The 406 Not Acceptable error occurs when a server understands a request but refuses to return a response because none of the available content formats match the client's requirements.
This error often appears after configuration changes, Content Management System (CMS) updates, or strict security rules, which makes it harder to diagnose than common client-side errors.
This guide will explain what the 406 error means, why it happens, how it affects SEO, and how to fix and prevent it.
What is 406 Error?
The 406 Not Acceptable error is an HTTP client error that occurs when a server understands a request but cannot return a response in a format allowed by the client’s request headers. These formats include response types such as HTML pages, JSON or XML data, media files, and other representations generated by the server.
When the client specifies strict content requirements, the server rejects the request instead of returning content in a different format. This behavior is expected and is part of HTTP content negotiation.
This error is most often associated with strict content negotiation, API requests, security rules, or applications that enforce narrow response formats rather than falling back to a default.
Note: Another error from the 4xx group is error 408.
406 Error Examples
Platforms rarely show raw HTTP 406 errors to users. Instead, they wrap backend network or content-negotiation failures in platform-specific error codes.
Common platforms that demonstrate this behavior include Hulu, Netflix, Xbox, Google Play, Square Enix Games, and Windows gaming services.
On modern streaming and gaming platforms, HTTP 406 errors are abstracted behind branded, numeric, or alphanumeric codes, each paired with a concise, user-friendly message. The purpose is to maintain a consistent user experience (UX) while signaling content or network requests failed.
Across these platforms, 406 errors typically appear as:
- Branded or numeric error codes (NW, P‑DEV, 0x…).
- Short, user-friendly messages (“Something went wrong,” “We’re having trouble playing this”).
- Minimal technical detail exposed to avoid confusing non-technical users.
For instance, Netflix almost never displays raw HTTP status codes. Errors like HTTP 406 are handled internally and show as network or playback codes, such as NW-2-5.
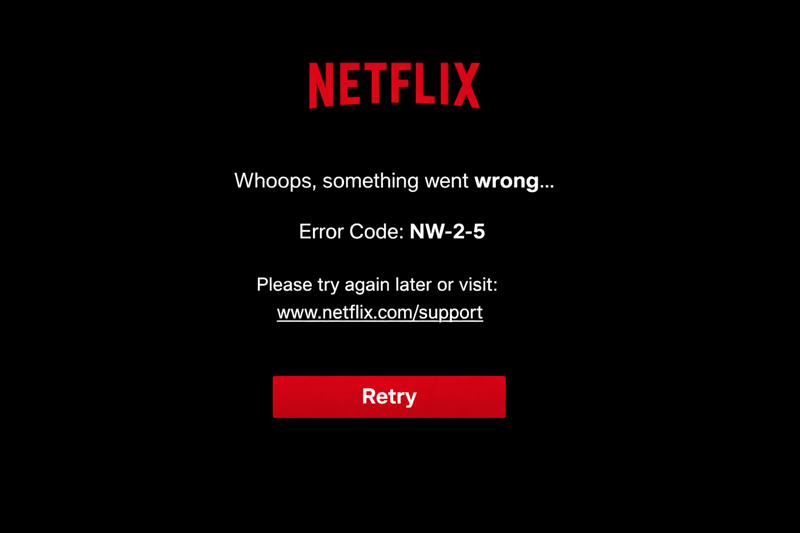
This code signals the Netflix app failed to receive a usable response from the server. The causes are different, including a 406 response. However, users only see the generic NW-2-5 message with a “Whoops, something went wrong” prompt.
Hulu uses numeric playback and network error codes instead of raw HTTP responses. A 406 error at the server or HTTP layer is usually mapped to a generic code, such as P-DEV320.
