Python dictionaries are a built-in data type for storing key-value pairs. The dictionary elements are mutable and don't allow duplicates. Adding a new element appends it to the end, and in Python 3.7+, the elements are ordered.
Depending on the desired result and given data, there are various ways to add items to a dictionary.
This guide shows how to add items to a Python dictionary through examples.

Prerequisites
- Python version 3.7 or newer.
- A text editor or IDE to write code.
- A method to run the code, such as a terminal or IDE.
How to Add an Item to a Dictionary in Python
Create an example dictionary to test different ways to add items to a dictionary. For example, initialize a dictionary with two items:
my_dictionary = {
"one": 1,
"two": 2
}
print(my_dictionary)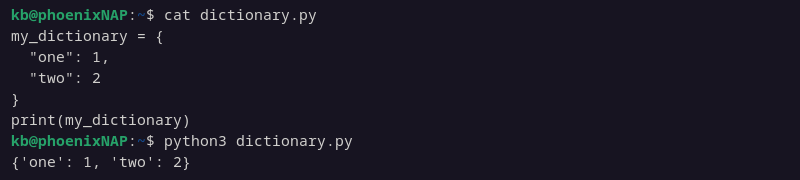
The methods below show how to add one or more items to the example dictionary.
Note: Adding an item with an existing key replaces the dictionary item with a new value. Provide unique keys to avoid overwriting data.
Method 1: Using The Assignment Operator
The assignment operator (=) sets a value to a dictionary key:
dictionary_name[key] = valueThe assignment operator adds a new key-value pair if the key does not exist. For example:
my_dictionary = {
"one": 1,
"two": 2
}
my_dictionary["three"] = 3
print(my_dictionary)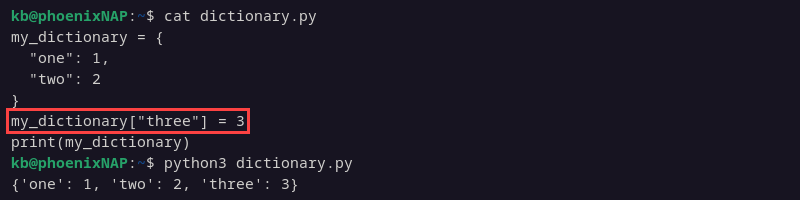
The code shows the updated dictionary contents after adding a new item.
Method 2: Using update()
The update() method adds a new element to an existing dictionary:
dictionary_name.update({key:value})The method also accepts multiple key-value pairs. To use the update() method, see the example below:
my_dictionary = {
"one": 1,
"two": 2
}
my_dictionary.update({"three":3})
print(my_dictionary)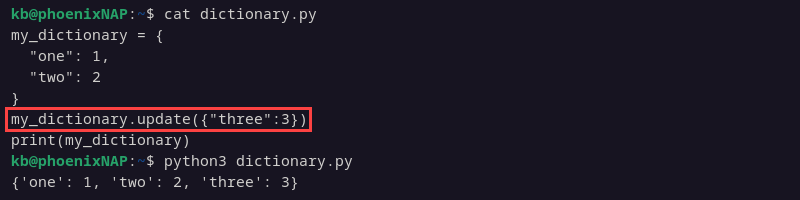
Use this method to add new items or to append a dictionary to an existing one.
Note: Learn how to add elements to a list in Python.
Method 3: Using dict() Constructor
The dict() constructor allows creating a new dictionary and adding a value to an existing one. When using the second approach, the method creates a copy of a dictionary and appends an element to it.
The syntax is:
new_dictionary = dict(old_dictionary, key=value)For example:
my_dictionary = {
"one": 1,
"two": 2
}
new_dictionary = dict(my_dictionary, three=3)
print(new_dictionary)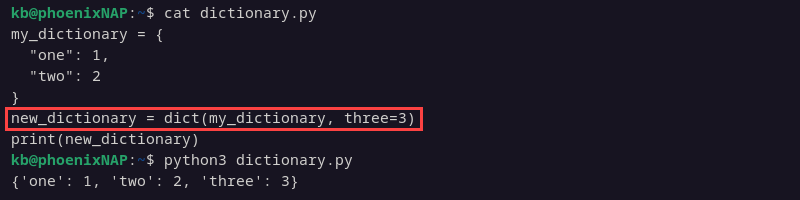
The method preserves the original dictionary and updates the new copy.
Method 4: Using __setitem__
The __setitem__ method is another way to add an item to a dictionary. The syntax is:
dictionary_name.__setitem__(key,value)For example:
my_dictionary = {
"one": 1,
"two": 2
}
my_dictionary.__setitem__("three", 3)
print(my_dictionary)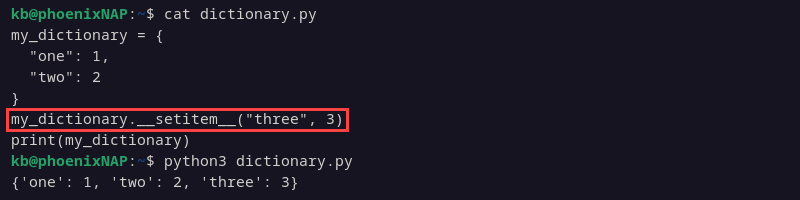
The method sets the item key as "three" with the value 3.
