firewalld is a dynamically managed firewall that supports network zoning and is the default firewall tool on CentOS and Rocky Linux servers. System admins use it to dynamically allow or deny incoming and outgoing traffic for both IPv4 and IPv6.
To secure your system, keep firewalld active and enabled at all times. Administrators disable the firewall when testing or switching to another firewall tool, such as iptables.
This tutorial shows how to disable and stop firewalld on CentOS and Rocky Linux.

Prerequisites
- A user with sudo privileges.
- Access to a command line interface/terminal.
- A machine with Rocky Linux or CentOS.
Check firewalld Status
firewalld is enabled by default on every CentOS and Rocky Linux machine. To see the status, run the following command:
sudo systemctl status firewalld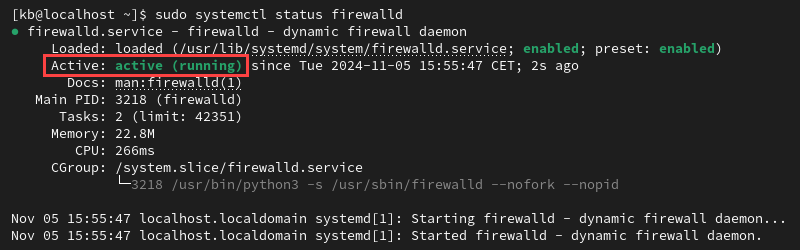
If the firewall is running, the status shows as active (running).
Disabling Firewall on CentOS or Rocky Linux
There are two ways to disable the firewall: temporarily or permanently. The sections below provide instructions for both.
Temporarily Stop firewalld
To temporarily stop the firewalld service, use the following command:
sudo systemctl stop firewalldThere will be no confirmation message. Verify that firewalld is disabled:
sudo systemctl status firewalld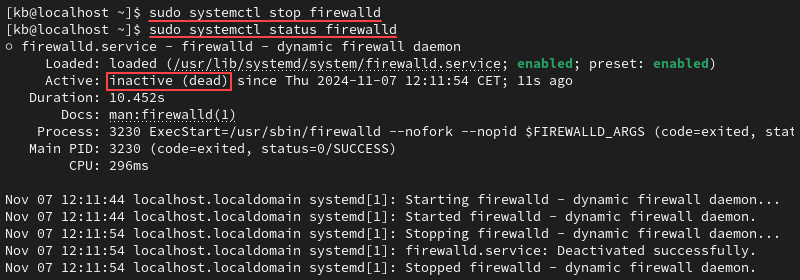
The status shows as inactive (dead). After the system reboots, the firewalld service reactivates.
Permanently Disable firewalld
To permanently turn off the firewall on CentOS or Rocky, stop and disable the firewall service:
1. Stop the firewalld service:
sudo systemctl stop firewalld2. Disable the service from reactivating upon system boot:
sudo systemctl disable firewalld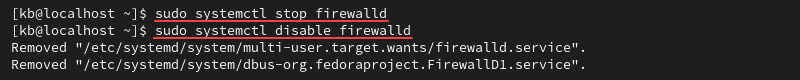
The command removes the systemd service symbolic links (symlinks).
3. Other active services can reactivate firewalld. To prevent other services from activating it, mask firewalld from other services on the system:
sudo systemctl mask --now firewalld
The command creates a symlink from the firewalld service to /dev/null. The firewall status switches to masked.
Conclusion
This guide showed how to stop and disable the firewalld service on CentOS and Rocky. We also showed how to mask the firewalld service from other active services to avoid reactivation. The best cybersecurity practices forbid disabling firewalls, especially on live servers. Always be cautious when doing so, even in test environments.
Next, see how to set up a firewall on a small BMC instance using iptables.