Copying files and directories in Linux is an essential administrative task. Copies are instrumental for backing up important files or transferring them to another location, for example, a data storage device.
The cp command is useful for basic copying needs, while rsync excels at complex tasks, such as selectively copying specific files or creating system-wide backups.
Learn how to copy files and directories in Linux using the cp and rsync commands.

Prerequisites
- A Linux system.
- Access to a command line/terminal window.
How to Copy Files in Linux Using cp Command
The cp command is the primary method for copying files and directories within a local Linux filesystem. The basic command syntax is:
cp [option] [source] [destination]The source is the file or directory you want to copy, while the destination represents the location where the copy should be placed. The destination can be a directory path or a new filename if the file needs to be renamed.
Use the listed cp command options below to specify different behaviors:
| OPTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| -v | Displays additional information about the copying process. |
| -p | Forces the system to preserve source file attributes (modification time, access time, user ID (UID), group ID (GID), file flags, file mode, access control lists (ACLs), and extended attributes (EAs)). |
| -f | If the destination file/directory exists, replaces it with the source. |
| -i | Prompts for confirmation before overwriting a file. |
| -r | Copies all files in a directory. |
| -u | Replaces files only if they satisfy the update condition. For example, when the destination file does not exist or when the source file is newer than the destination file. |
How to Copy a Single File
Enter the following command to copy a single file within the current working directory:
cp my_file.txt my_file2.txtThe system does not provide an output. Use the ls command to confirm that the file has been copied.

By default, the cp command runs in the same directory you are working in. However, the same file cannot exist twice in the same directory.
Note: Learn how to check or change the working directory using the cd command.
You must rename the target file to copy it to the same location. You can add _old to the name, or add a number or change the extension (e.g., .bak instead of .txt).
Note: The cp command in Linux does not provide a warning before overwriting existing files. Use the –i option for the system to prompt you before overwiting a file.
Enter the following command to copy a file from the current working directory to a different directory:
cp -v my_file.txt path/to/destinationReplace path/to/destination with the actual directory path. The -v option displays additional information about the copying process.

The command fails if the destination directory does not exist because cp does not create directories.

Note: Find out how to create directories in Linux with the mkdir command.
Use the following command to copy a single file to a different directory and rename it:
cp my_file.txt path/to/destination/my_file2.txtTo copy a file without having to change directories, specify a path for the source file and the destination directory:
cp -v ~/Documents/my_file.txt path/to/destinationReplace the example path in the command with the actual path on your system.

In this example, the -v option was used to verify that the file was copied successfully.
How to Copy Multiple Files
To copy more than one file at a time, list each file to be copied before entering the destination directory:
cp my_file.txt my_file2.txt my_file3.txt path/to/destinationThe system creates a copy of all three files in the destination folder.
The wildcard (*) character allows users to specify files that share a string of characters. The following command finds all the files with the .jpg extension in the pictures directory and copies them into the destination folder:
cp ~/pictures/*.jpg path/to/destinationIf one of the files or directories requires root or higher-level permissions, use the sudo command to elevate privileges temporarily.
Note: Learn how to transfer files between two Linux systems.
How to Copy Directories in Linux Using cp Command
To copy an entire directory and its subdirectories and files, use the –r option. The following command copies all files and directories from the Documents directory to the new_destination directory:
cp -r ~/Documents path/to/new_destinationThe -r option stands for recursive, which means "everything in that location."
Note: As an alternative to copying directories, learn how to move directories in Linux.
Copying Files Using rsync Command
The rsync command in Linux synchronizes or transfers data between two locations. Usage is similar to the cp command, but while cp only copies files locally. To transfer files and directories to remote systems, you can use rsync over SSH. The tool saves bandwidth and transfers files faster by compressing them and only transferring new or updated files.
In addition, rsync creates a new directory if the final part of the destination path specifies a non-existent location.
How to Copy a Single File Using rsync
To copy one file to another directory on a local machine, type the source file's full path, followed by the destination directory:
rsync -av ~/Documents/my_file.txt ~/destination/backups/Replace the source path and /destination/backups/ destination from the example with your system's actual path and destination directory.
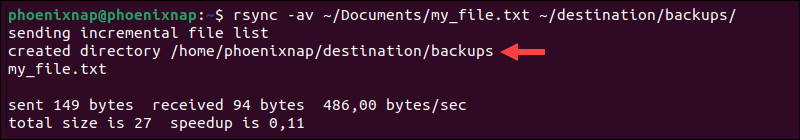
The -a option instructs rsync to preserve file metadata and other attributes such as permissions and timestamps. The -v option provides detailed output about the file transfer process.
How to Copy a Directory Using rsync
In this example, rsync is used to copy the contents of the /home/phoenixnap/anaconda3/doc/config/ directory to /home/phoenixnap/backups/anaconda3/:
rsync -av /home/phoenixnap/anaconda3/doc/config/ /home/phoenixnap/backups/anaconda/The trailing slash (/) at the end of the source and destination paths ensures you only copy the content of the source directory. Omitting the slash on the source directory creates a new subdirectory within the destination directory.
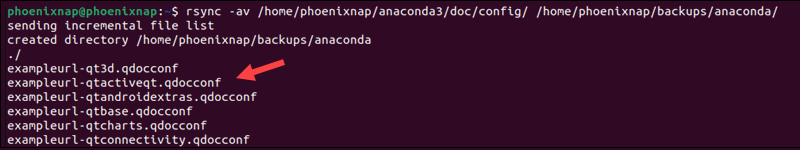
To prevent specific files from being copied, check out our guide on how to use rsync to exclude files and directories from a data transfer.
Conclusion
You now know how to copy files in a local Linux filesystem. The cp and rsync commands are versatile and powerful tools for managing and backing up files, especially when combined with other essential Linux commands.


