The Python programming language is known for its user-friendly syntax, simple semantics, and a vast collection of frameworks and libraries. Python is used extensively in web development, analytics, machine learning, and data science projects.
The python: command not found error occurs when the system cannot find the Python executable file, preventing users from executing Python commands or running scripts.
Learn how to resolve the python: command not found error and continue coding without interruptions.

Prerequisites
- A user account with root or sudo privileges.
- Access to a command line/terminal window.
What Causes the "python: command not found" Error?
The main causes of the python: command not found error include the following:
- Python is not installed.
- The PATH variable does not contain the Python executable path.
- The Python symbolic link is not configured correctly.
To fix the python: command not found error:
- Verify the Python installation and install Python if necessary.
- Edit PATH variable to include the Python executable path.
- Add or modify symbolic links to ensure correct Python version usage.
Install Python
The fastest way to determine if Python is installed is to check the Python version. Use the following command to check the Python 3 version:
python3 --version
If Python is installed, the terminal displays the version number. In this example, the Python version is 3.9.2.

If you receive the python: command not found error, use the instructions for your Linux distribution to install Python 3.
| Linux Distribution | Step 1: Update Package Lists | Step 2: Install Python 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Debian | sudo apt update | sudo apt install python3 |
| Ubuntu | sudo apt update | sudo apt install python3 |
| Fedora | sudo dnf update | sudo dnf install python3 |
| Arch Linux | sudo pacman -Syu | sudo pacman -S python |
| Rocky Linux | sudo dnf update | sudo dnf install python3 |
| CentOS | sudo dnf update | sudo dnf install python3 |
Install Python on Ubuntu
Note: In Debian-based distributions, like Ubuntu, users must run the python3 or python2 command, depending on the installed Python version, or create a corresponding symlink to use the python command.
To install Python on Ubuntu:
1. Access the command line and update the Ubuntu packages list:
sudo apt update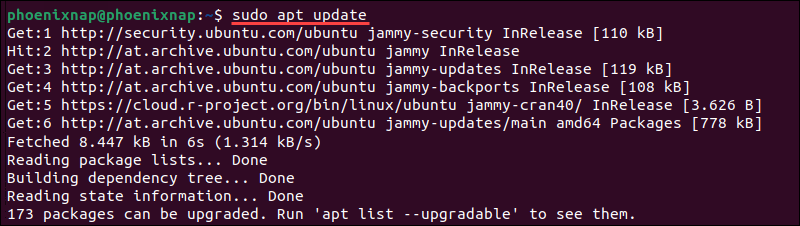
2. Python 3 is the default and recommended Python version. Enter the following command to install Python 3:
sudo apt install python3 -y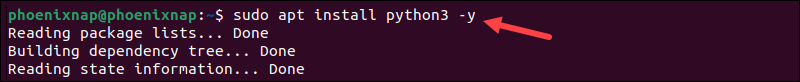
Python 2 is deprecated and no longer actively supported. However, some legacy applications still rely on Python 2.
Type the following command if you need to install Python 2 from Ubuntu repositories:
sudo apt install python2 -y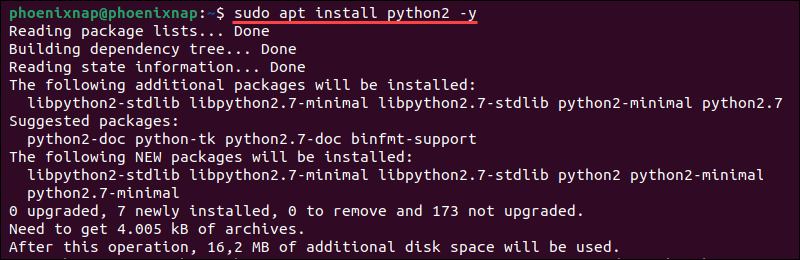
3. Check the Python version to confirm Python was successfully installed:
For Python 3:
python3 --version
For Python 2:
python2 --version
Refer to the Check Python Symbolic Links section to learn how to create Python symlinks.
Install Python on Fedora
Note: In the latest Fedora-based distributions, the python command is symlinked to the Python 3 executable directory by default. Users can execute the python command and utilize Python 3 without creating a corresponding symlink manually.
To install Python 3 on Fedora:
1. Use the dnf package manager to update the Fedora packages list:
sudo dnf update -y
2. Enter the following command to install Python 3 on Fedora:
sudo dnf install python3 -y
Python 2 is deprecated and no longer actively supported. However, some legacy applications still rely on Python 2.
Type the following command if you need to install Python 2 directly from Fedora repositories:
sudo dnf install python2 -y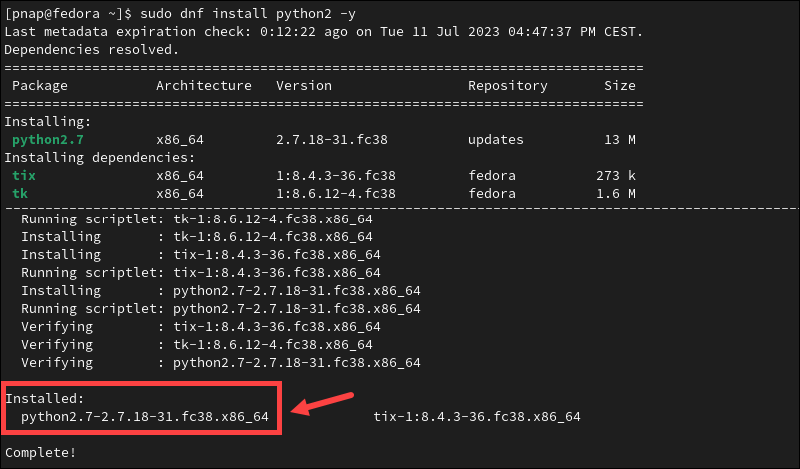
The system confirms the installation is Complete! and displays the Python version. In this example, the Python version is 2.7.18.
Access the Python interactive shell by entering the following command:
For Python 3:
python
For Python 2:
python2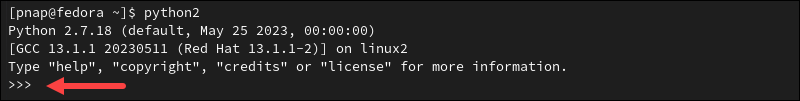
Install Python on Debian
Note: In Debian 11, users must utilize the python3 or python2 command, depending on the version they use, or create a corresponding symlink to invoke the python command.
To install Python on Debian:
1. Access the terminal window and update the Debian packages list:
sudo apt update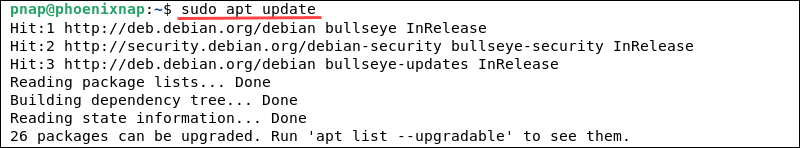
2. Python 3 is the default and recommended version. Use the following command to install Python 3:
sudo apt install python3 -y
Python 2 is deprecated and no longer actively supported. However, some legacy applications still rely on Python 2.
To install Python 2 from Debian repositories, enter the following command:
sudo apt install python2 -y3. Verify the installation by accessing the Python 3 interactive shell:
python3The system displays the Python interpreter version.

