A working directory is where a Python script looks for and saves files during execution. Changing the working directory in Python is essential for efficient Python file handling and management, as it simplifies code and improves productivity when going through the file system.
This guide shows how to change the working directory in Python.

Prerequisites
- Python 3 installed and configured.
- A Python IDE or text editor.
- The
osmodule for communicating with the operating system.
Get Current Working Directory in Python
The getcwd() function from the os module fetches the current working directory location. The function returns the full path starting from the root directory to the current working directory. The working directory is where a Python script executes all the commands.
The syntax is:
os.getcwd()To check the current working directory, import the os module and print the getcwd() function's results. For example:
import os
print(os.getcwd())If using a text editor, save the code and run the script with the following command:
python3 [filename].py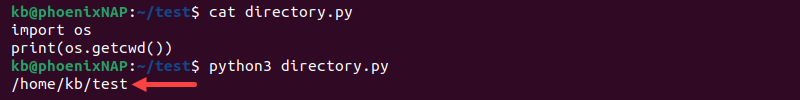
The code prints the script's current working directory.
Note: If running the code results in an error, Python might not be installed or added to PATH. See how to fix the python: command not found error.
Change Current Working Directory in Python
To switch the current working directory in Python to a different location, use the chdir() function from the os module and provide the absolute path as a string. The syntax is:
os.chdir('[path]')To test how the function works, import the os module and print the current working directory. Change the location using the chdir() function and print the working directory again.
The example below demonstrates how to change the working directory:
import os
print(os.getcwd())
os.chdir('[path]')
print(os.getcwd())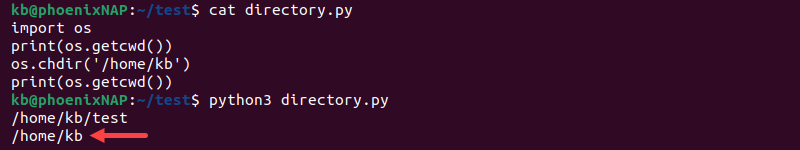
The code prints the working directory before and after the change. The current working directory changes to the location provided in the chdir() function.
Alternatively, save the path as a string and provide the variable to the function. For example:
import os
path = '[path]'
print(os.getcwd())
os.chdir(path)
print(os.getcwd())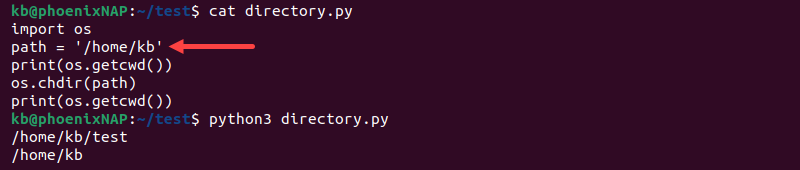
Storing the path string in a variable allows multiple locations to be stored in different variables at the beginning of the code. Multiple variables can reside in a list, enabling easy looping through the list and changing directories.
Conclusion
After reading this guide, you know how to check the current working directory and change it to a different location. Python uses the os module to communicate with the underlying operating system to commit the changes.
Next, learn how to read from stdin in Python.



