The ELK Stack and Splunk are two widely used platforms in data analytics and management. Although the tools serve similar purposes, key differences set them apart.
This article presents ELK Stack vs. Splunk - the ultimate comparison to help you choose the right platform.
ELK Stack vs. Splunk: Definitions
The ELK Stack (now known as the Elastic Stack) and Splunk are powerful tools for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing machine data.
Both platforms offer robust solutions for log management, security analysis, compliance monitoring, and business analytics and provide a range of features, user-friendly interfaces, and scalable architecture.
While both platforms serve similar purposes, distinctions exist.
What is ELK Stack?
The Elastic Stack is an open-source toolset that collects, searches, and visualizes large volumes of machine data. It's flexible and suitable for various use cases.
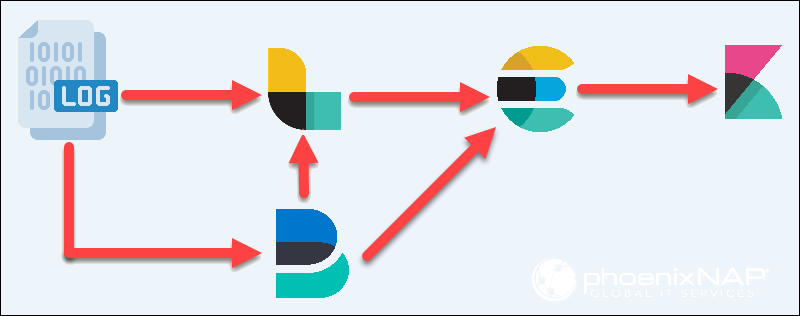
Initially, the stack consisted of Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana (ELK), but then Beats was added:
- Elasticsearch. A search and analytics engine that enables fast and scalable full-text searching, real-time analytics, and data visualization. It acts as a NoSQL database built on Apache Lucene.
- Logstash. A data processing and transportation pipeline that collects, parses, and transforms logs from various sources before indexing the data in Elasticsearch.
- Kibana. A user-friendly visualization dashboard that facilitates exploration, analysis, and report generation based on the indexed data stored permanently in Elasticsearch.
- Beats. Local data collectors that gather and send data from different sources to Elasticsearch or Logstash. Beats are resource-friendly and suitable for deployment on various systems, including servers, containers, and edge devices. However, the data is sometimes collected only by Logstash and not Beats.
Note: Check out our ELK stack tutorial to learn about the basic ELK Stack usage and functionality.
What is Splunk?
Splunk is a commercial security, log management, and analysis platform. It provides centralized log collection, indexing, searching, real-time monitoring, security analysis, compliance monitoring, and business analytics.
The platform supports advanced analytics, data visualization, alerting, machine learning, and security analytics through its Splunk Enterprise Security module.
Splunk handles large volumes of machine-generated data using the proprietary Search Processing Language (SPL). It connects with different data sources, securely stores and indexes the data, and provides users with powerful search and analysis capabilities.
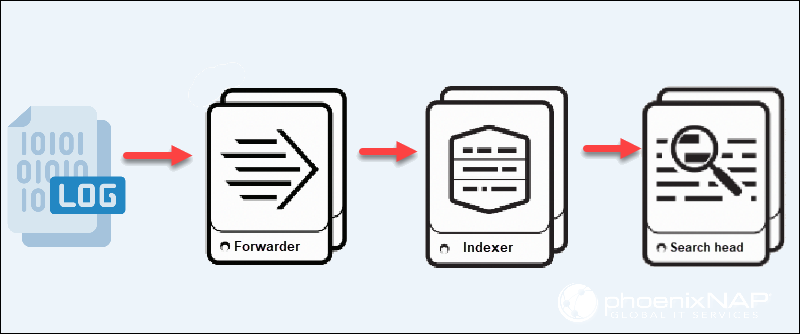
The three critical components of Splunk are:
- Forwarder. Ingests data and transports it to the Indexer.
- Indexer. Stores and indexes data and responds to search requests.
- Search head. The interface where these components are combined or distributed across servers.
