Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses store and access data, offering remarkable scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, with these advantages also come unique security considerations.
Unlike traditional on-premises setups, where data and applications reside within your physical control, cloud services disperse resources across a vast network of servers. Furthermore, data in the cloud is subject to complex access control challenges, especially as it traverses the internet to reach end users or integrate with other services. This situation potentially exposes it to vulnerabilities if not properly secured.
This article outlines twelve cloud security best practices and tips to fortify your cloud security.

Cloud Security Best Practices and Tips
Your cloud security strategy should include the following best practices to ensure a robust defense.
1. Understand Your Responsibility
Cloud security is a shared responsibility, but it is not a 50/50 split. The cloud provider's responsibility is to secure the underlying infrastructure, while the customer must protect the data and applications. You need to be aware of what security measures the provider offers and what you need to implement on your own.
Carefully review your cloud provider's policies to fully understand these shared responsibilities and eliminate potential security gaps.
2. Implement Robust Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Controlling access to cloud resources is vital. Establish a comprehensive IAM framework to ensure that only authorized users can access your data.
The IAM framework should encompass:
- Enforcing strong password policies. Implement complex password requirements, including a minimum length, character variety (uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols), and regular password changes.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA). 2FA adds an extra layer of security. It requires users to verify their identity beyond just a password, often through a code sent to their phone or a security token.
- Role-based access controls (RBAC). These controls grant users access based on the least privilege principle, meaning users can only access the data and functionalities necessary for their roles.
3. Educate Your Staff
The human element is critical in 88% of data breaches. Regular security awareness training empowers your staff to identify and mitigate different types of cyber attacks.
Training should cover:
- Phishing and social engineering attack awareness. Train employees to recognize suspicious emails, texts, or phone calls attempting to steal credentials or sensitive information.
- Secure password creation and management. Educate staff on creating strong passwords and proper password hygiene practices, including avoiding password reuse and employing password managers.
- Security policies and compliance requirements. Ensure staff understand your organization's IT security policy and relevant industry regulations.
4. Establish and Enforce Clear Cloud Security Policies
Well-defined, documented cloud security policies are the cornerstone of secure cloud usage.
These policies should standardize the following:
- Acceptable cloud service use. Define authorized cloud services and applications to prevent shadow IT (unauthorized cloud use).
- Data classification and handling procedures. Classify data based on sensitivity and establish clear procedures for handling, storing, and transmitting this data.
- Security protocols for accessing cloud services. Mandate the use of secure connections like VPNs and require strong Wi-Fi security practices when accessing cloud services remotely.
5. Secure Your Endpoints
Unsecured devices, such as laptops and smartphones, introduce vulnerabilities and reduce endpoint security. Fortifying your defenses in this area should involve:
- Implementing endpoint protection platforms (EPP) and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions. These tools provide comprehensive protection against malware, ransomware, and other threats on user devices.
- Performing updates and patching consistently. Regularly update operating systems, applications, and firmware to address known vulnerabilities.
- Enforcing secure connections. Mandate the use of VPNs for remote access to cloud resources to encrypt data transmissions and prevent unauthorized access on public Wi-Fi networks.
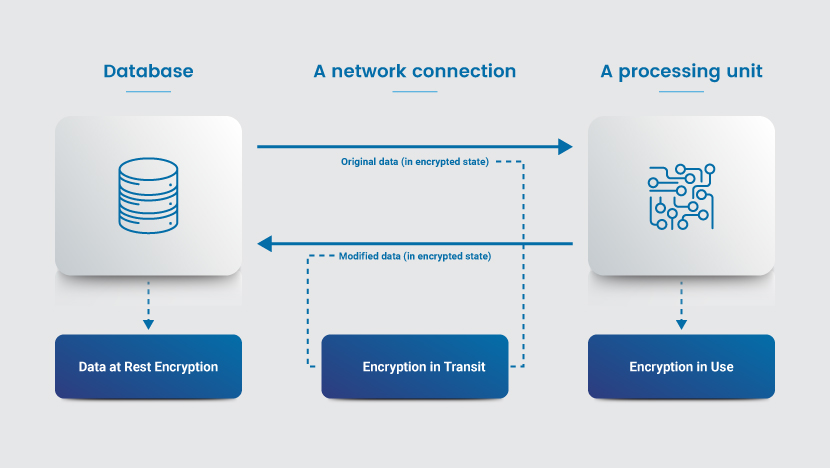
6. Encrypt Data
Encryption scrambles data, making it unreadable without a decryption key. This extra step safeguards your data from unauthorized access, whether it’s at rest, in transit, or in use.
