Users seeking an alternative to proprietary operating systems usually face a dilemma between Linux Mint and Ubuntu. Both popular distributions share a common Debian ancestry, but differ in design philosophy, desktop interface, and software management.
This article compares Linux Mint and Ubuntu, analyzes their differences, and provides tips for choosing the right distribution.
What Is Linux Mint?
Linux Mint is a community-driven operating system designed to provide a classic desktop experience with minimal configuration. It emphasizes a "works out of the box" philosophy by including essential codecs and tools by default.
The project maintains three primary editions based on different desktop environments: Cinnamon, MATE, and Xfce. Each version targets specific hardware profiles while maintaining a consistent user experience.
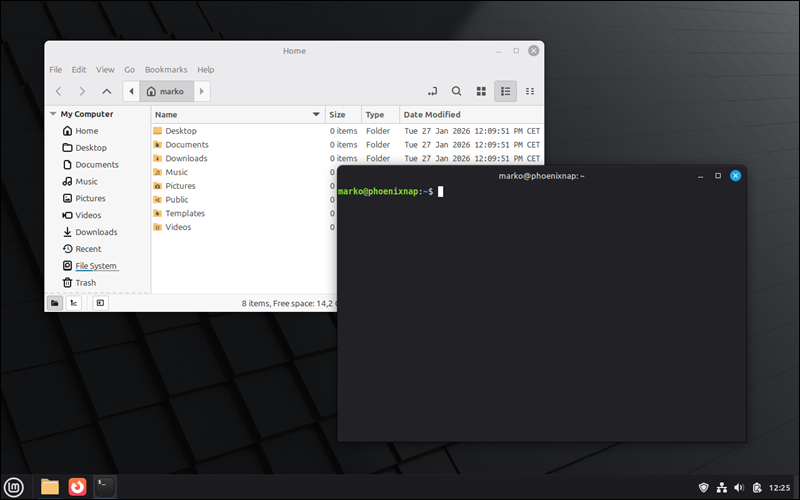
The image below shows Linux Mint with the Cinnamon desktop environment.
Linux Mint Features
The operating system includes a suite of custom-built applications (X-Apps) for basic tasks like text editing, image viewing, and media playback. These tools are created to be desktop-agnostic, GTK-compatible, and functional across different distributions.
Other important Linux Mint features include:
- Cinnamon desktop. A traditional, Windows-like interface with a taskbar and start menu.
- Update manager. A tool that categorizes updates by stability and risk level.
- Software manager. A graphical interface for installing thousands of applications via APT and Flatpak.
- System snapshots. Integrated Timeshift support for creating and restoring system backups.
- Driver manager. A utility that identifies and installs proprietary drivers for hardware compatibility.
Linux Mint Advantages
The most important benefit of Linux Mint is efficiency, as it uses fewer background processes than its competitors. This lightweight architecture allows users to maximize the performance of their existing hardware, with the Xfce and MATE editions operating efficiently even on legacy hardware.
Aside from being efficient, Linux Mint is also:
- Familiar. The interface layout reduces the learning curve for Windows users.
- Private. The system avoids telemetry collection and does not track user activity.
- Stable. The developers base their releases on Ubuntu Long-Term Support (LTS) versions.
Linux Mint Disadvantages
Linux Mint's conservative approach to software updates means users may not always have access to the latest app versions, and the default kernel versions lack support for the latest hardware releases. Furthermore, the reliance on a smaller community team can lead to longer wait times for less urgent bug fixes.
What Is Ubuntu?
Ubuntu is a Linux distribution developed by Canonical Ltd. that focuses on a modern interface and broad enterprise support. It serves as the primary choice for many developers, cloud infrastructures, and server deployments worldwide.
The operating system utilizes the GNOME desktop environment, which features a custom, productivity-oriented layout.
Canonical provides professional support services, making it a standard in corporate environments.
Ubuntu Features
Ubuntu integrates with cloud services and enterprise security protocols, creating a foundation for professional environments. It is a good choice for managing large workstation deployments with automated tools.
Other essential Ubuntu features include:
- GNOME desktop. A modern interface with an activities overview. Ubuntu modifies the vanilla GNOME with a vertical dock that shows on the desktop.
- Snap Store. A centralized repository for applications containerized with all their dependencies.
- Ubuntu Pro. An optional subscription service for extended security maintenance and compliance.
- Active Directory integration. Built-in tools for connecting to corporate network infrastructures.
- Broad architecture support. Official versions exist for x86_64, ARM, and RISC-V platforms.
Ubuntu Advantages
Broad industry adoption of Ubuntu ensures that most hardware and software vendors treat it as the primary target for Linux compatibility. Users benefit from rapid patch deployment and commercial support.
Below are some other advantages of Ubuntu:
- Professional support. Commercial assistance is available for business and enterprise use cases.
- Cloud integration. The distribution is a top-tier choice for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud environments.
- Hardware certification. Major manufacturers like Dell and Lenovo certify hardware specifically for Ubuntu.
Ubuntu Disadvantages
The shift toward Snap applications has introduced performance overhead that some users find unnecessary for daily tasks. Additionally, the inclusion of diagnostic data collection remains a point of contention for privacy-focused individuals.
Linux Mint Vs. Ubuntu: Comparison
Linux Mint and Ubuntu share a common base but address different user preferences and system philosophies. While Ubuntu focuses on modern interface innovation and enterprise support, Linux Mint prioritizes a traditional desktop experience.