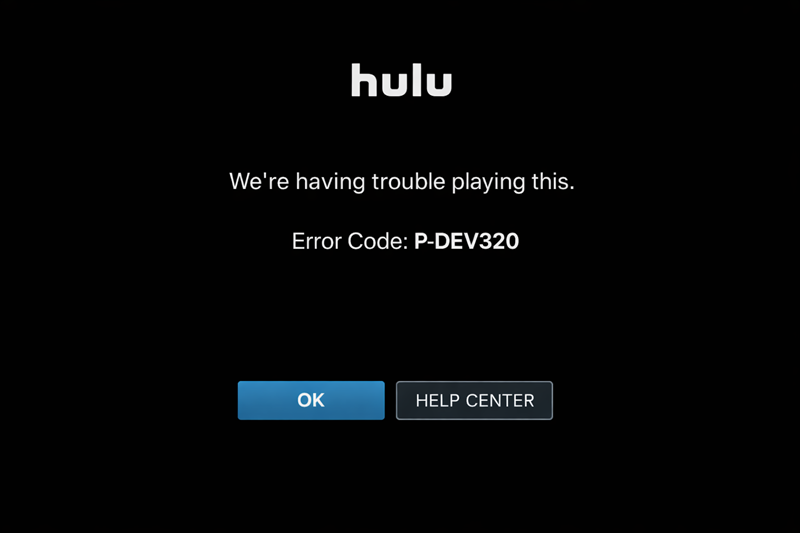
Users see a short message that indicates playback failure without technical details. In rare cases, the 406 appears in developer tools or browser network logs, but not in the standard User Interface (UI).
With Xbox, the UI displays structured system and service error codes. HTTP 406 errors can contribute to these failures, often mapped to error codes such as 0x801901F7 or 0x87DD0006.
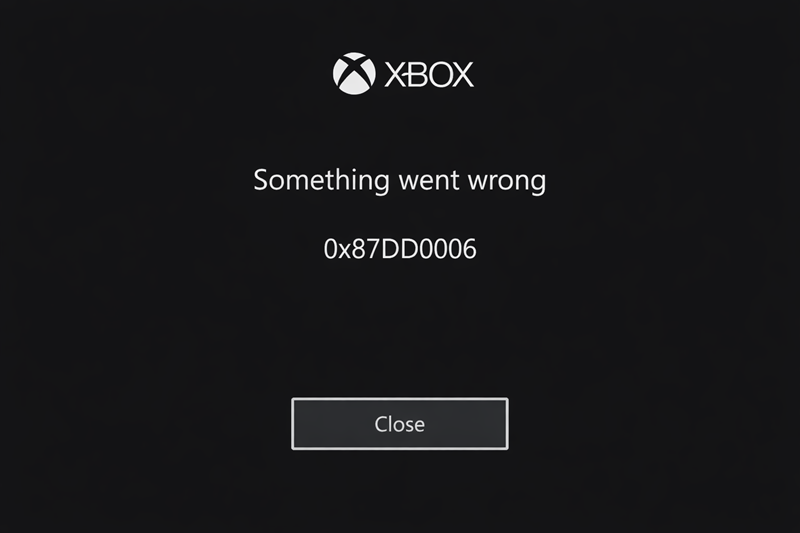
Users see a brief, branded message, such as “Something went wrong”, along with the numeric code. While closer to real backend responses than Netflix or Hulu, raw HTTP status codes are still hidden from the user.
What Causes 406 Error?
When you understand the causes of a 406 Not Acceptable error, it helps you diagnose and resolve the issue efficiently.
The following list presents the most common factors that trigger this error, whether on websites, APIs, or application platforms:
- Strict Accept headers. Accept headers tell the server which response formats the client can receive. The client specifies formats, character sets, or encodings that the server cannot provide.
- Unsupported media types. The server cannot generate a representation in the requested content type, such as JSON, XML, or HTML.
- Server-side content negotiation rules. Some servers enforce strict content negotiation policies that reject requests instead of returning a default format.
- Corrupted or incompatible request headers. Malformed, missing, or conflicting headers prevent the server from matching content.
- CMS or platform misconfigurations. Updates, plugins, or modules that alter response handling sometimes inadvertently block certain content types.
- Security rules and firewalls. Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) or server security policies sometimes reject requests that appear suspicious or invalid.
- Proxy or caching layers. Intermediate proxies, Content Delivery Network (CDN), or caching systems filter responses or block content if they cannot satisfy header requirements.
- API or service limitations. Some APIs reject requests when strict content types are enforced or when the client request is incompatible with the service's response format.
406 Error and SEO
A 406 Not Acceptable error affects SEO because search engines cannot access the page content. If a crawler encounters a 406 response, it may not index the page, or it can remove it from search results.
