Remote and hybrid work have become standard practice in many industries. Companies require solutions that allow employees to access their workstations remotely while simultaneously protecting sensitive company data from potential cyber-attacks.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) and VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) are technologies designed to address these needs but serve different purposes.
Learn the differences between VPN and VDI and decide which solution best fits your organizational requirements.

What Is VPN?
VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a technology used to securely connect an endpoint device, like a PC or laptop, to a remote VPN server. Once the connection is established, data transfers between the device and server are encrypted to prevent unauthorized access.
In a business setting, the VPN server is part of a company's network, and it routes traffic to specific resources within the system. Companies set up VPNs to ensure that only authenticated users have remote access to sensitive information and essential digital assets.
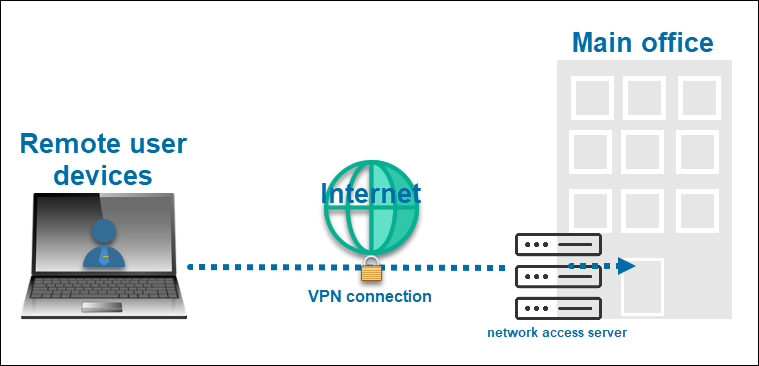
Note: A VPN also conceals the user's public IP address and replaces it with the VPN server IP. VPNs are popular among individual users who want to maintain privacy and enhance security while browsing public networks.
What Is VDI?
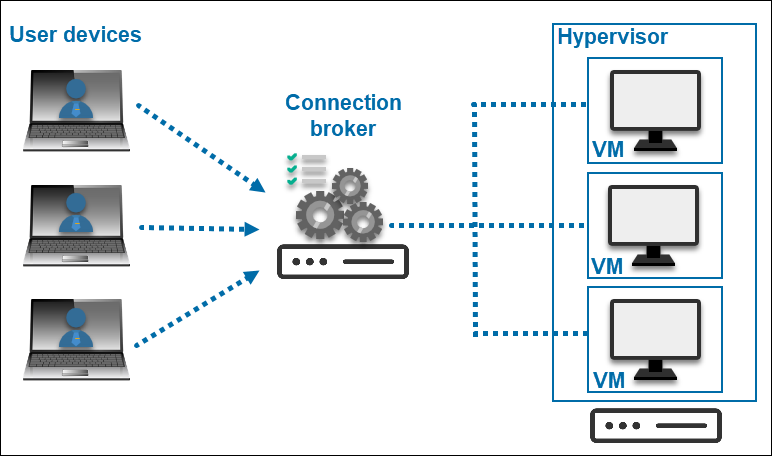
VDI, or Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, is a technology that virtualizes desktop environments and delivers them to users over a network.
In this system, a central server in a data center or office runs multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM operates a dedicated desktop environment for remote users. VDI is device-agnostic and doesn’t rely on the end-user hardware, which means that users can connect to their virtual desktop from any remote device.
Centralized management is a key feature of VDI. System administrators can efficiently update, configure, or install software on multiple systems. A master version, a so-called golden image, is used to replicate a software setup across various desktops within a cluster.
VPN vs. VDI: What are the Differences?
VDI allows users to access a dedicated and fully developed remote desktop environment. A VPN establishes an encrypted tunnel between the end user and an organization’s private network.
The following table compares VPN and VDI functions and features and provides a useful overview of the differences between the two technologies.
| VPN | VDI | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Smaller initial investment and lower operational costs. | High upfront costs. |
| Hardware Dependency | The client's network adapter influences the throughput and reliability of the VPN connection, while the processor determines the efficiency of the encryption and decryption process. | End-user hardware does not affect VDI performance, as most processing occurs on the server side. |
| Data Storage and Security | Data transmission is secure, but users can increase the attack surface by storing data on local devices. | Data is stored and protected centrally, which reduces the chance of data leakage or loss. |
| Performance | Varies based on the end user's hardware and network connection speeds. | Consistent and robust performance as resources are hosted on powerful company hardware. However, the user's network must be reliable. |
| Management and Maintenance | It is challenging to manage and troubleshoot off-site user devices. | Easier to deploy updates and changes across all virtual desktops. |
| Scalability | It is easy to add or remove user accounts. | Adding a new environment often requires additional server capacity. |
| User Experience | UX depends on the quality of the user's local machine. | Consistent user experience regardless of local device capabilities. Provides a complete desktop experience. |
| Network Dependence | Depends on internet connectivity for access. Some work may be done offline if data is stored locally. | Reliant on robust network connections, especially for high-performance tasks. |
Is VPN Better than VDI? How to Choose
VPN and VMs have distinct roles, but they are not mutually exclusive. Many companies use VDI and VPNs together for remote work and in different virtualization scenarios.
