The DROP TABLE statement removes a table from a MySQL database. It deletes the entire structure and content of the table.
The tutorial explores the DROP statement commands and shows how to drop tables from MySQL databases.
Prerequisites
- Access to the terminal.
- A system running MySQL.
- A working database.
- A MySQL user with the necessary privileges (
DROPprivileges required).
MySQL DROP TABLE Syntax
To remove a table in MySQL, use the DROP TABLE statement. The basic command syntax is as follows:
DROP TABLE table_name;The more extended syntax is:
DROP [TEMPORARY] TABLE [IF EXISTS] table_name [, table_name] [RESTRICT | CASCADE];Let’s break down the syntax:
- The
DROP TABLEstatement deletes a table and its rows permanently. - The
[TEMPORARY]option ensures you remove temporary tables only. - The
[IF EXISTS]option drops a table only if it exists. - The
[RESTRICT]ensures a parent row is not deleted if a child row references a value in the said parent row. - The
[CASCADE]option ensures that when you delete a row, all rows in the related tables referencing the row are also deleted.
Note: When deleting a MySQL table, all user privileges associated with that table remain. If you create a new table with the same name as the deleted one, the existing user privileges are assigned. Consider whether that impacts your security.
To remove user privileges along with a table in MySQL, you need to revoke the privileges before or after dropping the table. To revoke all privileges on the table from the user, run:
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES ON database_name.table_name FROM 'username'@'host';MySQL DROP TABLE Examples
There are several ways to delete a table in MySQL. The following text elaborates on them.
DROP a Table
To permanently remove a table, enter the following statement within the MySQL shell:
DROP TABLE table1;
The command deletes table1. Replace table1 with the name of the table you want to delete. When you delete a table, all its data is permanently removed along with the table structure.
DROP Existing Tables
MySQL generates an error if you try to drop a table that does not exist. This issue occurs when you include the DROP statement in a predefined script.

To check if a table exists, run the following command:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS table1;The IF EXISTS option generates a warning if table1 does not exist.

Using this option prevents a script from getting stuck on an error. Display the warning by entering:
SHOW WARNINGS;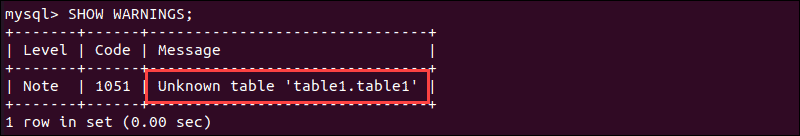
The warning shows that the table does not exist.
DROP Multiple Tables
To drop multiple tables with a single DROP statement, do the following:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS table1, table2, table3;
The IF EXISTS option shows one warning as table1 does not exist. Other tables are deleted.
Note: Consider identifying duplicate values in MySQL databases and then deleting them to improve data efficiency.
DROP a Temporary Table
Temporary tables are used to generate and store a data set shortly before using it.
For example, you might decide to store the results of a SELECT statement with multiple JOIN statements in a temporary table. Instead of repeating the entire query each time, query the temporary table directly.
To remove temporary tables without risking losing regular tables, use the TEMPORARY option:
DROP TEMPORARY TABLE IF EXISTS table4;
DROP Tables Based on Character Strings
MySQL does not have a built-in command to drop tables that match a given string. Instead, use a script to help perform this task. For example, you have a testdb database with three tables: temp_table1, temp_table2, and permanent_table.
The goal is to drop all tables in the testdb database whose names start with temp_. Take the following steps to do this:
1. Define the database and string of characters you want to filter:
set @schema = 'tableselection';
set @string = 'table%';Replace tableselection with your database name. Replace table% with the string of characters you want to select and delete. Make sure to leave the % wildcard at the end.
In our example, it looks like this:
SET @schema = 'testdb';
SET @string = 'temp_%';
2. Create a MySQL statement to drop tables matching the pattern:
SELECT CONCAT('DROP TABLE ', GROUP_CONCAT(CONCAT(@schema, '.', table_name)), ';')
INTO @droptool
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = @schema
AND table_name LIKE @string;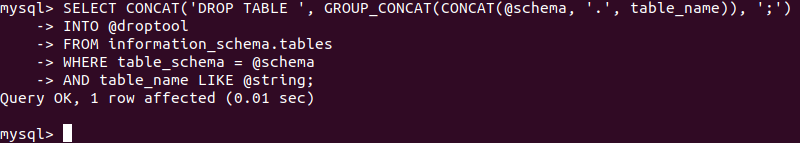
This code consists of:
- The
SELECTstatement. Constructs aDROP TABLEcommand for all tables in the specified database that match the given pattern. - The
CONCATfunctions. Builds the full table names and combines them into a single command.- The
GROUP_CONCATfunction. Combines the table names into a comma-separated list.
- The
- The
INTO @droptoolclause. Stores the constructed command in the@droptoolvariable. - The
FROM information_schema.tablesclause. Specifies the source of table information. - The
WHEREclauses. Filters the tables to match the specified database and name pattern.WHERE table_schema = @schema. Ensures only tables from the specified database are considered.AND table_name LIKE @string. Ensures only tables whose names match the specified pattern (e.g., starting withtemp_) are included.
3. Create a selection from the code results:
SELECT @droptool;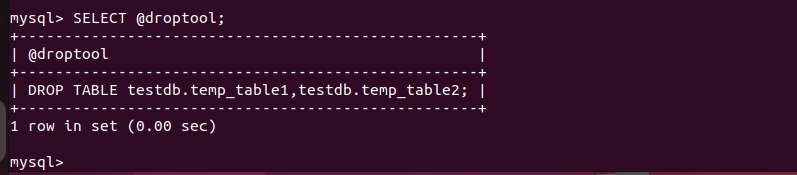
The command retrieves and displays the @droptool variable contents. This step allows you to view the generated DROP TABLE statement before executing it.
4. Prepare and execute the generated DROP TABLE statement:
PREPARE stmt FROM @droptool;
EXECUTE stmt;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt;The command consists of:
- The
PREPAREstatement. Prepares the SQL statement stored in the@droptoolvariable. It sets up the command so it can be executed. - The
EXECUTEstatement. Executes theDROP TABLEcommand, which deletes the specified tables. - The
DEALLOCATEstatement. Frees up the resources associated with the prepared statement.
Note: If you are interested in how to create an index in a new table, read our guide MySQL Index: Usage, Management & Troubleshooting.
MySQL DROP TABLE vs. TRUNCATE
There are two ways to remove all data from the table: the DROP TABLE and TRUNCATE TABLE commands. However, they work differently and have different effects.
The DROP TABLE statement completely removes the table, including its structure and data. The TRUNCATE TABLE command deletes the data but leaves the structure.
TRUNCATE TABLE is especially useful if you want to delete a table and create a new table with the same structure. Instead of using DROP TABLE and CREATE TABLE, use TRUNCATE TABLE.
Conclusion
This tutorial explained how to use DROP TABLE to remove tables from a MySQL database. Additionally, the text elaborated on how to find and delete tables based on character strings.
Next, learn about the most important MySQL commands and how to use them in our MySQL commands cheat sheet.