Docker images offer a flexible and portable way to package applications for easier deployment and distribution. While end-users download images from a container registry, developers and testers often need a quicker sharing method.
This article shows how to save a Docker image to an archive for sharing, backup, or migration.
Prerequisites
- Docker installed (see tutorials for installing Docker on Ubuntu and installing Docker on Rocky Linux).
- Command-line access.
- Administrative privileges.
docker save Command
The docker save command enables users to package the content of one or more Docker images and their metadata into a TAR file. The following is the basic syntax for docker save:
docker save [image] > [filename].tarAlternatively, use the option -o or --output to provide the name of the destination file.
docker save -o [filename].tar [image]To include more than one image in a single tarball, list them all in one command:
docker save -o [filename].tar [image1] [image2] [image3] [...]Note: docker save is an alias of the docker image save command. The two commands are interchangeable.
docker save Examples
The design of docker save allows users to create uncompressed and compressed archives, as well as TAR files with multiple versions of a single image. The following sections provide examples of the command's various uses.
Save Docker Image to Tarball
The simplest scenario for docker save involves packaging a single image into a tarball. The command below uses the image called custom-ubuntu:v1 to create a TAR archive named export.tar:
docker save -o export.tar custom-ubuntu:v1If successful, the command does not print any output. The ls command shows the created tarball in the working directory.

Save Docker Image to TAR.GZ File Using gzip
To compress the contents of the tarball, pipe the output of the docker save command to the gzip command. Use the following syntax:
docker save [image] | gzip > [filename].tar.gzThe example below archives and compresses the image named test-app into a test-app.tar.gz file:
docker save test-app | gzip > test-app.tar.gzThe command provides no output.
Note: Learn how to extract the files compressed with gzip by reading How to Extract or Unzip .tar.gz Files in Linux.
Save Docker Image Based on Tag
The docker save command can archive different versions of a single image, allowing for selective backup and distribution. To create a tarball with multiple image versions, type:
docker save -o [filename].tar [image]:[tag] [image]:[tag2] [...] For example, to create a tarball named test-versions.tar containing only the versions of the test-app tagged v1, v3, and v5, type:
docker save -o test-versions.tar test-app:v1 test-app:v3 test-app:v5Note: Learn also about docker export command, used to archive and distribute a container filesystem to another machine.
Load Archived Image with docker load
The images packaged into a tarball can be extracted with the docker load command. The syntax for the command is the following:
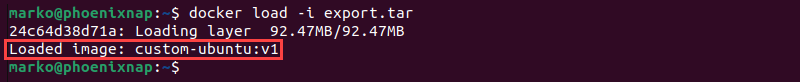
docker load -i [filename]The -i or --input argument instructs Docker to read from a file. For example, to extract the custom-ubuntu:v1 image from the export.tar archive, type the following command:
docker load -i export.tarThe output confirms that the image has been loaded into the system.
To load images from standard input (STDIN), use the following syntax:
docker load < [filename]The command accepts TAR and TAR.GZ files.
Note: Suppress the command output by adding the -q or --quiet option to the docker load command.
Conclusion
This article explained how to save Docker images and load them on a different system. The tutorial also introduced the two relevant commands, docker save and docker load, and provided examples.
If you are starting to work with Docker, check out our Docker Commands Cheat Sheet and download a handy PDF reference for navigating the Docker CLI.