Essential encryption practices include:
- Employing strong encryption standards. Use robust encryption algorithms like AES-256 for data at rest.
- Encrypting data in transit. Ensure data transmissions are encrypted using protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security).
- Secure management of encryption keys. Store encryption keys securely, preferably with a cloud-based key management service.
7. Leverage Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) continuously monitor cloud environments for suspicious activity, while Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively block these threats. These systems offer:
- Real-time network traffic monitoring and analysis. IDS systems continuously analyze network traffic for anomalies that might indicate a cyber incident.
- Alerts for suspicious activity. IDS systems generate real-time alerts for suspicious activity, enabling an immediate response to potential threats.
- Automated threat mitigation. IPS systems automatically block identified threats, minimizing potential damage.
8. Double-Check Your Compliance Requirements
Organizations that manage sensitive data must comply with relevant regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), or PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard). Compliance is more challenging in a cloud environment because deployments are often fluid, with data and applications constantly moving. This dynamism makes it challenging to maintain consistent visibility and control.
Here is how you ensure compliance:
- Align cloud services and policies with regulations. Verify that your cloud services and security policies adhere to the data protection and privacy laws applicable to your industry or region.
- Conduct regular audits. Regularly assess your cloud environment for compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Partner with compliant cloud providers. Select cloud service providers that offer compliance certifications relevant to your specific needs.
Need a secure, compliant cloud solution? phoenixNAP has you covered. We are PCI-DSS compliant and HIPAA-ready.
Contact us to learn more!
9. Consider a Cloud Access Security Broker or Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB) and Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP) significantly enhance organizational security by providing visibility, security, threat protection, and compliance management across multiple cloud infrastructures, including private, public, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments.
These tools provide:
- Visibility into cloud application usage and shadow IT. CASBs and CNAPPs provide insight into cloud application usage across an organization and identify unauthorized or unsanctioned cloud services (shadow IT).
- Data loss prevention (DLP) capabilities. CASBs and CNAPPs prevent sensitive data from being accidentally or intentionally exfiltrated from your cloud environment.
- Enforced security policies across cloud services. CASBs and CNAPPs centrally enforce your organization's security policies across all subscribed cloud services.
10. Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Regular security assessments are vital for proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in your cloud environment.
These evaluations should include:
- Vulnerability assessments. Regularly scan your cloud resources for weaknesses in services, configurations, and applications.
- Penetration testing. Simulate cyber attacks to test the effectiveness of your defenses and identify potential security gaps.
- Reviews of access controls and permissions. Regularly review and update access controls and permissions to ensure they align with your needs and policies.
11. Enable and Monitor Security Logs
Logging and monitoring cloud activity is essential for detecting unauthorized access and maintaining the integrity of your environment.
Here is how to establish effective logging and monitoring:
- Enable logging features in cloud services. Configure cloud services to log access attempts, user activities, and system events.
- Use security information and event management (SIEM) systems. SIEM systems aggregate and analyze log data from various sources, providing a holistic view of security events across your IT environment.
- Regular review of logs for anomalies. Analyze logs to identify suspicious activity or potential incidents.
12. Understand and Mitigate Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations of cloud resources introduce security vulnerabilities as they can expose data or create entry points for attackers to exploit. To prevent these errors:
- Conduct configuration reviews. Schedule regular reviews of cloud resource configurations to ensure they comply with security best practices.
- Use automated tools for real-time detection and correction. Automated tools monitor configurations and identify and rectify misconfigurations in real time.
- Train staff on secure configuration practices. Educate staff on how to securely configure your cloud resources and the importance of adhering to established guidelines during cloud provisioning and management.

Concerned about cloud security? Consider phoenixNAP’s Data Security Cloud, a secure infrastructure platform built in collaboration with Intel and VMware.
It provides multi-layered data protection through a secure hardware foundation, strict virtualization and segmentation controls, threat intelligence, and advanced physical security.
Strengthening Your Cloud Security Framework
By implementing these essential cloud security tips, you can safeguard your valuable data in the cloud and improve your organization’s security posture. Remember that cybersecurity is a process. Continuous vigilance, adaptation, and adherence to cybersecurity best practices are vital to protecting your organization from threats.



