Docker Compose allows users to launch, execute, and manage multiple containers with a single command. It helps users define and run multi-container Docker applications and configure service dependencies (caches, databases, web service APIs, etc.).
This tutorial will show you how to install Docker Compose on Ubuntu, introduce frequently used commands, and provide a container deployment example.
Prerequisites
- A system running Ubuntu (this guide uses Ubuntu 24.04)
- A user account with administrative privileges.
- Docker installed.
- Command-line access.
How to Install Docker Compose on Ubuntu
Note: This tutorial provides steps to install Docker Compose V2, the current version of the application featuring the docker compose command. The previous V1 version that worked with the docker-compose command is now deprecated.
The easiest way to deploy Docker Compose on Ubuntu is to install Docker Desktop, an application that provides a GUI. Docker Desktop includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI, and Docker Compose.
However, Docker Desktop may not be practical for developers with Docker already deployed on Linux, as the application creates a custom Docker context and a parallel Docker installation. The recommended way to install Docker Compose for Linux Docker engine users is via the official Docker repository.
Follow the steps below to install Docker Compose using the Docker repository on Ubuntu.
Note: It is possible to install Docker Compose from the Ubuntu repository by running sudo apt install docker-compose-v2. However, the Ubuntu repository may not contain the latest version of the application.
Step 1: Install Required Packages
Use the following commands to install the packages necessary for adding third-party repositories to an Ubuntu system:
1. Update the list of packages:
sudo apt update2. Install ca-certificates, a certificate authority package for verifying third-party identities, and curl, a data transfer tool:
sudo apt install ca-certificates curlStep 2: Add Docker Repository
To use the Docker repository, add Docker's official GPG key and add the repository to the APT sources. Follow the steps below to complete this procedure:
Note: None of the commands listed below provide output if successfully executed.
1. Set ownership permissions for the /etc/apt/keyrings directory:
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings2. Download the key with curl:
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc3. Set read permissions for the key:
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc4. Add the Docker repository to the list of APT sources:
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/nullStep 3: Install Docker Compose Plugin
Once the Docker repository is registered on the system, install the Docker Compose plugin via APT by following the steps below:
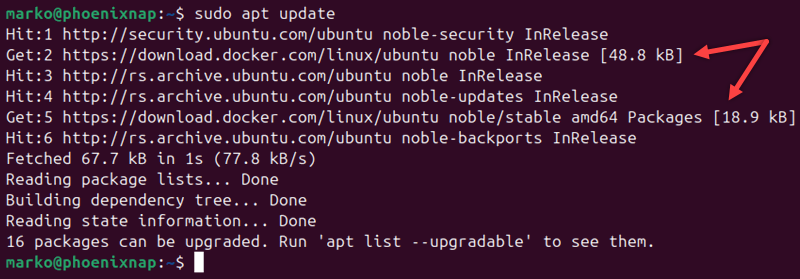
1. Update the repository list:
sudo apt updateThe Docker repository appears in the output.
2. Install Docker Compose:
sudo apt install docker-compose-plugin -y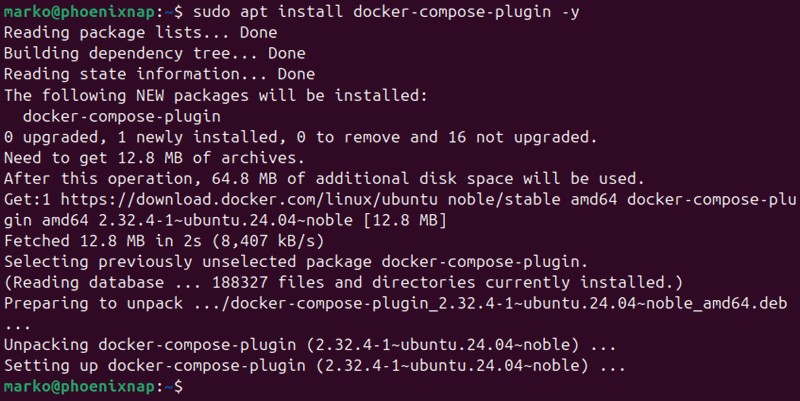
3. After the download completes, confirm that Docker Compose is installed by typing:
docker compose versionThe output shows the Docker Compose version number.

Test Run Docker Compose
Run a sample container with Docker Compose to test the installation. The following section provides an example of this procedure using the hello-world Docker container.
1. Create and go to the hello-world directory:
mkdir hello-world && cd hello-world2. Create a file named compose.yml to store container deployment instructions:
nano compose.yml3. Paste the following code into the file. The code defines a service container named hello-world, which uses the hello-world:latest Docker image as the template.
version: '2'
services:
hello-world:
image:
hello-world:latest4. Save the file and exit.
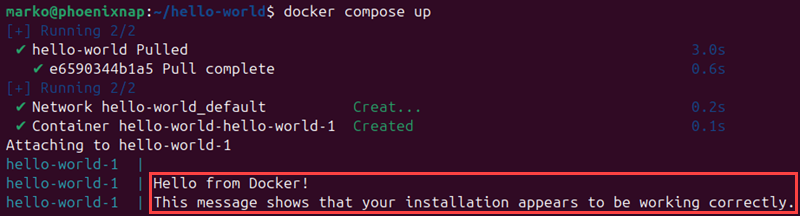
5. Run Docker Compose by running the following command:
docker compose upDocker Compose reads compose.yml and then creates and runs a container based on the instructions. The output shows the sample app that runs from the hello-world container.
Docker Compose Basic Commands
The docker compose command has the following syntax:
docker compose [subcommand] [arguments]The command has multiple subcommands, allowing for simple creation and management of container deployments. Some of the most frequently used commands include:
up. Create and start containers based on the compose.yml file in the current directory.down. Stop and remove containers.start. Start existing service containers.pause. Pause running service containers.unpause. Unpause running service containers.stop. Stop service containers.kill. Force stop service containers.restart. Restart service containers.run. Run a command inside a service container.cp. Copy files/directories between the local filesystem and a service container.
Note: If you are new to Docker, check out our Docker commands cheat sheet.
Uninstall Docker Compose on Ubuntu
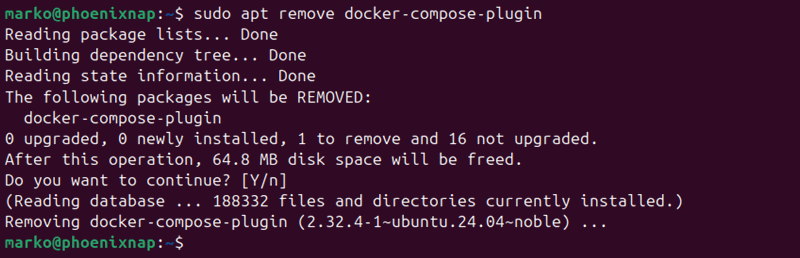
The procedure for removing Docker Compose is the same as for any other application installed via APT. Uninstall Docker Compose by typing:
sudo apt remove docker-compose-pluginConfirm that you want to remove the application by entering Y when prompted.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you should know how to set up Docker Compose on Ubuntu 22.04/24.04. The article provided installation instructions, a list of frequently used Docker Compose commands, and an example deployment.
Next, learn how to update Docker Images and Containers.