The decision to implement VDI or VPN depends on your specific use case, company size, industry, and available workforce. Before deciding, consider the factors in the sections below.
Cost
A VPN is an efficient and scalable solution for companies that have a large and fluctuating workforce or focus on short-term projects. VPNs require minimal hardware as users do not need dedicated environments, allowing businesses to extend network access to multiple devices using a single account.
Implementing VDI is typically more expensive than setting up a VPN. The additional costs for VDI stem from the software required to host the system, server hardware, and dedicated resources for each virtual workstation. VDI operational expenses decrease over time due to its centralized management and maintenance system, making it a cost-effective option for long-term projects.
Hardware Dependency
In a VPN, most of the data processing occurs on client devices. Outdated operating systems and obsolete user hardware can impact performance and productivity. Organizations that use VPNs may need to supply newer and higher-quality hardware to employees who work on resource-intensive tasks.
VDI has minimal end-user hardware requirements, and devices are often irrelevant to the overall experience. Processing is done server-side using dedicated resources assigned to the virtual machine running the virtual desktop. Companies may need to invest in buying servers or renting additional servers and network infrastructure when setting up or expanding a VDI environment.
Data Storage and Security
A VPN protects data in transit by sending it over an encrypted tunnel. However, the data is vulnerable once it is on the client's machine. The employee can move and copy data to other devices without restrictions. Copying company files locally increases the risk of potential data breaches.
When using VDI, the data remains in the workstation's virtual environment. VDI system administrators can restrict data transfer outside the corporate network and protect it on company servers or the cloud. Organizations that collect or handle personal customer information may need to use VDI to limit data proliferation and keep it in a secure and centralized location.
Performance
VPN performance is influenced by the capabilities of the employee's device as it uses the device's resources for encryption and decryption operations. Internet connection speeds impact VPN performance when handling large data sets.
VDI provides a more uniform and potentially faster user experience. Each virtual desktop in a VDI setup has allocated resources from a centralized server, which ensures performance is not affected by the user hardware. Resource-intensive applications and environments that require high consistency across different user sessions can benefit from VDI.
Management and Maintenance
Setting up a VPN server is straightforward and less expensive than establishing a full VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) system. However, remotely configuring and troubleshooting client devices can be challenging as users utilize a variety of devices and operating systems.
A VDI connection gives administrators close control over virtual environments. They can easily update and fix issues on multiple devices via a centralized management system. This is an efficient solution when dealing with a less technical workforce.
Scalability
Adding new user accounts to a VPN does not typically require allocating additional resources. The VPN server is designed to handle multiple connections, and its resource usage per user is usually minimal. Once their accounts are configured, users can connect and access company resources through the VPN almost immediately.
In a VDI setup, each user has a dedicated virtual environment. Adding new users to a VDI system requires careful planning in terms of resource allocation. Provisioning new server resources for each user can be expensive and time-consuming.
User Experience
VPN users have different experiences, which depend on various factors, including their internet connection speeds and the quality of their devices. The experience can be inconsistent even when using the same device.

The VDI virtual environment is standardized and offers a consistent digital workplace experience regardless of the employee's location or client device capabilities.
Network Dependence
VPN and VDI cannot provide the services they are designed for without network access. However, VPN users can download and access resources on their local devices. This means that if there is a temporary network outage or connectivity issue, users may still be able to continue working on the resources they've retrieved through the VPN.
VDI environments require a continuous network connection. Since the virtual desktop environment and all its resources are hosted on a server, interruptions in network connectivity prevent users from accessing the system and its applications.
FAQ
Can VDI Replace VPN?
VDI is not a direct replacement for VPN.
Centralized maintenance and the added security layer are a big draw for implementing VDI as a remote solution, especially if a company has decided to employ a permanent remote workforce.
However, VPNs can also elevate security by introducing new ways to verify users, such as two-factor authentication, and limit the attack surface by restricting which systems users can access. Despite the advantages of VDI, VPNs remain relevant due to their flexibility, lower cost, and ease of deployment.
Does a Virtual Machine Work as a VPN?
It does not. These are two different concepts.
Virtual machines emulate a computer and run an operating system and applications in an isolated environment. A VPN is a network technology that creates a secure and encrypted tunnel between a device and a server for transferring data.
What Is the Disadvantage of VDI Over VPN?
Each virtual desktop in a VDI must be provided with enough computing power and memory to ensure a responsive and functional experience for the user. This often involves significant investment in server hardware and infrastructure.
Setting up and troubleshooting in VDI is more expensive and complex than configuring a VPN solution. For example, scaling a VDI environment by provisioning and de-provisioning virtual desktops is resource-intensive and requires dedicated staff with specific IT knowledge.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you understand the difference between VPN and VDI. You also know how both solutions work and which would fit your business needs better.
Next, learn about the differences between persistent and non-persistent VDIs.