4. Press Ctrl+D to exit the Python shell.
To execute commands in Python 2, use the python2 command.
Install Python on Arch Linux
Note: In Arch Linux, the python command prompts Python 3 by default. Users do not need to create a corresponding symlink manually. Python 2 has been removed from Arch Linux repositories and cannot be installed using this method.
To install Python 3 on Arch Linux:
1. Access the command line and update the Arch Linux packages list:
sudo pacman -Syu
2. Use the pacman package manager to install Python 3 on Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S python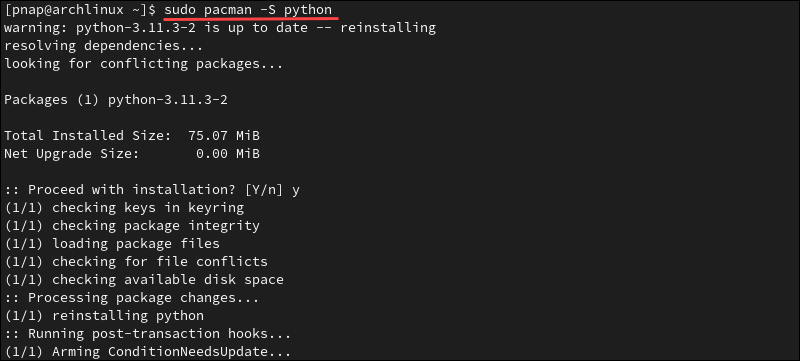
3. Open the Python interactive shell to verify the Python installation:
pythonThe installed Python 3 version is displayed, and you now have access to the Python interactive shell.

