Helm charts optimize the deployment of Kubernetes resources by packaging resource manifests into reusable YAML template bundles.
Users can easily configure the charts to adapt to any scenario, which allows for efficient and consistent deployment of complex applications.
This article provides step-by-step instructions on how to create and deploy a Helm chart.
Prerequisites
- Command-line access.
- Kubernetes cluster installed and configured (for assistance, follow our guides on How to Install Kubernetes on Ubuntu and How to Run Kubernetes on Windows).
- Helm installed.
Note: To confirm Helm has been installed properly, run which helm in the terminal. The output should return a path to Helm.
How to Create Helm Chart
Creating a Helm chart involves generating the chart directory using the Helm CLI. Enter the following command to create a new chart:
helm create [chart_name]For example:
helm create phoenixnapThe output confirms Helm executed the action successfully.

List the chart structure with the ls command:
ls [chart_name]
The Helm chart directory contains the following items:
- charts - The directory storing dependent charts.
- templates - The directory for configuration files.
- Chart.yaml - The file containing chart metadata.
- values.yaml - The file with default chart parameter values.
How to Configure Helm Chart
Configuring a helm chart involves customizing parameters such as the image pull policy, name override, service account, and service type. Follow the steps below to learn how to edit these parameters in the values.yaml file.
Configure Helm Chart Image Pull Policy
The image pull policy determines how a container image is pulled from a registry. The default policy value is IfNotPresent, meaning that Kubernetes pulls an image only if it is not already on the system. To change this behavior:
1. Open the values.yaml file in a text editor such as Nano:
nano [chart_name]/values.yaml2. Locate the image section.
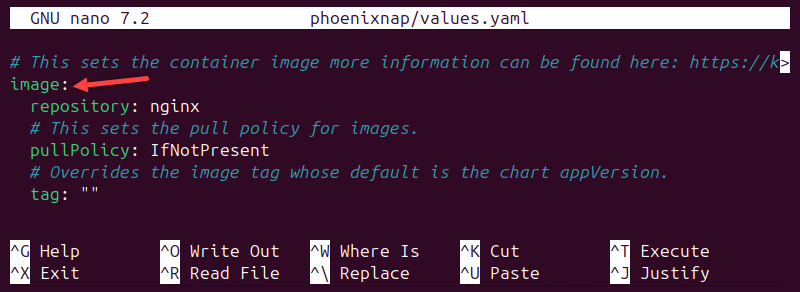
There are three possible values for pullPolicy:
IfNotPresent- Download the image if it does not exist in the cluster.Always- Pull the image on every restart or deployment.Latest- Pull the most up-to-date version available.
3. Change the pull policy from IfNotPresent to Always:
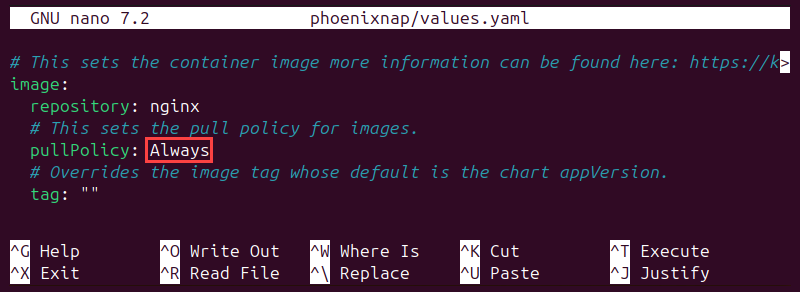
Helm Chart Name Override
To override the chart name in the values.yaml file, add values to nameOverride and fullnameOverride fields. The following example adds phoenix-app as the nameOverride value and phoenix-chart as fullnameOverride.
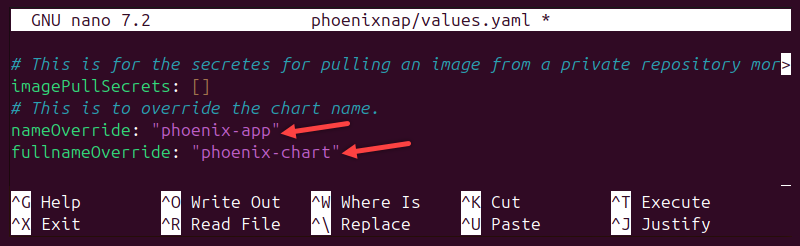
Overriding the Helm chart name ensures configuration files also change.
Specify Service Account Name
The service account name for the Helm chart is generated when you run the cluster. However, it is good practice to set it manually and ensure the application is directly associated with a controlled user in the chart.
To provide a custom service account name, locate the serviceAccount value in the values.yaml file and specify the name of the service account. The example below shows phoenixnap as the name of the service account.