Method 5: Using The ** Operator
The ** operator merges an existing dictionary into a new dictionary and enables adding additional items. The syntax is:
new_dictionary = {**old_dicitonary, **{key:value}}For example, to copy an existing dictionary and append a new item, see the following code:
my_dictionary = {
"one": 1,
"two": 2
}
new_dictionary = {**my_dictionary, **{"three":3}}
print(new_dictionary)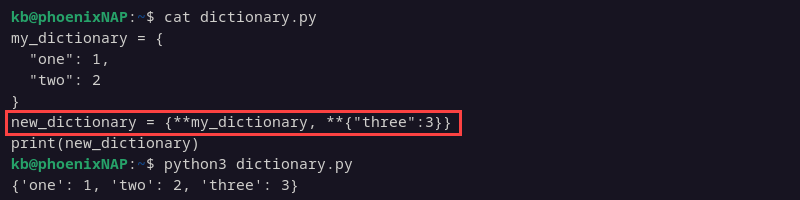
The new dictionary contains the added item while preserving the old dictionary. This method avoids changing the dictionaries and instead creates a copy for changes.
Method 6: Checking If A Key Exists
To avoid overwriting existing data, use an if statement to check whether a key is present before adding a new item to a dictionary. The example syntax is:
if key not in dictionary_name:
dictionary_name[key] = valueFor example:
my_dictionary = {
"one": 1,
"two": 2
}
if "three" not in my_dictionary:
my_dictionary["three"] = 3
print(my_dictionary)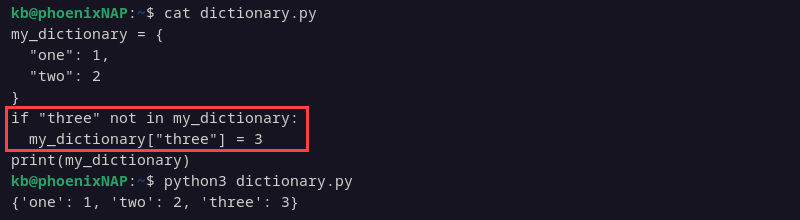
The code checks whether a key with the provided name exists. If the provided key exists, the existing key value is not updated, and the dictionary remains unchanged.
Method 7: Using A For Loop
Add key-value pairs to a nested list and loop through the list to add multiple items to a dictionary. For example:
my_dictionary = {
"one": 1,
"two": 2
}
my_list = [["three", 3], ["four", 4]]
for key,value in my_list:
my_dictionary[key] = value
print(my_dictionary)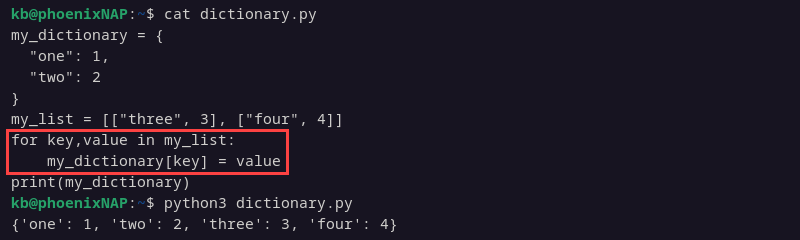
The for The loop iterates over the pairs in the list and adds two new elements.
Note: A for loop and a counter are also used to identify the length of a list. Learn more by reading our guide How to Find the List Length in Python.
Method 8: Using zip
Use zip to create dictionary items from two lists. The first list contains keys, and the second contains the values.
For example:
my_dictionary = {
"one": 1,
"two": 2
}
my_keys = ["three", "four"]
my_values = [3, 4]
for key,value in zip(my_keys, my_values):
my_dictionary[key] = value
print(my_dictionary)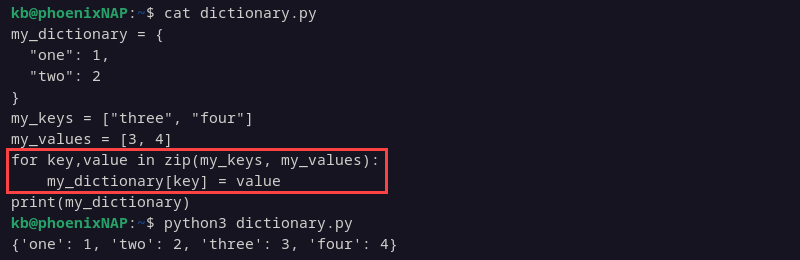
The zip function matches elements from two lists by index, creating key-value pairs.
Conclusion
This guide showed how to add items to a Python dictionary. All methods provide unique functionalities, so choose the one that best suits your program and situation.
For more Python tutorials, refer to our article on how to pretty print a JSON file using Python, Python dictionary comprehension, or learn about the Python map() function.