Redis is an open-source solution for storing data structures. It is primarily used as a key-value store, which enables it to serve as a database, cache, and message broker.
In this tutorial, we will cover different ways to delete these key-value pairs (keys) and clear the Redis cache.
Prerequisites
- The latest version of Redis (see our guide on how to install Redis on Ubuntu, on Mac or run Redis on Docker)
- Access to the command line / terminal window
Clear Redis Cache With the redis-cli Command
The easiest way to clear Redis cache is to use the redis-cli command.
Databases in Redis are stored individually. Using the redis-cli command allows you to either clear the keys from all databases or from a single specified database only.
redis-cli Command Syntax
The redis-cli command uses the following syntax:
redis-cli [database number] [option]Where:
[option]allows users to choose between clearing all databases or one specific database.[database number]enables users to specify the database to clear.
Note: Once you delete keys from a database, they can no longer be recovered.
Deleting All Keys
To delete keys from all Redis databases, use the following command:
redis-cli flushall
As of version 4.0.0, Redis can clear keys in the background without blocking your server. To do this, use the flushall command with the async parameter:
redis-cli flushall asyncDeleting Keys from a Specific Database
Use the following command to clear a specific database only:
redis-cli flushdbUsing the flushdb command without any parameters clears the currently selected database. Use the -n parameter with the database number to select a specific database you want to clear:
redis-cli -n [database number] flushdbYou can also use the async option when clearing keys from individual databases:
redis-cli -n [database number] flushdb asyncAutomating Cache Clearing Using Ansible
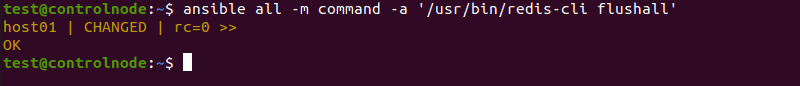
If you have many Redis servers running, manually clearing the cache on each one takes time. To speed this process up, use a tool like Ansible to clear the cache on all your Redis servers at the same time:
ansible all -m command -a '/usr/bin/redis-cli flushall 'Running this command applies the flushall command to every server in your Ansible inventory file:
allallows users to choose all the remote hosts in the Ansible inventory file.-menables users to select a module to execute.-aprovides an argument for the module. In this case, the command module runs theflushallcommand withredis-cli.
Conclusion
After going through this tutorial, you have learned how to use the redis-cli and flush commands to clear your Redis cache.
Next, learn more about Redis by exploring Redis Data Types.