Press Ctrl+D to exit the Python interactive shell.
Install Python on Rocky Linux
Note: In the Fedora-based distributions, like Rocky Linux, the python command is symlinked to the Python 3 executable directory by default. Users do not need to create a corresponding symlink manually.
To install Python on Rocky Linux:
1. Open a terminal window and update the Rocky Linux packages list:
sudo dnf update -y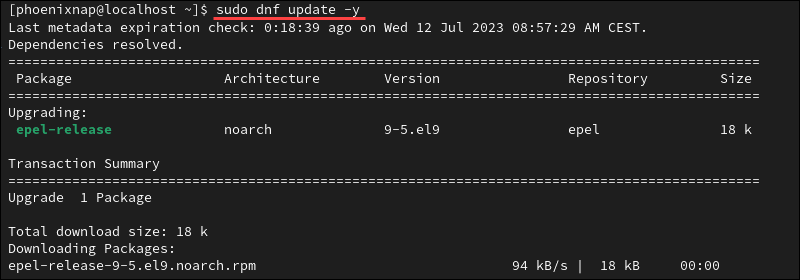
2. Use the following command to install Python 3 on Rocky Linux:
sudo dnf install python3 -y
Note: It is not possible to install Python 2 on Rocky Linux.
3. Use the python command to verify the Python version:
python --version
In this example, Python version 3.9.16 has been installed.
Install Python on CentOS
Note: CentOS users must utilize the python3 or python2 command, depending on the version they use, or create a corresponding symlink to invoke the python command.
To install Python on CentOS:
1. Access the command line and use the dnf package manager to update the CentOS packages list:
sudo dnf update
2. Enter the following command to install Python 3 on CentOS:
sudo dnf install python3 -y
Python 2 is deprecated and no longer actively supported. However, some legacy applications still rely on Python 2.
Type the following command if you need to install Python 2 from CentOS repositories:
sudo dnf install python2 -y
The system confirms that the installation is Complete! and displays the Python version. In this example, the Python version is 2.7.18.
3. Use the following command to access the Python interactive shell:
For Python 3:
python3
For Python 2:
python2
Press Ctrl+D to exit the Python terminal.
Check PATH Variable
The PATH variable is a list of directories that the operating system searches for executable files without needing to provide the full file path.
Enter the following command to check if the Python executable directory is in the system's PATH:
echo $PATHThe output must contain the path to the Python installation directory.

If the Python path is not included in the PATH variable, add it manually.
Note: The default Python installation directories are /usr/bin/pythonx.x or /usr/local/bin/.
To set the system's PATH environment variable in Linux:
1. Use a preferred text editor, in this example, nano, to access the .bashrc file:
sudo nano ~/.bashrc2. Append the following line at the end of the .bashrc file:
export PATH="$PATH:/path/to/python/executable/"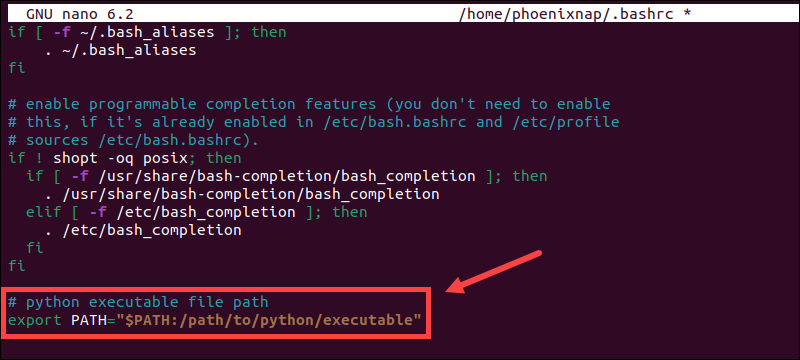
Replace /path/to/python/executable/ with the Python directory path on your system.
3. Save the file and close the text editor.
4. Enter the following command to apply the changes:
source ~/.bashrc5. Restart the terminal to complete the PATH update.
6. Use the echo command to confirm the new PATH variable has been added:
echo $PATH
Check Python Symbolic Links
Symbolic links, or symlinks, are provisional files that point to other files or directories. They are often used to create aliases or shortcuts for Python executables.
If you have multiple Python versions installed on your system, symbolic links can determine which version is invoked by default and which command to use.
Enter the following command to list Python symlinks:
ls -l /path/to/python/executableReplace /path/to/python/executable with the actual path to your Python directory.
The command displays details of the Python executable file, including any symbolic links. In this example, executables in the ./python3.11 directory can be invoked using the python3 command.

To enable users to utilize the python command to run Python 3, you need to create a new symlink:
sudo ln -s /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/pythonYou can now utilize the python command to execute commands in Python 3.
If necessary, use the rm command to remove unused or broken symlinks:
sudo rm /usr/bin/pythonConclusion
You have successfully resolved the python: command not found error and know how to verify the Python installation, check the PATH variables, and modify Python symlinks.
Find out how Python IDEs and code editors help you automate tasks and streamline app development in Python.