via apt
The simplest way to install Node.js on Debian is from the official repository. This method is straightforward and sufficient for development purposes.
Note: The Node.js version included in the repositories may be outdated. While older Node.js versions are suitable for development environments, they are not recommended for production environments.
Follow the steps below to install Node.js using the APT package manager.
Step 1: Update the Repository
Before installing Node.js, make sure the repository is up to date. To update system repositories, run the following apt command:
sudo apt update
Then, upgrade packages to the latest version:
sudo apt upgrade
After updating and upgrading the repository, proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Install Node.js
Use apt install to install Node.js and the Node Package Manager (NPM), the default package manager for Node.js.
Run the following command:
sudo apt install nodejs npm -y
The command also installs any required dependencies for both packages.
Step 3: Verify the Installation
Run the node command with -v to check the Node.js version and verify the package installation:
node -v
Confirm NPM is installed with:
npm -v
Both commands show the program version.
Method 2: Install Node.js via NodeSource PPA
The latest version of Node.js may not be available in the APT repository. To get a newer version, use the PPA repository by NodeSource. This method lets you choose a specific version that isn't available in the repositories.
Step 1: Install the curl Command
Installing Node.js from PPA requires the curl command. To install the latest curl version, run:
sudo apt install curl
The output shows that curl is up to date. If not, the system updates the command. To verify the installation, run:
curl --version
Step 2: Add PPA to the System
Add PPA to the system and install it with:
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_18.x | sudo -E bash -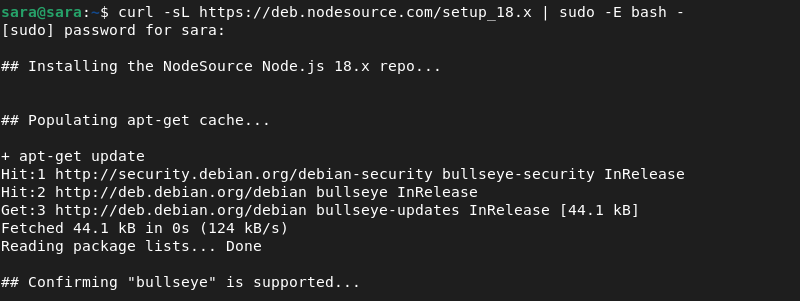
The command downloads and runs the Bash script to add the package to the repository listing.
Note: NodeSource offers different Node versions. The example above uses 18.x. To download another version, replace 18.x in the previous command with another version number.
Step 3: Update the Repository
Once the system adds the PPA, update the repository:
sudo apt update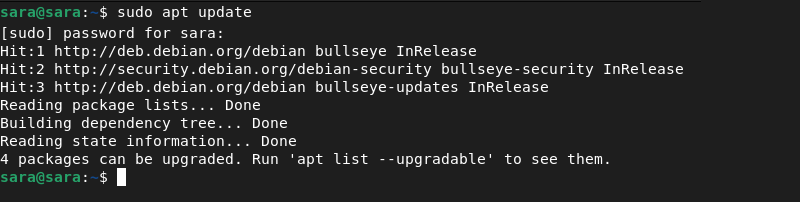
Check for upgrades with:
sudo apt upgrade
Step 4: Install Node.js and NPM
When installing from the PPA, Node.js and NPM are bundled together. Install both with:
sudo apt install nodejs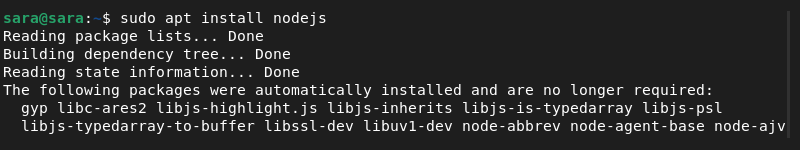
Step 5: Verify the Installation
To confirm Node.js and NPM are installed, check their versions:
node -v
npm -v
Method 3: Install Node.js via NVM
Another way to install Node.js on Debian is with the Node Version Manager (NVM). NVM manages installed Node.js versions and enables switching between them in the terminal. Use this method to work with multiple Node.js versions on the same system.
Note: Learn about the differences between NVM vs. NPM.
