Removing Docker from Ubuntu frees system resources and ensures a clean, dependency-free environment before a new installation. When performed correctly, the process ensures the complete removal of the Docker engine, Docker CLI, and associated configuration files.
This article teaches you how to uninstall Docker on Ubuntu.

Backup Docker Data
Before uninstalling Docker, back up critical data. Docker volumes and custom configuration files often hold essential application states and settings. Manually copy contents to a safe location outside the Docker storage path, or use the following volume backup procedure:
1. Find the name of the volume to back up:
docker volume ls
2. Enter the docker run command below and replace [volume] with the actual volume name and [backup_path] with the desired backup location on your host:
docker run --rm \
-v [volume]:/volume \
-v [backup_path]:/backup \
alpine sh -c "cd /volume && tar czf /backup/[volume]<em>backup</em>$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz ."The following example shows a command that backs up a volume named test to the directory named project:
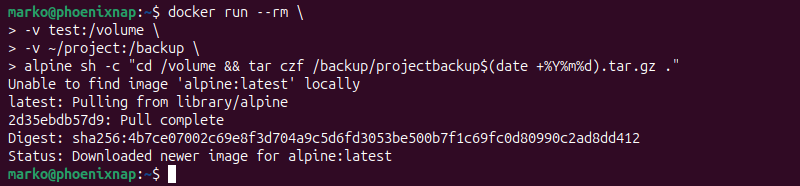
The command runs a temporary container (using the alpine image for efficiency) that mounts the target volume and a local directory for the backup. It then uses the tar command to compress the volume's contents and save the resulting archive to the host.
To restore the data to a new (or existing) volume, use the process described below:
1. Ensure the target volume exists:
docker volume create [new_volume]2. Run the following command to restore the volume contents, replacing [new_volume] and [backup_file] with the appropriate values:
docker run --rm \
-v [new_volume]:/volume \
-v ~/backup/:/backup \
alpine sh -c "cd /volume && tar xzf /backup/[backup_file]"Note: You can also use the docker commit command to back up containers, and docker export to archive container filesystems.
Uninstall Latest Docker Version
The following step removes the core Docker components by using apt purge. Execute the following command to uninstall Docker Engine, CLI, Containerd, and Docker Compose:
sudo apt purge docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin docker-ce-rootless-extras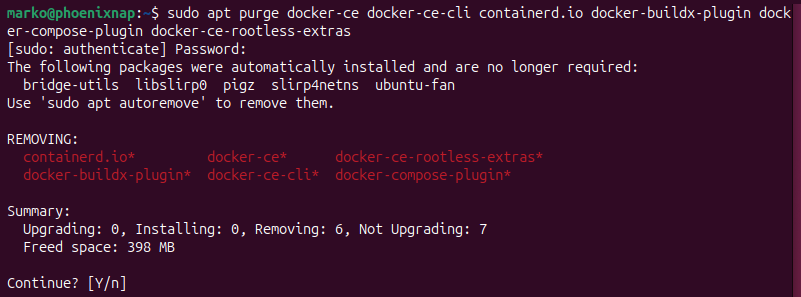
The package manager prompts for confirmation. Press Enter to proceed with the removal.
Uninstall Previous Docker Versions
In scenarios where Docker was installed using older methods or with different package names, these older packages need to be removed as well.
For example, to remove the docker.io package, type the following command:
sudo apt purge docker.io
Press Enter to confirm the removal.
Remove Docker Completely
Removing app packages does not fully remove a Docker installation, as persistent data and directories still remain on the system. To remove them, use the commands below:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerdWarning: This action permanently deletes all images, containers, and local volumes not explicitly backed up.
Use the autoremove command to delete any residual dependencies that were installed with Docker and are no longer required by any other package:
sudo apt autoremove -y
Conclusion
This article provided instructions for completely removing Docker from an Ubuntu system. It also showed how to remove legacy packages and persistent data from your system.
Next, learn how to manage Docker container logs.