ELK Stack vs. Splunk: Comparison
The two data analytics and management tools are similar in the ability to collect, analyze, and visualize machine data. However, certain features set the platforms apart. The following table elaborates on the key similarities and differences between the ELK Stack and Splunk.
| Features | ELK Stack | Splunk |
|---|---|---|
| Data Management | Supports structured and unstructured data. Requires scripting language knowledge. Uses Elasticsearch for fast searching. | Offers convenient options for data collection. Forwarders come pre-configured for data sources. Utilizes proprietary SPL for powerful search. |
| Visualizations | Uses Kibana, a user-friendly interface for data exploration and analysis, interactive dashboards, and reports. | Uses powerful visualization tools for customized dashboards and reports, such as Splunk Pivot and Splunk Dashboard. |
| User Management | Offers options for user authentication. Provides role-based access control (RBAC) with a paid Security plugin. Provides user auditing capabilities. | Offers role-based access control (RBAC). Supports user auditing for accountability. Facilitates management of large-scale deployments. |
| Search Capabilities | Fast and flexible searches using Elasticsearch. Uses query DSL (Domain-Specific Language). Full-text search, filtering, and aggregation as the main search features. Fields must be defined in advance. No need for piping. | Advanced search functionalities using proprietary Search Processing Language (SPL). Utilizes SPL (Search Processing Language). Real-time searches, correlation, and analysis as the main features. Dynamic exploration possible for non-configured fields. Supports piping commands for complex analysis. |
| Integrations | Extensive input and output plugins through Logstash. | More than a thousand applications and add-ons. Splunk Connect for various platforms, RESTful APIs, and SDKs. |
| Ease of Use | Manual configuration and setup that requires technical knowledge are necessary. Provides flexibility and customization options for advanced users. | User-friendly interface with intuitive workflows and pre-built dashboards. Offers guided search and reporting capabilities for varying skills. |
| Support | Community support, commercial support, and consulting services. Comprehensive and well-documented resources. Large user community. Educational sessions and global support for learning. | Professional services, training programs, dedicated support portal. Robust documentation. Community forum. Virtual and on-site instructors. Enterprise-level support offered at different levels. |
| Releases | Continuous release cycle and regular updates. | Regular updates and major version releases. |
| Pricing | Open-source and free. Paid additional features and enterprise support. | Commercial pricing based on data ingestion volume and number of users. |
| Customer Base | Small to medium-sized businesses, startups, and large enterprises. | The enterprise market, financial services, healthcare, telecommunications. |
Features
To determine how suitable ELK Stack and Splunk are for addressing specific data analysis needs, compare important features, including data management, visualizations, user management, and search capabilities. These elements are crucial for effective data analysis, organization, secure access, and efficient information retrieval.
Data Management
Both ELK Stack and Splunk provide robust data management capabilities, making the tools effective in handling big data. Moreover, both platforms offer efficient storage and retrieval mechanisms.
The ELK Stack accepts data from any source and format through its components Logstash and Beats. Users can search and analyze logs, events, and metrics, both in structured and unstructured formats.
The data is transported to Elasticsearch, ensuring fast and scalable full-text searching and real-time analytics. However, a downside is the configuration process. Logstash is challenging to configure for users unfamiliar with scripting languages like Bash, Python, or Ruby. Still, online support is available, making Logstash accessible to users with different levels of scripting language experience.
Splunk indexes and analyzes machine-generated data from various sources and supports data ingestion in multiple formats, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Additionally, Splunk provides convenient options for data collection through ingest services, forwarders, and streaming connectors, streamlining the process of importing data into the platform.
Unlike ELK Stack, sending data to Splunk is straightforward. The forwarders come pre-configured to handle various data sources, ensuring seamless data import. Splunk's indexing capabilities, powered by the proprietary Search Processing Language (SPL), enable fast and powerful search functionality, enhancing data exploration and analysis.
Visualizations
Both platforms offer powerful visualization capabilities, enabling users to create interactive dashboards, generate reports, and present data in visual formats. Splunk provides a user-friendly interface for creating reports and leveraging machine learning models.
