PostgreSQL is an open-source, object-relational database system with a strong reputation for feature robustness, extensibility, and technical standards compliance. Combined with Ubuntu, it provides a dependable and performant platform for your database needs.
This tutorial will provide two different ways of installing the latest PostgreSQL version on Ubuntu.
Prerequisites
- A machine running Ubuntu.
- Access to the terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T).
- A user account with root privileges.
How to Install PostgreSQL On Ubuntu
There are two ways to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu:
- From the PostgreSQL repository.
- From the default Ubuntu repository.
Installing PostgreSQL via the Ubuntu repository provides the PostgreSQL version that is officially packaged and maintained by the Ubuntu developers. On the other hand, installing from the PostgreSQL repository gives you the option to get the latest version directly from the PostgreSQL project, potentially providing newer features and bug fixes not yet available in the Ubuntu repositories.
The sections below provide the steps for each installation method.
Method 1: Install PostgreSQL from PostgreSQL Apt Repository
The PostgreSQL Apt Repository provides the latest PostgreSQL version, as well as all previous server packages, extensions, and modules. Having the latest version provides access to newer features, performance improvements, and bug fixes sooner than they are available in the Ubuntu repositories.
However, note that while installing from the PostgreSQL repository can provide access to the latest PostgreSQL releases, it may require more manual work and attention to security updates.
Follow the steps in the sections below to install PostgreSQL from the PostgreSQL repository.
Step 1: Add PostgreSQL Repository
Run the following command to add the PostgreSQL repository to your system:
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb https://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt $(lsb_release -cs)-pgdg main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgdg.list'The command adds the repository to the system's apt package manager, instructing it to use the PostgreSQL repository for package management.
Step 2: Add the Repository Signing Key
The next step is to fetch the repository's GPG key and add it to APT's trusted keyring. This allows APT to verify the authenticity of packages downloaded from the PostgreSQL repository.
Run the command below:
wget --quiet -O - https://www.postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | sudo apt-key add -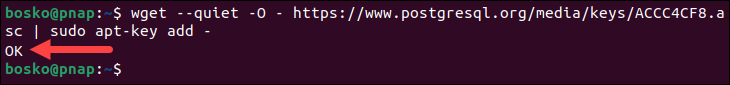
Step 3: Update the Package List
After adding the official PostgreSQL repository, update the package list to ensure you install the latest PostgreSQL package.
sudo apt updateStep 4: Install PostgreSQL
To install PostgreSQL and the PostgreSQL contrib package (which provides additional features), run the following command:
sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contribBy default, the software creates a <strong>postgres</strong> user once you successfully install the database system. This user account has the default postgres role.
Method 2: Install PostgreSQL from Local Ubuntu Repository
The PostgreSQL packages provided by the Ubuntu repositories are maintained and supported by the Ubuntu developers. This ensures compatibility with the Ubuntu system and adherence to Ubuntu's packaging standards.
However, the PostgreSQL versions available in the Ubuntu repositories may not always be the latest releases. The reasoning is that Ubuntu prioritizes stability and long-term support over providing the newest features.
Follow the steps below to install PostgreSQL from the default Ubuntu repository.
Step 1: Check Available PostgreSQL Version
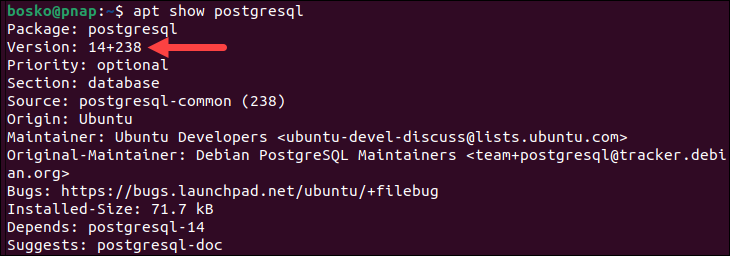
Before you decide whether you want to set up PostgreSQL from the Ubuntu repository, verify which versions are available. Update the repository and then run the command:
apt show postgresqlThe output provides all the necessary information about the package, including the release number and size.