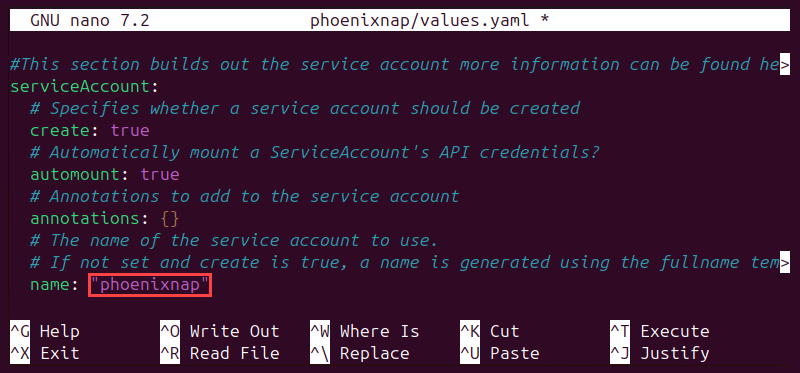
Change Networking Service Type
Depending on the cluster, a deployment may require different networking service types. For example, when using Minikube for testing, the recommended networking service type is NodePort.
To change the networking service type, locate the service section and change the value in the type field. The example below shows NodePort set as the new service type.
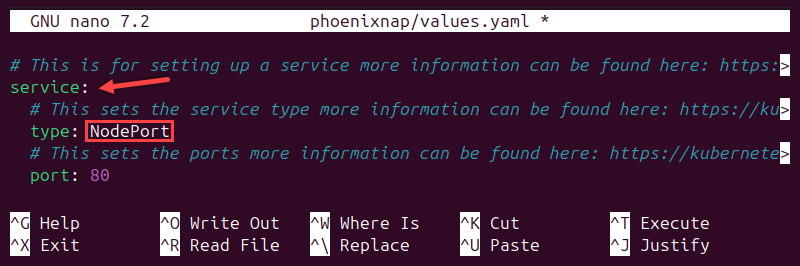
How to Deploy New Helm Chart on Kubernetes
After configuring the values.yaml file, deploy the application using Helm commands. Proceed with the steps below to complete this action.
Step 1: Install Helm Chart
Install the Helm chart using the helm install command:
helm install [full_name_override] [chart_name]/ --values [chart_name]/values.yamlFor example:
helm install phoenix-chart phoenixnap/ --values phoenixnap/values.yaml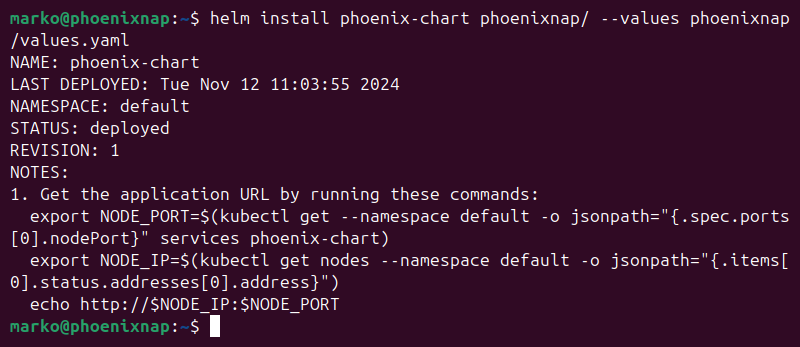
The helm install command deploys the app.
Step 2: Export Node Port and IP Address
Run the two export commands printed in the NOTES section of the helm install output. For example, the output for the phoenix-chart deployment in the default namespace generates the following commands:
export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace default -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services phoenix-chart)export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace default -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}")The commands produce no output but store the IP and port values in respective environment variables.
Step 3: View the Deployed Application
To view the contents of the environment variables from the previous step, enter the following echo command:
echo http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORTThe output shows the full address of the deployed application.

Copy the address and paste it into a web browser. The application screen appears.
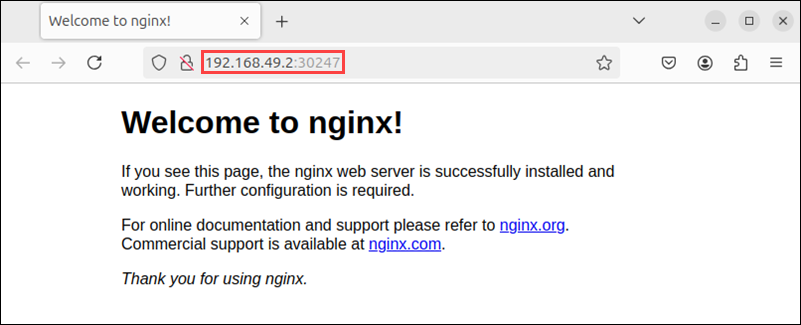
Note: Learn how to delete a Helm deployment and namespace to remove unwanted or multiple copies of Helm deployments.
Conclusion
By following this step-by-step guide, you learned how to create a Helm chart tailored to your needs. Once configured, the chart can be seamlessly deployed to your Kubernetes cluster.
Now that you know how to create a Helm chart, learn How to pull and push Helm charts and add Helm chart repositories.