ELK Stack relies on Kibana, which offers a user-friendly interface for exploring and analyzing data, creating real-time visualizations, alerts, interactive dashboards, and generating reports.
It offers a variety of visualization types, including line graphs, bar charts, tables, and pie charts. The search filter is always displayed above various views in Kibana to apply any query to the dashboard elements.
Splunk provides a user-friendly interface with advanced reporting and data visualization capabilities. These tools enable the creation of various visualizations, including graphs, charts, and other visual elements. The interface is flexible and allows users to modify and add components as needed.
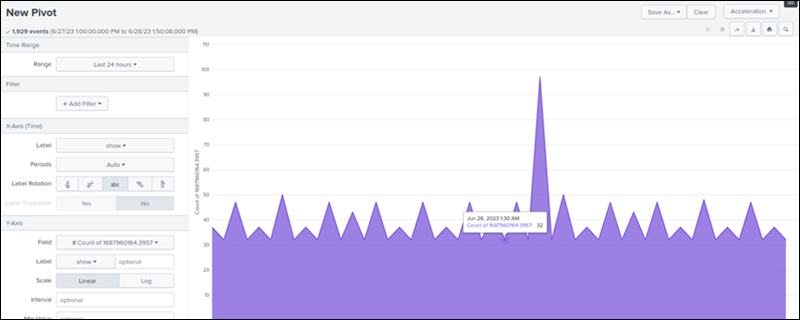
Splunk also supports visualizations on mobile devices. Users can leverage and adjust customizable application and visualization components using XML.
User Management
ELK Stack and Splunk have built-in user management services, including user auditing. These user management capabilities contribute to maintaining data security, managing access privileges, and ensuring accountability.
The ELK Stack provides options for user authentication and access control. It offers a paid tool called the Security plugin, which provides role-based access control (RBAC) capabilities.
Splunk provides comprehensive user management capabilities, including user auditing and role-based access control. It allows administrators to track user activities and maintain a secure environment.
Splunk also supports RBAC to allow administrators to define roles and assign permissions to users and groups. Moreover, Splunk offers features for managing large-scale deployments, facilitating the administration of user accounts and permissions across multiple instances.
Search Capabilities
Both Splunk and Elastic Stack provide powerful search capabilities. However, the platforms employ different approaches.
The ELK Stack uses the query DSL (Domain-Specific Language) for searching and analyzing data through Elasticsearch. The component supports full-text search, filtering, aggregation, and complex queries. In the ELK Stack, Elasticsearch fields must be defined in advance for log property aggregation to work correctly.
Kibana uses the Lucene query syntax for search queries. Kibana's search capabilities allow users to generate query results without additional transformations, making it straightforward and efficient.
Splunk utilizes its proprietary SPL (Search Processing Language) to query collected datasets. The platform offers advanced search functionalities, including real-time searches, correlation, and statistical analysis.
Splunk allows dynamic data exploration, even for non-configured fields, by formatting data appropriately for searching. Unlike the ELK Stack, where query results are generated directly, in Splunk, consecutive commands are chained using the pipe character. This enables the output of one command to serve as input for the next.
Integrations
Both ELK Stack and Splunk offer integrations with various data sources and technologies.
Although the ELK Stack has less extensive coverage than Splunk, the platform offers integrations through plugin support. Integrations also include community-contributed plugins.
The Elastic Stack provides a variety of integrations with different technologies, including databases, messaging systems, cloud platforms, and more.
Splunk supports over 1500 applications and add-ons in different categories to enhance users' data analysis capabilities. Splunk also provides integrations through its Splunk Connect, RESTful APIs, and SDKs for custom integrations.
Ease of Use
ELK Stack and Splunk differ in ease of use, each with distinct characteristics.
The ELK Stack requires technical expertise for setup and configuration, especially when dealing with more complex use cases requiring a deeper understanding of distributed systems. However, it provides flexibility and customization options for advanced users. Elastic offers paid courses for those seeking more structured learning.
However, Splunk is considered more user-friendly and easier to start with. The dashboard and user interface provide intuitive features, making it user-friendly for administrators and analysts.