Step 1: Get the Installer Script
To install NVM, download the installer from GitHub. Run the following command:
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/creationix/nvm/master/install.sh | bash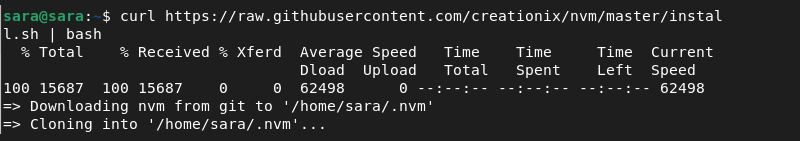
The command downloads and runs the Bash script to install NVM.
Step 2: Reload the Bash Profile
To add the path to the NVM script in the current shell session, restart the terminal or source the .profile file:
source ~/.profile
Both methods apply the file contents to the shell session and enable using the nvm command.
Step 3: List Node.js Versions
Run the following to list all available Node.js versions:
nvm ls-remote
The command prints all available Node.js version numbers.
Step 4: Install Node.js
Use nvm install to download and install your preferred Node.js version. For instance, to install version 12.1, run:
nvm install 12.1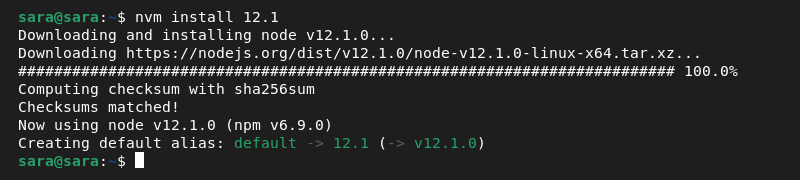
The installed version becomes the system's default Node.js. To confirm, run:
node -v
The newly installed version is shown in the output.
Step 5: Switch Versions
NVM allows users to download and install multiple Node.js versions on the same system. For instance, you can download and install versions 18.1 and 16.5:
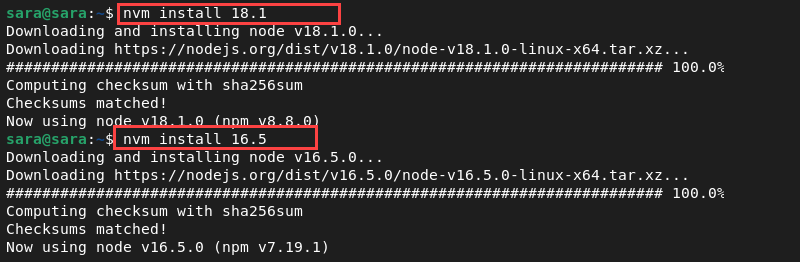
List all installed versions with the following command:
nvm ls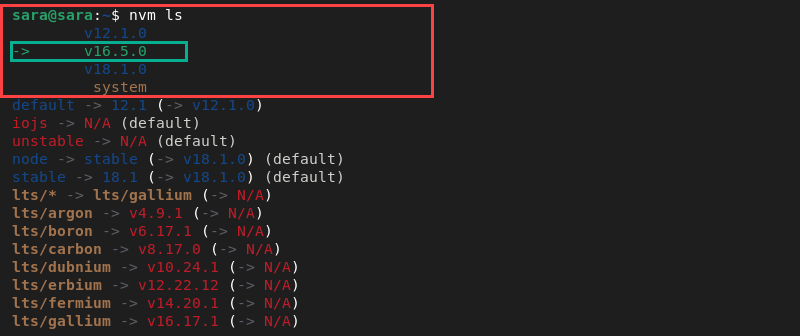
The command shows three versions, with the currently active one shown with a pointer printed in green.
To switch to another installed version, use:
nvm use 18.1
The nvm ls output also shows the current default version as 12.1.
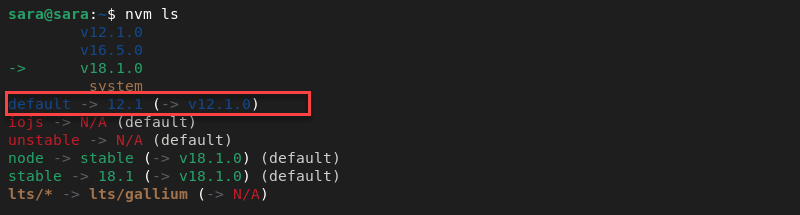
To change the default Node.js version, use:
nvm alias default 18.1
Node.js now defaults to the selected version.
Conclusion
This guide demonstrated various methods for installing Node.js on Debian. It also showed how to use NPM to manage Node.js packages and handle different Node.js versions.
Next, learn how to update Node.js to the latest version or how to build a Node.js app with Docker.