Step 2: Install PostgreSQL Package
To install the PostgreSQL version accessible from the local repository, use the following command:
sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contribWait for the process to finish, and you have successfully installed PostgreSQL on Ubuntu.
Verify PostgreSQL Installation
Verify that PostgreSQL has been installed by checking the PostgreSQL service status. Run the command below:
sudo systemctl status postgresql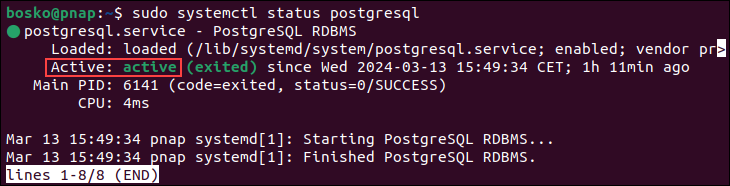
If everything is installed correctly, the output shows the PostgreSQL service status as active.
Connect to PostgreSQL
To establish a connection with the database, log into the postgres account with:
sudo su - postgresNext, open a postgres prompt using the command:
psql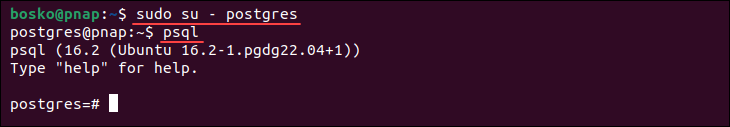
Create a New User on PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL includes the client utility, which allows you to create a new user from the terminal without connecting to the database. The syntax for creating a new user is:
sudo -u postgres createuser -e [username]Replace [username] with the actual user name of the user you want to create. For example:
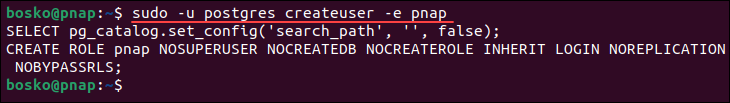
Note: For other ways of creating a user in PostgreSQL and securing access, refer to our in-depth tutorial for creating a PostgreSQL user.
Create a New Database on PostgreSQL
There are three ways of creating a new database in PostgreSQL:
- Using the
CREATE DATABASESQL statement. Creates a database from the PostgreSQL shell prompt and requires appropriate privileges. - Via the command line. Uses the
createdbcommand, which can be directly run from the command line. - Using the GUI pgadmin program.
For this tutorial, we will focus on using the CREATE DATABASE statement.
Follow the steps below:
1. Log in to the postgres prompt as a user that has the appropriate privileges for creating a database. We will log in as postgres:
sudo su - postgrespsql2. Use the following syntax to create a database:
CREATE DATABASE [dbname];
Replace [dbname] with the database name. For example:
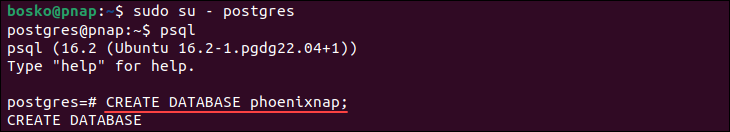
Note: See how to delete a database in PostgreSQL.
Check Connection Information
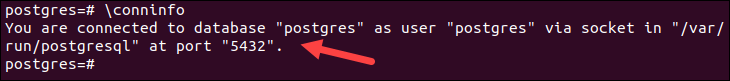
If you are connected to PostgreSQL and want to see details of the connection, use the command:
\conninfoThe output displays information on the database name, the account you are logged in, the socket path, and the port number.
Conclusion
This article should help you set up PostgreSQL. Whether you decide to install from the PostgreSQL repository or the local Ubuntu repository, both installations are simple and easy to do.
Next, see how to set up and connect to PostgreSQL with SQL Workbench or how to install PostgreSQL on Windows.