Splunk's guided search and reporting capabilities cater to users with varying technical skills. The company offers a trial period and comprehensive documentation to assist users. However, advanced Splunk educational courses come at a higher cost than alternative options.
Support
Both ELK Stack and Splunk offer different customer support options to assist users and provide necessary assistance and resources.
The ELK Stack offers community support through forums, documentation, and a large user community. Elastic provides commercial support and consulting services. Comprehensive and well-documented resources for each tool are available, making onboarding easier. In addition, Elastic offers educational sessions globally.
Splunk provides customer support platforms, including professional services, training programs, and a dedicated support portal. Different levels of support exist, including enterprise-level support.
The robust documentation and community forum provide additional resources. Splunk's education program offers virtual and on-site instructors to ensure users have ample support.
Releases
ELK Stack is an open-source solution that follows a continuous release cycle, with regular updates and new features introduced by the community and Elastic. The Elastic Stack releases are organized by component.
Similarly, Splunk releases regular updates and major versions to introduce new functionalities and improvements to the platform.
Both platforms prioritize stability and security in their releases.
Pricing
The ELK Stack and Splunk have different pricing structures. Splunk has a higher initial cost than the ELK Stack but offers various licensing options to accommodate different organizations. Furthermore, the ELK Stack is free to use, but additional features and managed services from Elastic Cloud come with associated costs.
The ELK Stack is open-source and free to use. However, additional features and enterprise-level support require a subscription from Elastic. Moreover, Elastic offers a service called Elastic Cloud, which provides a cloud-based platform for running and managing the ELK Stack. Elastic Cloud pricing is separate from the open-source ELK Stack and offers additional features, benefits, and managed services. These added services come with associated costs.
Splunk follows a commercial pricing model based on data ingestion volume and the number of users. Different licensing options and two primary pricing plans are available:
- Workload Pricing involves paying for the computing and storage resources required to run workloads in the Splunk Platform.
- Ingest Pricing is a volume-based pricing approach where users pay based on the daily amount of data ingested into Splunk products.
Customer Base
ELK Stack and Splunk cater to different industries and organizations of various sizes. The ELK Stack's open-source nature and cost-effectiveness initially gained popularity among small to medium-sized businesses and startups. This model offered flexibility, customization, and scalability for log management and analysis solutions. Over time, it has become a trusted choice for numerous large enterprises.
ELK Stack's customer base includes notable companies such as T-Mobile, Audi, Adobe, Cisco, P&G, Comcast, Equinox, Booking.com, BMW, Volvo, Kroger, Pfizer, and Walmart.
On the other hand, Splunk has established a strong presence in the enterprise market as a commercial platform. Its comprehensive features, security, and scalability make it a preferred choice for large organizations and industries with complex data requirements. Splunk's unified platform empowers SecOps, ITOps, and engineering teams to collaborate and achieve set goals.
Among Splunk's extensive clientele are over 12,000 customers and 80 Fortune 100 companies, including renowned organizations like Coca-Cola, Slack, Zoom, Porsche, Yelp, McLaren, Puma, Heineken, Tesco, and Lenovo.
ELK Stack vs. Splunk: How to Choose
When deciding between the ELK Stack and Splunk, it's essential to carefully evaluate the company's specific needs and consider several key factors. These factors include data requirements, availability of expertise, and financial considerations.
If the company requires flexibility and the ability to handle diverse data sources and formats, the ELK Stack's open-source nature is the way to go. However, when dealing with large volumes of machine-generated data, Splunk is a better fit. The platform is better suited for companies prioritizing real-time monitoring and analytics.
Another factor to consider is the level of expertise and resources available within the team. The ELK Stack requires technical proficiency for setup and configuration. In contrast, Splunk offers a user-friendly platform with an intuitive interface and guided search functionality, enabling quick adoption by team members with varying technical expertise.
From a financial perspective, it's important to note that the ELK Stack's base software is free. However, additional features and enterprise-level support from Elastic come with associated costs. In contrast, Splunk follows a commercial pricing model based on data ingestion volume and the number of users.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you know the key differences between the ELK Stack and Splunk and have a better understanding of how to choose the best platform for your use case.
Next, learn about the different data integration tools available.