A 406 differs from other 4xx errors because the server understands the request but cannot provide a response in an acceptable format. Repeated 406 responses signal content delivery issues rather than missing pages.
Search engines often request content in multiple formats. If the server rejects all acceptable formats, the page may be temporarily or permanently excluded from search results.
To reduce SEO impact, ensure the server responds correctly to standard user-agent requests and does not block crawlers with overly strict content rules. Standard formats like HTML or JSON should always be available, and plugins, security rules, or caching systems should not interfere with search engine requests.
How to Fix 406 Error
When you address a 406 Not Acceptable error, you restore access to content and maintain a consistent user experience. Unresolved 406 errors disrupt browsing, break API calls, and negatively affect SEO.
The following steps provide practical guidance to help you identify and resolve the error across websites, CMS platforms, APIs, and application services.
Check URL
A 406 error occurs if the requested URL contains typos, unsupported characters, or malformed query parameters.
Verify the URL is correct, properly encoded, and points to the intended resource. Often, when you correct the URL, it resolves the error.
Perform Resets
Temporary client-side issues can trigger 406 errors. To address them:
- Clear the browser or application cache to ensure fresh content is requested.
- Remove cookies or local storage data that may interfere with request headers.
- Restart network devices if connectivity issues are suspected.
These resets often fix transient errors without server-side changes.
Roll Back CMS Changes
CMS updates or plugin installations trigger 406 errors.
If the error appears after recent updates, revert to the previous version to see if it resolves the issue. Once identified, adjust or replace the conflicting plugin or theme component.
Check Plugins, Themes, and Extensions
Third-party software sometimes interferes with request handling.
Temporarily deactivate plugins, themes, or browser extensions, then test whether the error persists. This method isolates conflicts caused by content filters, security modules, or custom scripts.
Check Database
Database issues prevent proper content delivery and trigger 406 errors.
Check queries return valid data, and the content is correctly formatted. Repair or restore corrupted tables if necessary. This step is especially important for dynamic websites, APIs, or applications that rely on database-driven content.
Check Server Logs
Server logs provide detailed insight into failed requests.
Review access and error logs to identify 406 entries, examine headers, and note patterns in blocked requests. Logs often reveal whether the error originates from headers, content negotiation, or security restrictions.
Check Accept Headers / Request Formatting
Some clients send overly restrictive Accept headers that the server cannot satisfy. To troubleshoot, take the following steps:
1. Inspect request headers with browser developer tools, Postman, or curl.
2. Ensure the Accept header includes standard content types such as text/html or application/json.
3. Adjust the client request to accept multiple formats if possible.
Review Security and WAF Rules
Security rules and Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) can sometimes block legitimate requests.
Check security logs for blocked requests and temporarily adjust rules to test resolution. Once confirmed, whitelist valid requests or fine-tune security policies while you maintain protection.
How to Prevent 406 Error in the Future
Prevent 406 Not Acceptable errors to maintain uninterrupted content delivery, ensure smooth user experience, and protect search engine visibility. Proactive measures reduce the likelihood of errors caused by content negotiation, misconfigured headers, or platform updates.
The following practices help minimize 406 errors:
- Validate URLs before deployment. Ensure links and requests are properly formatted and encoded to prevent malformed requests.
- Maintain up-to-date software. Regularly update CMS platforms, plugins, themes, and applications to avoid compatibility issues.
- Monitor and test request headers. Verify Accept headers and other client headers are compatible with server-supported formats.
- Review security rules regularly. Check firewall and WAF configurations to ensure legitimate requests are not blocked.
- Use consistent content formats. Provide standard response types such as HTML, JSON, or XML to meet broad client expectations.
- Test across devices and browsers. Ensure requests from multiple platforms and clients receive acceptable responses.
- Check caching and CDN configurations. Make sure proxies, CDNs, and caches do not block or alter acceptable content formats.
- Implement logging and monitoring. Track server and application logs for 406 responses and address recurring issues promptly.
- Document changes and rollback plans. Maintain records of updates or configuration changes to quickly revert if a new error arises.
Conclusion
This article explained what a 406 error is, its common causes, and its impact on SEO. It also provided several ways to fix and prevent the error.
Next, learn what error code 404 is and how to fix it.