The table below compares the technical specifications and operational characteristics of Linux Mint 22 and Ubuntu 24.04 LTS:
| Linux Mint | Ubuntu | |
|---|---|---|
| System requirements | 2GB RAM (4GB recommended), 20GB disk. | 4GB RAM (8GB recommended), 25GB disk. |
| Security | Firewall (GUFW), Timeshift snapshots. | AppArmor, Wayland by default, Ubuntu Pro. |
| Performance | High efficiency on older hardware. | Optimized for modern multi-core systems. |
| Hardware compatibility | Excellent for older peripherals. | Best for the newest GPUs and laptops. |
| Software availability | APT, Flatpak, PPA. | APT, Snap (default), PPA. |
| Update cycle | Follows Ubuntu LTS (every 2 years). | LTS (2 years) and Interim (6 months). |
| User-friendliness | High (Traditional Desktop). | High (Modern/Touch-friendly). |
| Support | Community forums, documentation. | Commercial support, large community. |
| Community | User-driven, volunteer-based. | Large, corporate-backed, developer-heavy. |
Package Management
Linux Mint
APT serves as the primary command-line interface for managing software. Mint includes native Flatpak support to provide access to sandboxed applications while explicitly disabling the Snap daemon to maintain independence from Canonical.
Ubuntu
Ubuntu prioritizes the Snap Store for modern application distribution and automatic background updates.
The system maintains full compatibility with traditional Debian packages for core utilities through the Ubuntu App Center interface.
System Requirements
Linux Mint
The system requires at least 2GB of RAM, though 8GB remains the standard for multitasking. It requires 20GB of disk space and functions at a minimum resolution of 1024x768 pixels.
Ubuntu
Ubuntu recommends 4GB of RAM as the minimum for a functional system, with 25GB of storage. The GNOME desktop environment targets modern 2GHz dual-core processors and benefits from 3D acceleration for interface rendering.
Security
Linux Mint
Mint utilizes a level-based Update Manager to categorize patches by their impact on system stability. The inclusion of Timeshift enables rapid system recovery after configuration errors or failed updates, and Gufw (Graphic User Interface for Uncomplicated Firewall) offers a simplified front-end for managing firewall rules.
Ubuntu
The AppArmor system provides Mandatory Access Control to restrict application capabilities. Ubuntu also offers Livepatch, which applies critical kernel updates without requiring a system reboot, and the Ubuntu Security Guide (USG), a compliance tool that automates system hardening based on industry benchmarks such as CIS.
Perfomance
Linux Mint
The Cinnamon desktop environment uses fewer resources than GNOME, resulting in faster menu responses on mid-range hardware. Mint also has a faster boot sequence due to a streamlined set of startup services.
Ubuntu
Ubuntu ships with performance-tuned kernels that benefit the latest processor architectures. It provides a stable base for compute-intensive tasks such as video rendering and AI development when paired with modern GPUs.
Hardware Compatibility
Linux Mint
The Driver Manager detects and installs proprietary firmware for Wi-Fi cards and GPUs through a dedicated tool. Mint provides edge ISOs that include newer kernels for the latest hardware releases.
Ubuntu
Canonical partners with manufacturers to certify specific laptop models for full compatibility. The system integrates with the Linux Vendor Firmware Service to provide BIOS updates directly through the software center.
Software Availability
Linux Mint
Mint includes a suite of homegrown applications designed to work across several desktop environments. Users can also utilize the Web App Manager to transform websites into standalone desktop applications.
Ubuntu
The Snap ecosystem provides access to a large library of proprietary and open-source software maintained directly by developers. Ubuntu is the primary Linux platform for professional tools such as Slack and Spotify.
Software Update and Release Cycle
Linux Mint
Mint builds exclusively on Ubuntu Long-Term Support releases to ensure five years of maintenance. It issues minor point releases every six months to introduce new versions of the Cinnamon desktop.
Ubuntu
Ubuntu publishes interim versions every six months for users who desire the latest software and kernel features. The project releases a Long-Term Support version every two years to maintain production stability.
User-friendliness
Linux Mint
The interface features a taskbar and start menu familiar to users of classic desktop layouts. A welcome screen guides newcomers through initial setup steps, including snapshots and driver installation.
Ubuntu
Ubuntu uses a vertical dock and an activities overview designed for modern window management. The system features a powerful central search that quickly finds applications and settings.
Support
Linux Mint
Mint maintains a comprehensive user guide covering installation and configuration. Active community forums provide a platform where experienced users assist others with specific hardware issues.
Ubuntu
Canonical offers paid professional support through Ubuntu Pro for business deployments. The Wiki and Ask Ubuntu sites host a massive knowledge base for community-based solutions.
Community
Linux Mint
The project remains volunteer-driven and relies on donations rather than corporate funding. Development priorities shift based on direct communication with the user base on the Mint blog.
Ubuntu
Ubuntu benefits from Canonical's resources, which ensure consistent development and marketing. It attracts a large number of software developers who use the platform as their primary environment.
Linux Mint Vs. Ubuntu: How to Choose?
The choice between Linux Mint and Ubuntu should focus on the trade-off between modern features and traditional stability. When making a decision, consider the age of the hardware and the specific software required for daily operations.
Another important factor is the user's preferred desktop paradigm. Testing both in a live ISO environment allows a direct comparison of interface performance on specific hardware.
Use Cases for Linux Mint
Linux Mint is an ideal platform for users who want a desktop that runs without constant modification. It is particularly effective for repurposing hardware that no longer supports current proprietary operating systems.
Use Cases for Ubuntu
Professional developers and cloud engineers often find Ubuntu best suited to their rigorous technical requirements. The extensive commercial backing makes it the logical choice for corporate workstations and secure production servers.
Conclusion
After reading this comparison article, you understand the difference between the community-focused approach of Linux Mint and the enterprise-oriented framework of Ubuntu. The article examined the specific features, advantages, and disadvantages of each distribution and compared essential technical points.
Next, read our comparison between Linux and macOS.