Python is a versatile programming language that enables users to tackle complex projects. Its simplicity, readability, extensive libraries, strong community support, and cross-platform compatibility make it ideal for rapid development, data analysis, AI, and web applications.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to get the current date and time using Python.
Prerequisites
- A user account with root privileges.
- Python installed (see how to install Python on Ubuntu, Rocky Linux, macOS, and Windows).
- A text editor (such as nano).
Get Current Date and Time in Python with datetime Module
The datetime module in Python lets you change dates, times, timedeltas (differences between two dates or times), timezones, and more. You can manipulate specific dates and times, format them, and perform arithmetic operations with them.
This section shows different ways of using datetime to get the current date and time.
Get Current Date with datetime
Follow the steps below to create a Python script and get the current date using the datetime module:
1. Open the terminal and run the command below:
sudo nano python_date.pyThe system creates a new, empty file.
2. Paste the code below into the script:
from datetime import date
today = date.today()
print("Today's date:", today)3. Save and exit the file.
4. Run the file with the command:
python3 python_date.pyThe output shows today's date using the datetime module:

Note: The latest stable Python version at the time this article was Python 3.12. In Linux, python is an alias or symlink that points to the default version of Python 2.x, while python3 is an alias or symlink pointing to the default version of Python 3.x. See how to check your Python version.
Get Date and Time with datetime
Python offers several options for configuring how dates and times are formatted. Follow the steps below:
1. Create a new Python script file:
nano sample_format.py2. Paste the following lines:
import datetime
e = datetime.datetime.now()
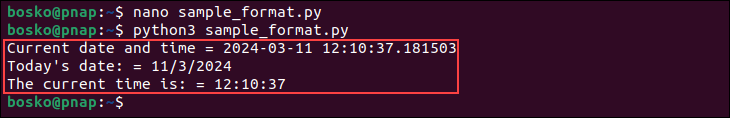
print ("Current date and time = %s" % e)
print ("Today's date: = %s/%s/%s" % (e.day, e.month, e.year))
print ("The current time is: = %s:%s:%s" % (e.hour, e.minute, e.second))3. Save the file and exit.
4. Run the file:
python3 sample_format.pyThe system displays the date and time, the date, and the time in three separate lines:
Get Timezone with datetime
The time zones are defined in the pytz library. Follow the steps below to print the timezone in Python:
1. Create a new script file:
sudo nano timezone.py2. Paste the following lines:
import datetime
import pytz
def get_current_timezone():
now = datetime.datetime.now()
timezone = pytz.timezone(pytz.country_timezones['US'][0])
# You can change 'US' to your desired country code
current_timezone = now.astimezone(timezone)
return current_timezone.tzinfo
current_timezone = get_current_timezone()
print("Current timezone:", current_timezone)3. Save and exit the file.
4. Run the file:
python3 timezone.py
The output shows the time in the selected timezone.
Get Time and Date Using strftime
The strftime method accepts several formatting options. This example shows how to get the current time and date and specify a format for the output. Follow the steps below:
1. Create a new script file:
nano test_format.py2. Paste the following lines:
import datetime
e = datetime.datetime.now()
print (e.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"))
print (e.strftime("%d/%m/%Y"))
print (e.strftime("%I:%M:%S %p"))
print (e.strftime("%a, %b %d, %Y"))3. Save the file and exit.
4. Run the file by typing:
python test_format.py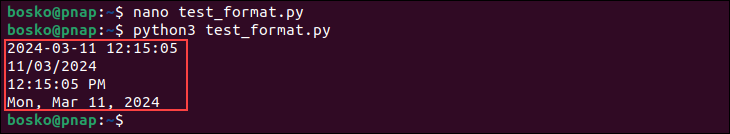
The output shows the date and time in multiple formats.
Note: The strftime method has many formatting options. All the available options are in the official documentation.
Get Current Time in Python with time Module
The time module in Python provides various time-related functions, such as getting the current time, converting between different time formats, and measuring time intervals. It operates primarily with time in seconds since the epoch (January 1, 1970).
In contrast with the time module, the datetime module offers higher-level functionalities for working with dates and times, all in a more user-friendly interface.
The following sections show how to get the current time in Python using the time module.
Get Time with strftime
The strftime method returns a string displaying the date and time using a date, time, or datetime object. Follow the steps below:
1. Create a new script using the command below:
nano python_time.py2. Depending on your needs, you can choose to display the time in a 24-hour or 12-hour format.
To display the time in a 24-hour format, paste the following lines:
import time
print (time.strftime("%H:%M:%S"))Alternatively, to display the time in a 12-hour format, paste the following:
import time
print (time.strftime("%I:%M:%S"))3. Save the changes and close the file.
4. Execute the script by running:
python3 python_time.pyThe result displays the time in the requested format:

Get Time in Milliseconds
If you need a more accurate value, you can use the time module to display time in milliseconds. Follow the steps below:
1. Create a new script:
nano milliseconds.py2. Paste the following lines:
import time
millisec = int(round(time.time() * 1000))
print("The time in milliseconds is: ", millisec)3. Save and exit the file.
4. Run the script:
python3 milliseconds.py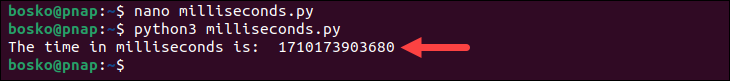
This script utilizes the time module to obtain the current time in seconds since the epoch and then converts it to milliseconds.
Get Time in Nanoseconds
To get an even more accurate reading, you can display time in nanoseconds. Follow the steps below:
1. Create a new script:
nano nanoseconds.py2. Paste the following lines:
import time
nanosec = time.time_ns()
print("Time in Nanoseconds:", nanosec)
Note: The time.time_ns() function is available in Python 3.7 and later.
3. Save and exit the file.
4. Run the file:
python3 nanoseconds.py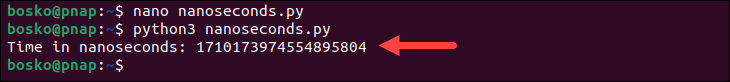
Conclusion
This guide showed you how to display the date and time in different formats using multiple options (%X values).
Next, learn how to set up time synchronization on Debian or the difference between R and Python.